Paisley terrain on Mars
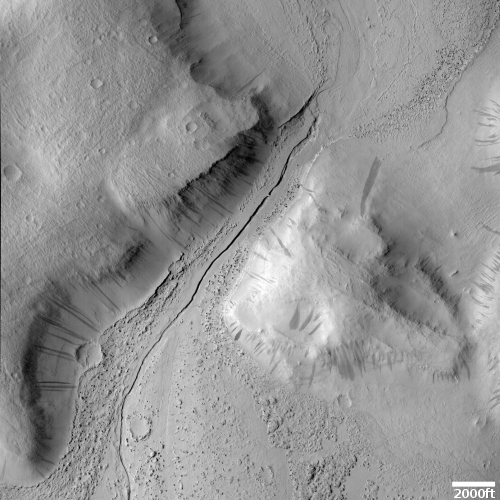
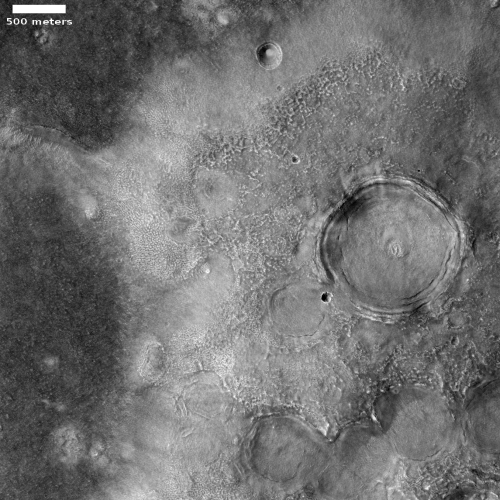
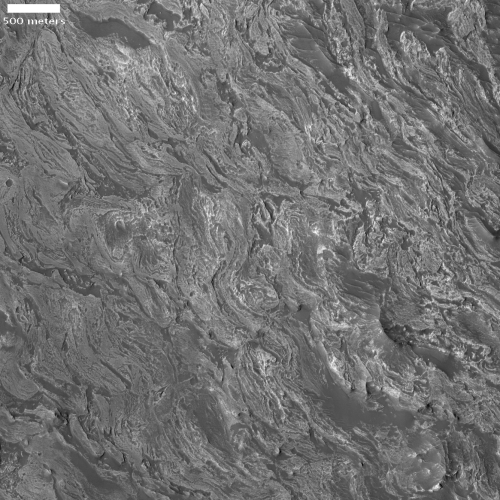
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is actually a somewhat old image from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It was taken more than a decade ago, on December 28, 2010, and featured as a captioned image one month later. I post it now because it was recently featured as MRO’s picture of the day, and thought it deserved a new look. As the caption from 2010, written by planetary scientist Alfred McEwen, noted,
Remember those paisley shirts during the summer of love in 1967? If so, this terrain may look somewhat familiar.
How did this terrain really form? One theory is that it’s a landslide deposit, perhaps associated with draining an ancient lake.
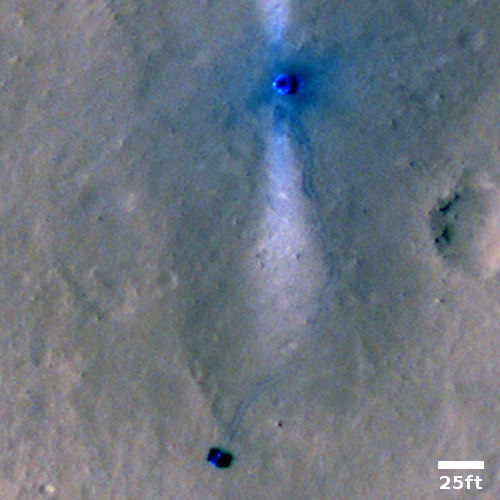
The overview map below might help make sense of this theory.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is actually a somewhat old image from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It was taken more than a decade ago, on December 28, 2010, and featured as a captioned image one month later. I post it now because it was recently featured as MRO’s picture of the day, and thought it deserved a new look. As the caption from 2010, written by planetary scientist Alfred McEwen, noted,
Remember those paisley shirts during the summer of love in 1967? If so, this terrain may look somewhat familiar.
How did this terrain really form? One theory is that it’s a landslide deposit, perhaps associated with draining an ancient lake.
The overview map below might help make sense of this theory.
» Read more