Lucy Thomas – Hallelujah
An evening pause: A brilliant simple cover of the Leonard Cohen song. Seems right to start the holiday season, right after Thanksgiving.
Hat tip Dan Morris.
An evening pause: A brilliant simple cover of the Leonard Cohen song. Seems right to start the holiday season, right after Thanksgiving.
Hat tip Dan Morris.
Engineers today successfully completed an engine burn that put Orion into the retrograde lunar orbit in which it will remain for the next week.
Due to the distance of the orbit, it will take Orion nearly a week to complete half an orbit around the Moon, where it will exit the orbit for the return journey home. About four days later, the spacecraft will harness the Moon’s gravitational force once again, combined with a precisely timed lunar flyby burn to slingshot Orion onto its return course to Earth ahead of splashdown in the Pacific Ocean on Sunday, Dec. 11.
As of now all systems seem to be working as intended.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay.
China also announced its Chang’e-7 and Chang’e-8 lunar landers will include “hoppers” aimed at exploring the Moon’s permanently shadowed craters for ice.
This was the sixth asteroid spotted before reaching Earth.
Apparently, a piece of the Japanese rocket, launched in 2012, broke up, and did so about the time it cut across the orbit of Chinese rocket debris, though the two did not hit each other.

Dr. Ashish Jha, government liar.
On November 23, 2022, the very same day White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Dr. Ashish Jha stated unequivocally that “If folks get their updated vaccines and they get treated … we can prevent essentially every COVID death in America,” the Washington Post reported a CDC-financed study showing that by August 2022 more people were dying from COVID who had gotten the jab than those who had not.
For the first time, a majority of Americans dying from the coronavirus received at least the primary series of the vaccine.
Fifty-eight percent of coronavirus deaths in August were people who were vaccinated or boosted, according to an analysis conducted for The Health 202 by Cynthia Cox, vice president at the Kaiser Family Foundation.
It’s a continuation of a troubling trend that has emerged over the past year. As vaccination rates have increased and new variants appeared, the share of deaths of people who were vaccinated has been steadily rising. In September 2021, vaccinated people made up just 23 percent of coronavirus fatalities. In January and February this year, it was up to 42 percent, per our colleagues Fenit Nirappil and Dan Keating.
“We can no longer say this is a pandemic of the unvaccinated,” Cox told The Health 202.
In other words, Jha was lying, and he was doing so in plain defiance of the data that has been accumulating exponentially in the past year. » Read more
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
Today’s cool image takes us back to a previous cool image, from December 2020. The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on August 22, 2022 as part of a regular monitoring program of these worm-shaped and tiger-striped dunes in 42-mile-wide Kunowsky Crater, located in the northern lowland plains of Mars at the high mid-latitude of 57 degrees north.
The tiger stripes appear to be the northern hemisphere’s version of what are called “spiders” in the south, where each spring the mantle of dry ice that settles on the surface in winter begins to sublimate away, from the bottom up. The trapped gas eventually escapes at the mantle’s weak points where it cracks.
When the gas escapes it spews dust onto the surface, creating the dark patches. In the southern hemisphere, the ground is generally stable, and the gas travels and escapes along the same routes each year, creating relatively permanent spider-like tributary patterns. In the north the ground is less stable, so the dark streaks form more randomly from year to year.
This monitoring campaign, first begun in 2008, is looking to see how these seasonal changes might change these northern dunes. The white rectangle in the image shows an area shown in close-up below, comparing 2020 with 2022 to see what changes might have occurred.
» Read more
According to Japan’s space agency JAXA, one of its astronauts, Satoshi Furukawa, falsified and fabricated the research results of a ground-based experiment run from 2015 to 2017.
The experiment asked a total of 42 test subjects to spend 14 days in a mock space station, during which blood and urine samples were collected.
A JAXA probe later found multiple misconduct with the research, including creating data without a supervisory researcher and intentionally rewriting evaluations. The study also lacked sufficient assessment methods and adequate research notes, and the credibility of the data wasn’t assured.
