Bob & Ray, Jane, Laraine & Gilda – Do Ya Think I’m Sexy?
An evening pause: Bob & Ray, performing live in 1979 with the three very talented ladies from the original Saturday Night Live crew.
Hat tip Charlie Tutino.
An evening pause: Bob & Ray, performing live in 1979 with the three very talented ladies from the original Saturday Night Live crew.
Hat tip Charlie Tutino.
UPDATE: The launch has been scrubbed for the day. No word on when they will reschedule, nor has Astra released any information as to what caused the launch abort, other than a “telemetry issue.”.
Capitalism in space: The second attempt by Astra to launch its first commercial satellites on its second orbital launch from Cape Canaveral aborted at T-0.
The launch on February 5th was scrubbed when some radar equipment used by the range failed.
The launch team is presently reviewing the data to see if they can recycle and attempt another launch today. This would be the second recycle today, as the first launch attempt was held about a minute before launch and then recycled, leading to the launch abort at T-0. The launch window still has about 100 minutes left.
The rocket is carrying four cubesats, three built by students at three different universities, with the fourth built by engineers at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in their effort to learn how to build cubesats for themselves.
I have embedded Astra’s live stream below the fold, for those who wish to watch.
» Read more
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News

Home-schooling: a example of liberty in action
Because of oppressive and racist policies that include mask mandates, remote schooling, and the teaching of the bigoted and Marxist program dubbed Critical Race Theory, Virginia has seen a huge increase in home schooling in the past two years.
Homeschooling in Virginia has increased by nearly 40% since 2019, which has been partly fueled by the implementation of critical race theory in classrooms and the coronavirus. “The children don’t belong to the state. I think parents really want to impart their own values to their children – their values and beliefs and their own worldview. And that is a major reason parents are home schooling,” Yvonne Bunn, director of government affairs for the Home Educators Association of Virginia, told the Virginia Mercury earlier this month.
There are currently about 62,000 homeschoolers in Virginia, according to Virginia Department of Education data. There were 44,226 homeschoolers in the state during the 2019/2020 school year, marking a more than 39% increase. The numbers this year are slightly down from the 2020/2021 school year, when 65,571 students were homeschooled.
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has now created an office to lobby governments worldwide to block the coming commercial launch of numerous satellite constellations.
The IAU claims that the first goal of this new office will be to study the effects of these satellites on ground-based astronomy accompanied by an effort to work with industry to mitigate those effects.
That is a lie. This is the office’s real purpose:
Another role for the center will be to create national and international laws and norms for what regulators allow in orbit. “We need to codify these good intentions, to have some backup,” says Richard Green of the University of Arizona’s Steward Observatory. “We’ll take a two-pronged approach: Cooperate and develop legislation to apply if necessary.” IAU and other bodies are working to convince the United Nations’s Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space of the need for legislation. “We are confident that we will have guidelines that will have to be followed by companies in the near future,” Benvenuti says. Cosmologist Aparna Venkatesan of the University of San Francisco says it would be good if there were laws in the United States and elsewhere that echoed the influential U.S. Clean Air Act: “Many of us dream of a Clean Skies Act.”
Rather than realize that things are changing and Earth-based astronomy is becoming obsolete, the astronomers wish to use the force of law to block progress by others so that they can continue to live in the past.
The time to have moved all cutting edge astronomical research off the planet arrived more than three decades ago. The astronomers refused to recognize this, focusing instead on building giant telescopes on the ground that had less capability than the Hubble Space Telescope and were dogged by political and engineering challenges that hindered their success.
Had astronomers instead focused on building many small orbiting optical telescopes, the threat of satellite constellations now would be minimal. Instead, astronomers would be poised to build the bigger space-based telescopes they need. Instead, they are grounded, with the needed future space-based telescopes possibly decades away.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, well worth your time, go here.
» Read more
InSight on February 5th resumed science operations, reactivating its seismometer to record Martian quakes.
As I suspected in my previous InSight update, the lander’s life is still coming to an end.
The mission, though, has been grappling with a gradual decline in the spacecraft’s power because of dust accumulating on its solar arrays. Unlike the Spirit and Opportunity rovers, whose arrays were regularly cleaned by atmospheric activity, dust has continued to accumulate on InSight’s arrays. At a meeting of MEPAG in June 2021, Banerdt projected that power levels would drop below that needed to keep the spacecraft alive in the spring of 2022.
That date has been pushed out slightly, but he said the long-term outlook for the lander still does not look promising. “Our current projections indicate that the energy will drop below that required to operate the payload in the May/June time frame and probably below survivability some time near the end of the year,” he said.
