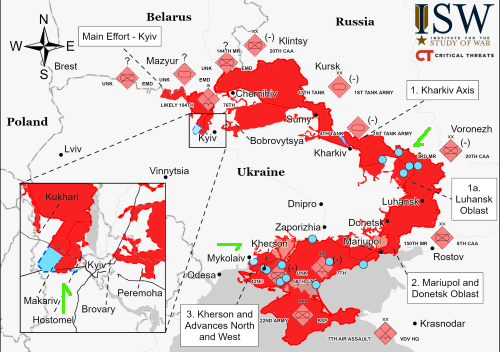
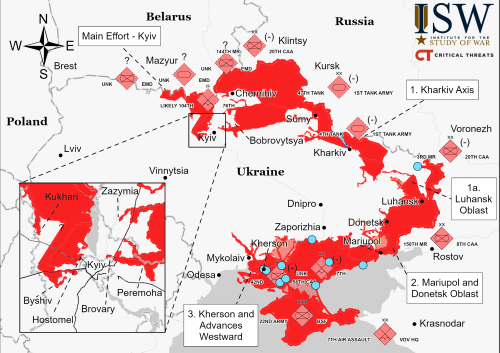
Sources suggest major job layoffs and salary cuts about to sweep Russia
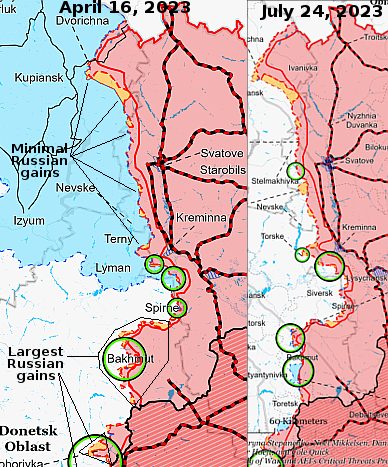
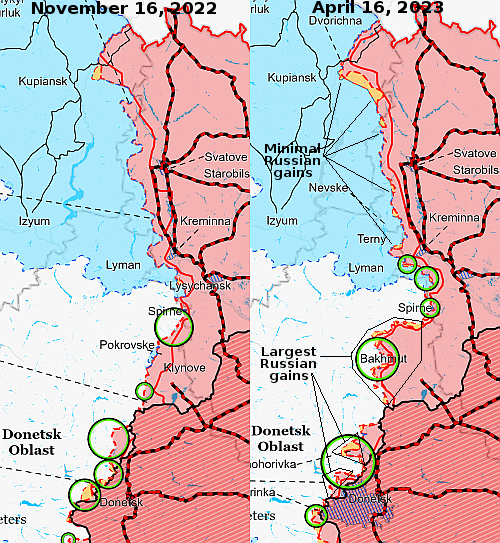
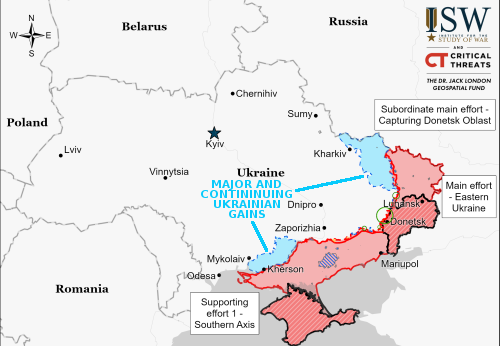
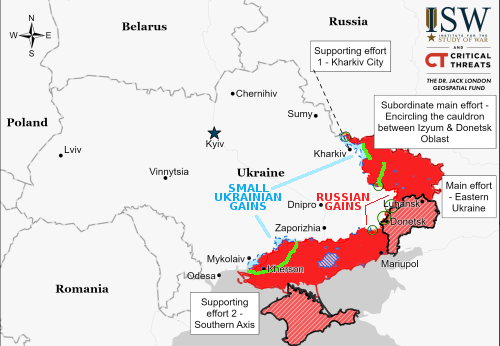
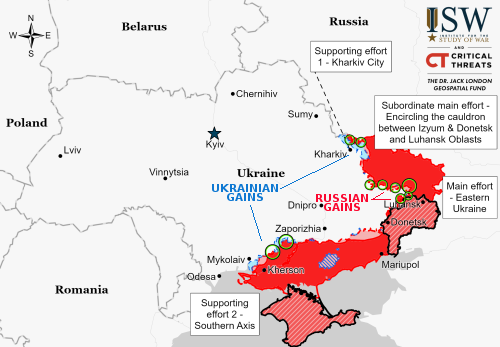
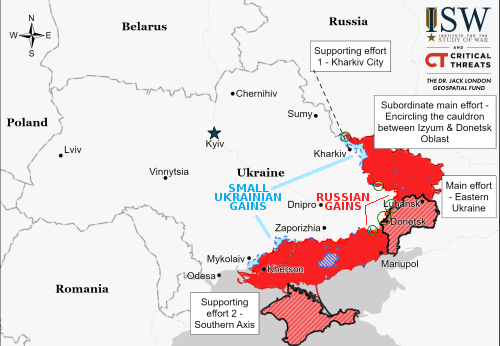
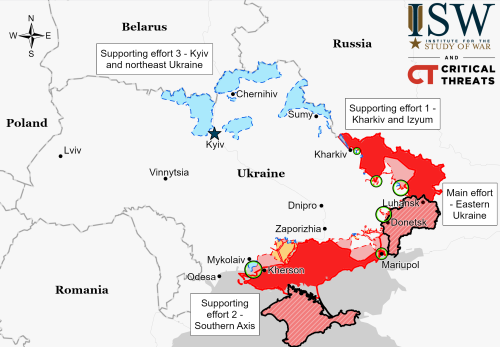
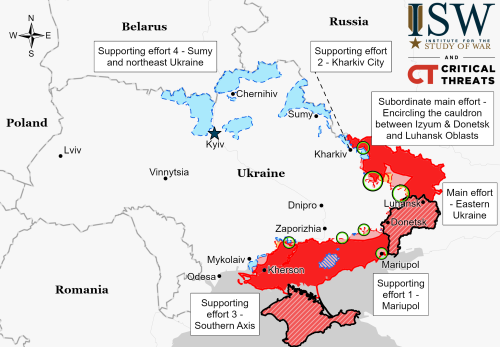
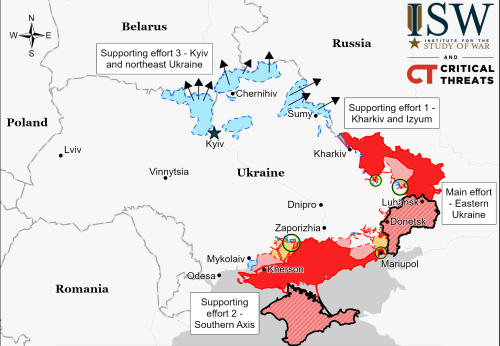
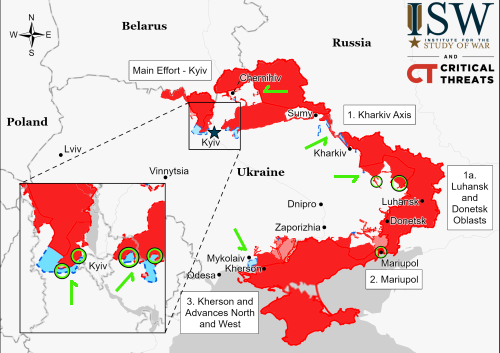
According to various sources, major job layoffs and salary cuts are about to sweep Russia, affecting 800,000 people working for nine different large companies.
The cuts include layoffs, salary cuts, shortened work hours, and unpaid leave, with many involved in the aviation industry.
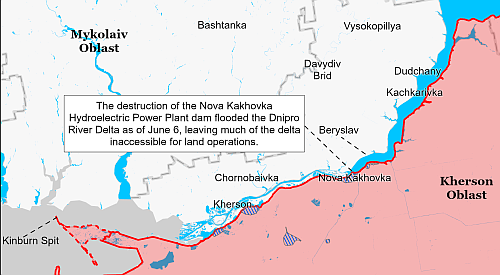
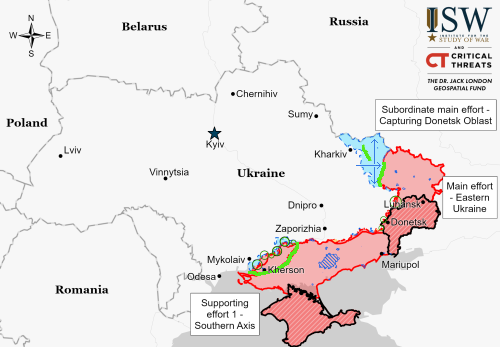
According to the tweet at the link, the blame goes to the Ukraine war and the collapse of the Russian economy because of it. That might or might not be true, but the speculation is certainly reasonable.
This collapse has been predicted now for several years. If it happens Putin’s future as head of Russia might finally be reaching its use-by date.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.
According to various sources, major job layoffs and salary cuts are about to sweep Russia, affecting 800,000 people working for nine different large companies.
The cuts include layoffs, salary cuts, shortened work hours, and unpaid leave, with many involved in the aviation industry.
According to the tweet at the link, the blame goes to the Ukraine war and the collapse of the Russian economy because of it. That might or might not be true, but the speculation is certainly reasonable.
This collapse has been predicted now for several years. If it happens Putin’s future as head of Russia might finally be reaching its use-by date.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.