These wrongdoings were discovered after the experiments had been completed, and since the research was subsequently suspended no papers were published.
Furukawa is scheduled to fly to ISS in ’23. Though JAXA says he and his research team will be punished, it is unclear whether that means his flight has been canceled.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
Capitalism in space: The governmental officials representing all of the partners in the European Space Agency this week decided to commit $122 million to a program designed to encourage private independent and competing space companies.
This budget represented a 17% increase.
The ScaleUp programme, which has two elements, supports a company along its entire life cycle. First, it assists in the development of the enterprise with business incubation, business acceleration, intellectual property and technology transfer services (ScaleUp Innovate), and then, it facilitates the scaling up of their products on new markets (ScaleUp Invest).
ScaleUp is business-focused and not technology or sector specific and applies within all ESA programmes. This programme targets start-up companies, applied research and innovation centres, and more mature companies such as SMEs, Mid-Caps and large system integrators.
While encouraging news, the language of the press release and the size of the budget indicates that these European governments are being dragged kicking and screaming into this new capitalist aerospace world. It is clear that ESA has been losing out by sticking with its government-run and government-owned Arianespace operation. At the same time, it is also clear that ESA officials and their governments are showing the same reluctance Congress showed in the last decade when NASA wanted to transition from its government-run and -owned system. At that time, Congress consistently resisted budgeting the commercial space line in NASA’s budget, thus delaying the launch of both Dragon and Starliner significantly.
In the end the effectiveness of competition, private property, and freedom however won out in the U.S. I expect it will do the same in Europe, though it might take another decade or so before Europe’s governments realize it.
Ispace yesterday announced that the launch of its Hakuto-R lunar lander, carrying a number of private and government payloads including the UAE’s Rashid rover, has been delayed two days to November 30, 2022 due to weather and scheduling issues.
The spacecraft will be launched from Cape Canaveral on a Falcon 9 rocket. The weather and the Thanksgiving holiday forced NASA and SpaceX to push back the launch of a cargo Dragon to ISS to November 26th. This in turn impacted Hakuto-R’s launch date.
An evening pause: As Linus most correctly notes, “Ours is the first country in the world to make a national holiday to give thanks,” and then adds, in saying grace before the dinner:
In the year 1621, the Pilgrims held their first Thanksgiving feast. They invited the great Indian chief Massasoit, who brought ninety of its brave Indians and a great abundance of food. Governor William Bradford and Captain Miles Standish were honored guests. Elder William Brewster, who was a minister, said a prayer that went something like this: “We thank God for our homes and our food, and our safety in a new land. We thank God for the opportunity to create a new world for freedom and justice.”
Accurate and well put. Keep Brewster’s prayer in mind the next time someone tries to slander the U.S.
The uncertainty of science: Though scientists had assumed the presence of an ancient delta that once flowed into Jezero Crater meant a lake once filled the crater, Perseverance data from its first year of roving has so far found no evidence that a lake every existed.
[A] summary of the first year of data from the rover, published in three different papers being released today, suggests that Perseverance has yet to stumble across any evidence of a watery paradise. Instead, all indications are that water exposure in the areas it explored was limited, and the waters were likely to be near freezing. While this doesn’t rule out that it will find lake deposits later, the environment might not have been as welcoming for life as “a lake in a crater” might have suggested.
Jezero Crater, like Gale Crater where Curiosity is roving, is located in the Martian dry equatorial regions. Though the data from Gale suggests a lake had once existed there, the data also suggests strongly that any water there acted more like water in cold climates like Iceland, existing mostly as glacial ice.
The jury is still out, but these results from Perseverance once again point to ice and glaciers as a possible explanation for many of the geological features on Mars that we on Earth automatically assume were caused by liquid water.
NASA yesterday awarded Rocket Lab the contract to put its constellation of TROPICS satellites into orbit, on two different launches.
This contract replaces Astra as the launch provider, which has abandoned launches while it develops a new rocket.