They might still squeeze a month or two more from the lander, but unless they are very lucky and a dust devil blows across it, the end is coming.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
Russia successfully completed its first launch in 2022 on February 5th, using its Soyuz-2 rocket to launch a secret military satellite.
The 2022 launch race:
6 SpaceX
2 China
1 Virgin Orbit
1 ULA
1 Russia
This report is a day late because I was out in the back country, hunting javelinas.
Engineers have now determined that the failure of one of the six reaction wheels that point the orbiting Gehrels-Swift Observatory was the cause of its shutdown into safe mode on January 18th, and are now reconfiguring the space telescope to operate with only five gyroscopes.
The team is currently testing the settings for operating the spacecraft using the five operational reaction wheels. After the tests for these settings have been completed, they plan to upload them to the spacecraft next week.
Swift can fully carry out its science mission with five wheels. After careful analysis, the team has determined that the five-wheel configuration will minimally impact the movements necessary for Swift to make science observations. The team expects the change will slightly delay the spacecraft’s initial response time when responding to onboard gamma-ray burst triggers, but this will not impact Swift’s ability to make these observations and meet its original operational requirements.
Only after getting Gehrels-Swift operating again will the engineers then consider trying to recover the failed reaction wheel.
Gehrels-Swift was one of the key space telescopes that made it possible for astronomers to solve the mystery of gamma ray bursts. It is also used today to help identify the source of mysteries like fast radio bursts and other supernovae events. It was designed to quickly begin observing in multiple wavelengths any spot in the sky where a mystery burst or new supernova has occurred, thus getting astronomers the earliest new data possible.
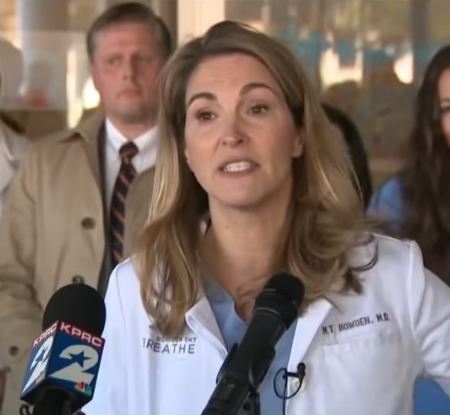
Dr. Mary Bowden, refusing to bow to the authorities
Pushback: Mary Bowden, a doctor who was suspended from working at Houston Methodist Hospital because she publicly opposed COVID shot mandates and used ivermectin in treating her Wuhan flu patients, has now sued the hospital to get data on the effects, pro and con, of those shots on its own patients.
The hospital had accused her of “spreading dangerous misinformation which is not based on science” because she had successfully treated about 2,000 COVID patients, none of which ever needed hospitalization, with both ivermectin and monoclonal antibodies.
Bowden apparently has publicly advocated choice by both doctors and patients, something the lords at Houston Methodist cannot tolerate.
Bowden added, “We all know that early COVID treatment works, it saves lives, and I’m not going to be silenced, intimidated, or bullied by Houston Methodist, Houston Chronicle, or anyone else who wants to target physicians that question the narrative.”
In November, [her Attorney Steve] Mitby said that Bowden had never peddled disinformation, as a Stanford University-trained physician who has had vast experience in treating coronavirus patients. “She is helping her patients, through a combination of monoclonal antibodies and other drugs, to recover from COVID. Dr. Bowden’s proactive treatment has saved lives and prevented hospitalizations,” he said at the time. “Dr. Bowden also is not anti-vaccine as she has been falsely portrayed. Dr. Bowden has opposed vaccine mandates, especially when required by the government. That is not the same as opposing vaccines.”
Hospitals nationwide have been blocking doctors from considering these other treatments, even though there is building evidence that they work. Bowden’s own success is an example of that evidence.
The lawsuit is not seeking damages. Instead, it wishes to obtain from the hospital its data on its own success at treating the Wuhan flu, as well as what it has gained financially by that treatment.
» Read more

Click for full resolution. Click here, here, and here for original images.
Cool image time! The panorama above was created from three photos downloaded today from Curiosity’s right navigation camera. It looks to the northeast of the rover, out across Gale Crater. The crater floor is about 1,750 feet lower.
This is dust season on Mars, which explains the thick haze in the crater. About 25 miles away the crater rim can be faintly seen through the dust haze as a mountain chain. If you look at the full resolution panorama you can see several buttes on the crater floor barely visible through that haze.