Astra’s contract, valued at $7.95 million, was for three launches on its Rocket 3.3 vehicle – a rocket that Astra later announced would be discontinued, in favor of a larger and more powerful Rocket 4.
But Rocket 4 is still under development – and may not be ready to launch until 2024. NASA decided not to wait that long, and said in September that it would modify the TROPICS launch contract with Astra for “comparable scientific payloads” on the new rocket.
Moreover, the launches will occur at Wallops Island, strengthening Rocket Lab’s presence there. The company will attempt its first launch there in early December, a launch delayed for two years because of holdups created by NASA’s bureaucracy. With this new contract, NASA’s management will now have an incentive to speed use of Wallops by Rocket Lab, not slow it down.
Ingenuity yesterday completed its 34th flight on Mars, a short vertical up-and-down flight lasting only eighteen seconds in order to test just installed new hazard avoidance software.
The tan dotted line on the map to the right shows Ingenuity’s recent flights and ends where it sits today. The white dotted line marks Perseverance’s travels.
Ingenuity’s navigation software was designed to assume the vehicle was flying over flat terrain. When the helicopter is flying over terrain like hills, this flat-ground assumption causes Ingenuity’s navigation software to think the vehicle is veering, causing Ingenuity to start actually veering in an attempt to counter the error. Over long flights, navigation errors caused by rough terrain must be accounted for, requiring the team to select large airfields. This new software update corrects this flat-ground assumption by using digital elevation maps of Jezero Crater to help the navigation software distinguish between changes in terrain and vehicle movement. This increases Ingenuity’s accuracy, allowing the pilots to target smaller airfields going forward.
The new software is part of an effort to use Ingenuity to test helicopter flying in Jezero Crater in preparation for the two sample return helicopters which will eventually land here to grab Perservance’s core samples and bring them to the ascent vehicle for return to Earth.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
An evening pause: For Americans, Charo is mostly known as a buxom crazy comic. Few know she is also considered a world class flamenco guitarist, having won awards.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
Courtesy of Jay, BtB’s stringer, trolling Tweeter so you don’t have to.
There is uncertainty here. An earlier update said only 18 pieces of debris would still be in orbit in three years. This update predicts 44 pieces in three years.
I think, but cannot prove it, that those are retired early Starship/Superheavy prototypes, not active ships.
This is a liquid fueled methane-oxygen smallsat orbital rocket.
Jay correctly notes, “The scale is off, the picture shows Tiangong-3 as larger than what it is.” Comparing the Russian modules on ISS with Tiangong-3’s modules, I estimate that Tiangong-3 is about 30% smaller than shown.
The tweet provides no information in English on the asteroid being targeted.
This will be the first SpaceX launch of satellites for its competitor OneWeb, picking up the business the Russians intentionally abandoned.
The launch of this long delayed rover is now targeting ’28. It was originally supposed to launch in ’20, was first delayed until ’22 because of parachute issues, then was delayed again when Europe and Russia ended their space partnership due to the Ukraine War.
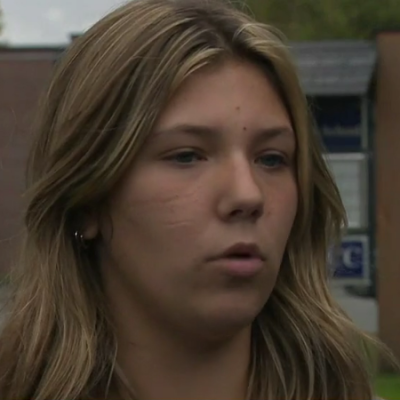

Blake Allen, punished for being a normal high school girl
We now return for the third time to the saga of Randolph Union High School in Vermont, a place where apparently you are not allowed to state the simple biological fact that a boy is a boy and a girl is a girl. Worse, you must allow boys to enter a girls’ dressing room and ogle them freely, and if you dare challenge this absurdity, you will be fired or suspended.
This craziness began in late September, when a boy claiming to be a girl (because he wanted to play on the girls volleyball team) entered the girls dressing room and watched the girls change, much to their discomfort. When the girls complained to school officials, the officials immediately banned those girls from using their own dressing room, reserving it now solely to this one boy.
The story became even more insane when the local television station, WCAX, decided to censor itself. It had covered this story with reasonable accuracy when the story broke. In mid-October however it decided that its job was publishing the agenda of the queer community, not reporting the news, and it censored its own story, removing it from the internet. (You can still watch it here however.)
Meanwhile, school officials have continued their track record of insanity. These officials not only locked the girls from their own locker room, they suspended one girl, Blake Allen, because she had been the most outspoken of all, appearing in that censored WCAX story. As part of her punishment, school officials demanded she admit 2+2=5 in a “reflective essay.”
» Read more
Hungary has budgeted $100 million to fly a Hungarian astronaut on a 30 day mission to ISS, arranged as a private mission though the American space company Axiom.
“This is a program which is being carried out with the cooperation of the American company Axiom Space and its extent is $100 million,” said [Péter Szijjártó, Hungarian foreign minister,] of the initiative. “This will end up in a 30-day-long research mission of a Hungarian astronaut with three other astronauts at the end of 2024 or beginning of 2025, depending on what time NASA confirms access to the International Space Station.”
NASA has yet to award missions to Axiom Space beyond its Ax-2 mission scheduled for the spring of 2023, but is evaluating proposals for two private astronaut missions that could include an Axiom Space flight in that timeframe.
It is clear that negotiations for arranging this mission between Axiom, NASA, and Hungary are on-going. Based on Szijjártó’s description, it is possible that the Hungarian astronaut could fly on a dedicated private Axiom mission to ISS, with two other paying passengers and an Axiom commander, or fly as an extra passenger on a normal ISS crew rotation flight. Furthermore, the ’24 or ’25 launch date suggests the vehicle might not be a Dragon capsule. By that time Boeing’s Starliner should be operational, thus giving Axiom and NASA an alternative. That time frame also corresponds to about when Axiom hopes to launch and dock its own module to ISS.
Nor is Hungary the only foreign country that has signed a deal with Axiom for a manned flight. Both Turkey and Saudi Arabia have agreements as well.
All told, the biggest obstacle right now to this new market is the number of ports on ISS. It seems Axiom has a strong incentive to get its own module launched and attached to ISS as soon as possible, if only to increase the docking ports available for these flights.
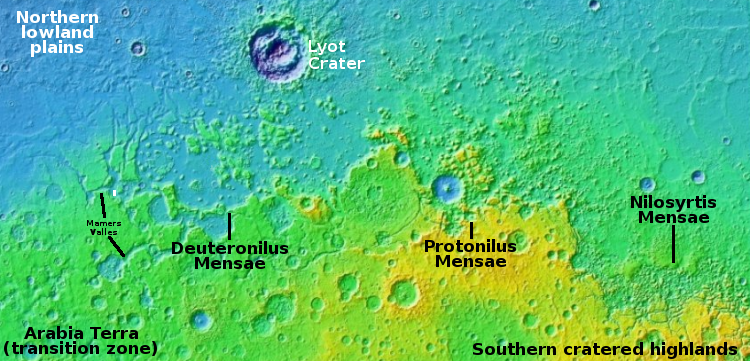
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on August 26, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Though the science team labels this image vaguely as showing “Features in Mamers Valles,” the features are likely glacial ice since this location is at the western end of the 2,000-mile-long northern mid-latitude strip I dub glacier country, where glacial features are seen everywhere.
The white dot marks this picture’s location in Mamers Valles, as shown on the overview map above. This particular Martian channel, that meanders in a wildly random manner (including a few sharp ninety degree turns), is theorized [pdf] by some scientists to have formed not by surface flows but by a subterranean drainage that created voids. On the surface the voids caused sagging, collapses, and the eventual formation of the surface channel.
Under such conditions, any ice in the channel would not necessarily have a clear flow direction, thus providing an explanation (though hardly certain) of the eddy-like shape of these features.