The map to the right gives the context. Curiosity’s present location is indicated by the yellow dot, with the yellow lines indicating the area covered by the panorama. The red dotted line indicates the rover’s future planned route.
For the last few weeks Curiosity has been working nestled to the base of a small butte the science team has dubbed “The Prow”, studying its numerous thin layers. I featured the Prow in this January 11th post, though at the time I overestimated its size, which is only about ten feet high. The butte is especially fascinating in that its top layers overhang outward in an unbelievable manner.
The rover is now about to move on, though where must still be decided by the science team. Based on their most recent update it appears they are not ready to leave this barren rocky hollow surrounded with many-layered buttes, and will take the rover to another.
Capitalism in space: Iceye, which launches commercial Earth observation satellites, has successfully raised another $136 million in private investment capital, bringing its total cash raised to $304 million.
With the latest cash infusion announced Feb. 3, Iceye is expanding manufacturing capacity and upping its launch tempo. Iceye plans to loft 11 satellites in 2022, after launching seven in 2021. Iceye also will devote additional resources toward natural catastrophe monitoring. In 2021, Iceye began working with insurance industry partners including Zurich-based Swiss Re and Tokyo-based Tokio Marine.
With the climate changing and natural catastrophes becoming more frequent, Iceye executives see increasing demand for updated information. SAR satellites are particularly useful for observing floods and other disasters because unlike optical sensors, they gather data at night and through clouds.
Essentially, commercial satellites like Iceye’s are replacing the government satellites that NASA and NOAA have been launching, but with far less frequency and far more cost in the last two decades. In fact, the inability of these agencies to get many new Earth observation satellites launched on time and cheaply has fueled this new private industry.
Like NASA’s manned program, the government will soon depend entirely on privately-built satellites for its climate and Earth resource research. And it will get more for its money and get it faster.
Capitalism in space: Two former NASA managers have teamed up with two commercial businessman to form a startup, dubbed Quantum Space, to launch an unmanned platform to lunar space to provide support for NASA’s Artemis program.
The team includes Steve Jurczyk, who spent thirty years at NASA and finished his career there before retiring serving as acting NASA administrator for the first three months of the Biden administration.
Jurczyk is one of the three co-founders of Quantum Space. Another is Ben Reed, former division chief of exploration and in-space services at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and who worked on satellite servicing projects there. He is the chief technology officer of Quantum Space. The third co-founder is Kam Ghaffarian, who also helped start commercial space station company Axiom Space and lunar lander developer Intuitive Machines after selling Stinger Ghaffarian Technologies. They’re joined by Kerry Wisnosky, the co-founder and former principal owner of Millennium Engineering and Integration, who is the chief operating officer of Quantum Space.
Their plan is to launch their platform and robots to the Earth-Moon L1 point, the spot where the gravitational spheres of influence of the Earth and Moon meet, about 40,000 miles from the Moon.
The outpost … would consist of two components. One is a spacecraft bus that serves as a platform for hosting payloads, using modular “plug-and-play” interfaces. The other is a spacecraft that would deliver payloads to the platform and install them using robotic manipulators.
Those payloads could include communications, navigation, remote sensing, space domain awareness and space weather sensors, Jurczyk said. Those payloads would primarily come from customers, but he said the company is looking at developing its own payloads, particularly for imaging of the Earth and moon.
They hope to launch their first satellite by ’25.
Like the insiders who run Axiom, these guys are taking advantage of their experience at NASA to build a private space company that will serve NASA’s needs. They are also recognizing that in the coming years, everything NASA “does” will be done by private companies. This company is their effort to jump on that bandwagon.
With the detection by one instrument of the first photons traveling through all of the mirrors of the James Webb Telescope the alignment of its many mirror segments begins.
This week, the three-month process of aligning the telescope began – and over the last day, Webb team members saw the first photons of starlight that traveled through the entire telescope and were detected by the Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) instrument. This milestone marks the first of many steps to capture images that are at first unfocused and use them to slowly fine-tune the telescope. This is the very beginning of the process, but so far the initial results match expectations and simulations.
The article at the link provides a very detailed description of the step-by-step process used by engineers to align the eighteen segments of the primary mirror.
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on September 22, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows an unnamed four-mile-wide crater in the high northern lowland plains of Mars, at 60 degrees north latitude.
At 60 degrees latitude, it is likely that the crater’s interior is filled with buried glacial ice. A close look at the crater’s interior rim shows that whatever material fills the crater does not quite reach the rim. Furthermore, there are areas in the interior where it appears some slight sublimation has occurred. These features suggest the interior material is buried ice, but do not prove it.