Astronomers have now completed the first detailed survey of an exoplanet’s atmosphere using the Webb Space Telescope, looking at a gas giant about one third the mass of Jupiter about 700 light years away.
Using three of its instruments, JWST was able to observe light from the planet’s star as it filtered through WASP-39b’s atmosphere, a process known as transmission spectroscopy. This allowed a team of more than 300 astronomers to detect water, carbon monoxide, sodium, potassium and more in the planet’s atmosphere, in addition to the carbon dioxide. The gives the planet a similar composition to Saturn, although it has no detectable rings.
The team were also surprised to detect sulfur dioxide, which had appeared as a mysterious bump in early observation data. Its presence suggests a photochemical reaction is taking place in the atmosphere as light from the star hits it, similar to how our Sun produces ozone in Earth’s atmosphere. In WASP-39b’s case, light from its star, slightly smaller than the Sun, splits water in its atmosphere into hydrogen and hydroxide, which reacts with hydrogen sulfide to produce sulfur dioxide.
The data also suggested the clouds in the atmosphere are patchy, and that the planet’s formation process was not exactly as predicted.
These observations are part of a program to study 70 exoplanets during Webb’s first year of operation, using its infrared capabilities to get spectroscopy not possible in other wavelengths.
According to an interview to Space.com by the four crew members on next year’s private manned Dragon flight financed by Jared Isaacman, the spacewalk, the first involving commercial passengers, will include all four passengers, since Dragon will not have an airlock and will be depressurized entirely when the hatch opens.
“We’ve collectively taken the position that we’re all going for an EVA,” Isaacman said, adding that the spacecraft cabin is to be depressurized in a hard vacuum. “Whether you’re sticking your head outside, you are doing an EVA. We are contemplating two people on the outside of the vehicle,” Isaacman said, “and two would be inside making sure that everything is going correct.”
To accommodate the spacewalk, this Crew Dragon will not be outfitted with a transparent dome, as was the case for the Inspiration4 mission.
The mission is presenting targeting March ’23 for launch.
Capitalism in space: France, Germany, and Italy yesterday signed an agreement [pdf] whereby they agreed to push European policy-makers to allow competition from independent European rocket startups for launch contracts.
At least, this is what I think they have agreed to. I have read the article and the agreement several times, and remain somewhat unsure of their intent. The agreement is couched in the typical bureaucratic language specifically designed to obscure meaning. The article does little to clarify things.
It appears this is the key language in the agreement:
The proposed acknowledgement of operational European NewSpace micro and mini launch systems for ESA satellite launch service procurements, upon its adoption by Council, would effectively represent a first step towards an evolution of the launch service procurement policy for ESA missions as referred to in the ESA Council Resolution adopted in 2005.
What I gather is that these three countries no longer want European launch contract awards limited to the Arianespace rockets Ariane-6 and Vega-C. They want bidding opened to all European rocket startups, and they want the elimination of rules that require all contracts distributed by quota to European countries.
Germany already has three commercial rocket startups on the verge of their first launch, and apparently wants the European Space Agency to stop favoring Arianespace in launch contracts. That France and Italy are going along with this is significant, since Ariane-6 is dominated by French developers and Vega-C is dominated by Italian developers.
NASA engineers unexpectedly lost all contact with Orion for 47 minutes just after midnight last night.
NASA’s Mission Control Center at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston unexpectedly lost data to and from the spacecraft at 12:09 a.m. CST for 47 minutes while reconfiguring the communication link between Orion and Deep Space Network overnight. The reconfiguration has been conducted successfully several times in the last few days, and the team is investigating the cause of the loss of signal. The team resolved the issue with a reconfiguration on the ground side.
At present the loss of signal caused no issues with the spacecraft. However, its cause has not yet been pinpointed.
SpaceX tonight successfully launched a geosynchronous communications satellite for Eutelsat. This was the third launch that SpaceX has done for this European company, which previously had traditionally been launched by Arianespace. Because of the delays and higher cost to use Arianespace’s new Ariane 6 rocket, the company chose to go with SpaceX instead.