What makes this crater intriguing however is the irregular depression at its center. When craters have a feature at the center, it usually is a central peak, caused at impact. The impact makes the ground act like a pond of water when you drop a pebble into it, with circular ripples (the crater rim) spreading outward and an uplift in the center (the central peak). In the case of a crater, the pond quickly freezes, locking those ripples and uplift in place.
Why a central depression then?
» Read more
Capitalism in space: SpaceX successfully completed its third launch in four days today, launching 49 Starlink satellites into orbit on its Falcon 9 rocket.
At the time of writing, the satellites themselves have not yet deployed. The first stage, flying its sixth mission, landed successfully. The two fairing halves were flying their sixth and fourth flights.
The 2022 launch race:
6 SpaceX
2 China
1 Virgin Orbit
1 ULA

A victory for liberty in Louisville
Do not comply: Policeman Matthew Schrenger has won a $75,000 settlement from the city of Louisville, Kentucky, for suspending him after he prayed, while off duty, in front of an abortion clinic.
Officer Matthew Schrenger was off-duty when he stopped to pray with his father on the public sidewalk outside the EMW Women’s Surgical Center nearly a year ago, on Feb. 20, according to the Thomas More Society. Schrenger arrived in the early morning, before the abortion provider opened, as part of 40 Days for Life, an international grassroots campaign dedicated to ending abortion through prayer and fasting.
Matt Heffron, senior counsel for the Thomas More Society, previously said that Schrenger, a 13-year police veteran, was praying the rosary, according to the local Fox affiliate, WDRB News.
For his actions, Schrenger was suspended for more than four months with pay, stripped of his police powers, and placed under investigation.
Capitalism in space: NASA on January 31st released its updated plan for transitioning all government manned orbital operations to commercial private space stations in the next eight years in preparation for the deorbiting of ISS in early 2031.
You can read the report here [pdf]. The key paragraph however is this:
NASA has … signed agreements with three U.S. companies (Blue Origin of Kent, Washington; Nanoracks LLC of Houston, Texas; and Northrop Grumman Systems Corporation of Dulles, Virginia) to develop commercial destinations in space that go directly to orbit, i.e., free-flyers. The awards, along with the Axiom concept [where the private station starts as part of ISS and then later separates], are the first part of a two-phase approach to ensure a seamless transition of activity from the ISS to commercial destinations. During this first phase, private industry, in coordination with NASA, will formulate and design [commercial space stations] capabilities suitable for potential Government and private sector needs. The first phase is expected to continue through 2025.
For the second phase of NASA’s approach to a transition toward [commercial space stations], the Agency intends to certify for NASA crew member use [commercial space stations] from these and potential other entrants, and ultimately, purchase services from destination providers for crew to use when available.
It is NASA’s goal to be one of many customers of commercial LEO destination services, purchasing only the goods and services the Agency needs. [Commercial space stations], along with commercial crew and cargo transportation, will provide the backbone of the human LEO ecosystem after the ISS retires. [emphasis mine]
The report predicts that, by using private stations instead of building its own, the agency will save up to two billion dollars per year, money it can than use of planetary missions. This of course is assuming NASA cancels SLS. If not, I predict that overpriced cumbersome rocket will quickly absorb all this money saved.
The highlighted sentence indicates that NASA continues to accept entirely the recommendations I made in my 2017 policy paper, Capitalism in Space [a free pdf download]. In fact, that sentence is almost an exact quote from one of most important recommendations.
Both NASA and SpaceX are now conducting an investigation into the delayed release of one of four parachutes during landing on two different Dragon missions recently.
The first incident occurred during the landing of the Dragon capsule Resilience carrying the Inspiration4 commercial crew in November. The second occurred on January 24, 2022 during the return of a cargo freighter.
In both cases there was no safety risk, as the capsules can land safely with only three chutes. However, both NASA and SpaceX want to know why this is happening, and work out a solution to prevent it in the future.
The new colonial movement: India’s space agency ISRO today announced that it has scheduled the launch of its Chandrayaan-3 lunar lander mission for August 2022.
The launch date was revealed by a government official, who also said that this launch will be one of eight total by India in 2022. If that number is completed, it would be the most India has ever accomplished in a single year, topping the seven launches that lifted off in 2018. It would also signal that India has finally put aside its fear of COVID that has shut down its aerospace industry for the last two years.
Capitalism in space: NASA announced yesterday that it as well as the other international partners for ISS have approved the crew and passengers who will fly on Axiom’s first commercial flight to the station, presently scheduled for launch on March 30, 2022, flying in SpaceX’s Endeavour capsule.