The first stage, which had flown ten times previously, successfully completed its eleventh flight, but was not recovered because all of its fuel was needed to get the satellite to its proper orbit.
The leaders in the 2022 launch race:
53 SpaceX
52 China
19 Russia
9 Rocket Lab
8 ULA
The U.S. now leads China 77 to 52 in the national rankings, but trails the rest of the world combined 80 to 77.
An evening pause: This interview of Burt Lancaster on the Dick Cavett Show took place on July 21, 1969 (the day after Neil Armstrong took that first step on the Moon).
I could not help noting how humble and gracious Lancaster seemed. He might have been one of the world’s most charismatic actors, but he surely did not appear full of himself. The second part of this interview can be watched here.
Hat tip Cotour.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay.
More damage can be seen here. NASA apparently considers this damage no big deal, other than demonstrating how powerful SLS is.
The deal is a first step toward becoming a launch provider for the Space Force. As Jay noted to me, “Wait, how many rockets does Blue Origin have again? How many have made it to orbit? How is that BE-4 going?”
Launch is scheduled for November 29th, and will facilitate the first on-station crew rotation on Tiangong-3.
It also says it had ten more launches planned through ’25.
This reduction follows a failed rocket launch in May, the third in four attempts.
The launch will place one Earth observation satellite and eight smallsats in orbit.

One of the posters that Clovis Community College officials agreed to
“gladly” remove because it made some students “very uncomfortable.”
Bring a gun to a knife fight: A federal judge has issued a preliminary injunction against Clovis Community College in California, ruling that it violated the free speech rights of its students when college officials removed posters put up by students from the college’s Young Americans for Freedom chapter that condemned communism and socialism.
The lawsuit [pdf] was filed for the students by the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE).
The college insists that it reserves the right to remove flyers over “inappropriate or [offensive] language or themes.” The lack of any definition for those vague terms would weigh heavily with the court in granting the preliminary injunction.
FIRE produced emails showing that a college administrator offered to “gladly take down” the flyers after “several people” said that they were “very uncomfortable” with the flyers, including a person who allegedly threatened a “harassment claim” if the posters were not taken down.

To see the original images, go here and here.
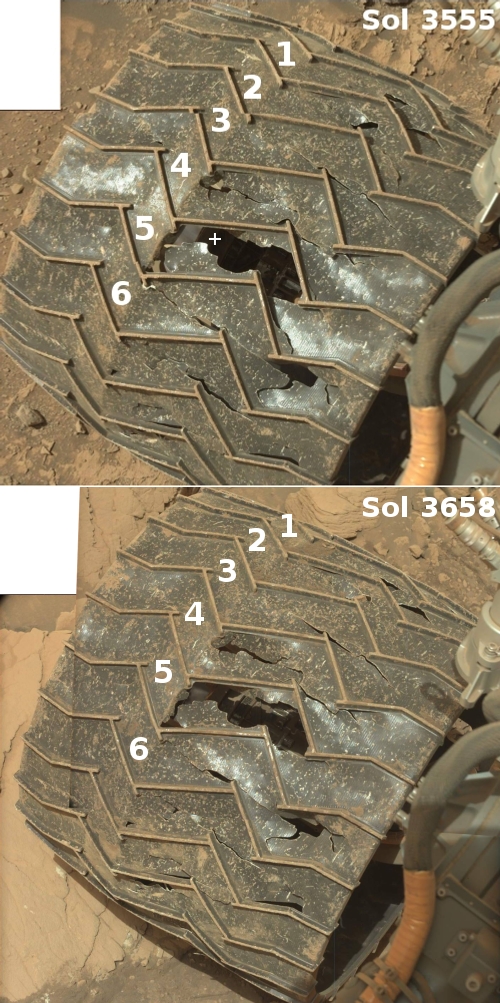
Today the science team for the Mars rover Curiosity downloaded more photos of its wheels, a survey taken routinely now after every 500 meters or 1640 feet of travel. Unlike the pictures made available yesterday that showed some of the worst damage to one of Curiosity’s middle wheels, these new images included the wheel I have been tracking since 2017 as a baseline to see if further damage has occurred.
The photos to the right show that wheel, with the top photo from August and the bottom created from two pictures taken on November 20, 2022. The numbers indicate the matching treads. The “+” sign in the top image indicates a location where new damage was spotted in August.
As you can see, this wheel does not appear to have experienced any additional damage in the more than three months since that August update. While the damage to Curiosity’s wheels remains very concerning, it does appear based on this one wheel that — despite the generally very rough terrain the rover has been traversing since it entered the foothills of Mount Sharp — the wheels in general seem to be holding up.
Though I have not done a careful comparison of these new wheel images with earlier ones, none of the new images appear to show any additional significant damage. It appears that the travel criteria the science team adopted years ago — right after discovering the wheel damage — continues to work to protect the wheels. It picks the rover’s path more carefully to avoid sharper rocks, and includes software that stops the rover should it sense it is crossing a rock sharper than desired.
Of the ten cubesats launched toward the Moon by SLS last week, six are still working while four have problems that are likely killing their missions.
The photo to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by ArgoMoon, an Italian cubesat that is working perfectly. The large impact basin visible is Orientale Basin, located just on the edge of the visible face of the Moon but partly hidden on the far side.
A summary of the status of all ten can be found here. Of the other five still functioning properly, all have been able to maintain proper communications.
Possibly the biggest disappointment however is the failure of Japan’s Omotenashi lander, which was going to attempt a lunar soft landing. Shortly after launch it began tumbling, and engineers were never able to regain full control or communications. The landing attempt has now been abandoned.
Side note: Orion itself also captured some images as it zipped past the Moon yesterday, but they do not appear as high quality as ArgoMoon’s pictures.
For only the sixth time, astronomers this past weekend were able to image an asteroid just before it hit the Earth’s atmosphere and burned up over Canada.
The mini-asteroid, less than 3 feet (1 meter) wide, was spotted by astronomer David Rankin at Mount Lemmon Observatory in Arizona, according to SpaceWeather.com. Subsequent observations by other astronomers confirmed that the rock, coming from the direction of the main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, was on a collision course with Earth.
Only three hours after the first detection, the object, since dubbed C8FF042, sliced through the sky above Canada and landed in Lake Ontario, according to NASA.
While it is believed that most of the meteorite’s pieces that reached the ground fell into Lake Ontario, there is a chance some pieces might still be found along the south coast of the lake between Hamiliton and Niagara Falls.
After experiencing serious tumbling shortly after launch, engineers have successfully put the technology test smallsat CAPSTONE into its planned lunar orbit (the same to be used by NASA’s Lunar Gateway space station), where it will spend at least six months gathering data.
In addition to studying this unique orbit, CAPSTONE’s mission also includes two technology demonstrations that could be used by future spacecraft. The Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System, or CAPS, is a navigational software developed by Advanced Space that would allow spacecraft operating near the Moon to determine their position in space without relying exclusively on tracking from Earth. CAPSTONE will demonstrate this technology by communicating directly with NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been in orbit around the Moon since 2009. CAPSTONE will also demonstrate one-way ranging using a chip-scale atomic clock, which could allow spacecraft to determine their position in space without the need for a dedicated downlink to ground stations.
CAPSTONE is also demonstrating a third technology as well as the use of capitalism in space. The third technology is demonstrating the viability of using a tiny inexpensive smallsat for these kinds of interplanetary missions. The capitalism is that CAPSTONE was built by a private company, Terran Orbital, not NASA, and is being operated by another private company, Advanced Space, not NASA. It was also launched by a private company, Rocket Lab, not NASA. All three have proved or are proving that it is faster and cheaper for the government to merely act as the customer to private enterprise, rather than being the builder/operator and boss.