Axiom Space astronauts Michael López-Alegría, Larry Connor, Mark Pathy, and Eytan Stibbe are prime crew members of the Ax-1 mission. López-Alegría, who was born in Spain, raised in California, and a former NASA astronaut, will serve as the mission commander. Connor, of Dayton, Ohio, will serve as pilot. Pathy, from Canada, and Stibbe, from Israel, will be mission specialists. The quartet is scheduled to spend eight days aboard the orbiting laboratory conducting science, education, and commercial activities before their return to Earth.
Because the four will be staying at this government station, they must work with NASA, which appears to be requiring them to do some research while on board. Those experiments are still “under review” though Axiom has already revealed a suite of microgravity experiments the crew will perform.
Capitalism in space: The British smallsat rocket company Orbex has now submitted its application for a launch license to the United Kingdom’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA).
The press release does not mention a launch date, but it does state that ground tests of Orbex’s Prime rocket, designed to launch smallsats, are about to begin.
The Orbex ‘Prime’ rocket is soon to be tested on the Orbex LP1 launch platform at a facility in Kinloss, close to the Orbex headquarters in Forres, where full ‘dress rehearsals’ of launch procedures will take place.
Actual launches will take place at Space Hub Sutherland in Scotland. A previous announcement in 2020 had suggested the first launch would occur in ’22. Whether that date can still be met is unclear, but without doubt Orbex is moving forward towards launch.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, well worth your time, go here.
» Read more
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base a National Reconnaissance Office spy satellite .
What made this launch unusual was that it used a new first stage, only the third time SpaceX has done so since the beginning of 2020. Last year, of 31 launches all but two used a used first stage. This new first stage landed successfully at Vandenberg.
5 SpaceX
2 China
1 Virgin Orbit
1 ULA

Freedom of speech banned at Plainwell High School.
They’re coming for you next: The faculty at Plainwell High School in Michigan suspended student David Stouts for three days because he dared to express his Christian religious beliefs in private texts to his friends.
Some of the things he discussed were the love God has for sinners, Stout’s love for his friends, and, here is where the “problems” began, Stout said he believed homosexuality is a sin and….drum roll…there are only two genders!
Before Stout was suspended, he claims he was asked by a faculty member [band leader Austin Hunt] why he didn’t turn himself in for his private discussions involving religion and “inappropriate” jokes shared amongst friends, (Stout allegedly chuckled at homophobic/racial jokes his friends made during band camp in July 2021).
Stout claims he was informed that speaking about religion on campus was verboten because he might hurt someone’s feelings, and that students who overhear his opinions (on text message???) might feel “unsafe.”
Jeff Foust of Space News today has a detailed article detailing NASA’s decision-making process that led to its awarding Blue Origin, Northrop Grummann, and Nanoracks development contracts for their proposed commercial and private space station.
The article not only describes NASA’s analysis of each winning bid, it also describes the analysis of some of the eight bids that lost. Most interesting were the strengths and weaknesses NASA saw from SpaceX’s bid.
The company won strengths based on its technical maturity linked to HLS proposal (the Starship lunar lander) and a “strong approach” to communications that appeared to be associated with SpaceX’s Starlink constellation. However, NASA assessed several weaknesses because of a lack of details about its concept, including how it will accommodate payloads and scale up an environmental control system for long-duration missions. [emphasis mine]
While SpaceX so far has proven itself to be a brilliant rocket and engineering company — achieving things that everyone else said couldn’t be done and doing so so quickly it takes your breath away — the company has so far appeared to have little understanding or knowledge about the complexities of building an interplanetary manned vessel. This NASA analysis, as noted by the highlighted phrases in the quote above, underlines that impression.
None of this precludes SpaceX from gaining that knowledge and applying it to the engineering of future Starship designs. This information however shows that the company still lacks this knowledge. It apparently has still not tackled the job of designing the insides of Starship, only its rocketry for getting into orbit.
With the posting yesterday by NOAA of its monthly update to its graph showing the long term trends in the Sun’s sunspot activity, it is time for me to do my own update, showing this graph below with annotations in order to provide some context.
While sunspot activity dropped slightly in January, the activity still remained well above the prediction made by NOAA’s panel of solar scientists in 2020, with the upward trend towards a solar maximum much steeper than predicted as well.
» Read more
Astronomers have now confirmed that an asteroid discovered in 2020, dubbed 2020 XL5, is an orbit that makes it the second Earth Trojan asteroid discovered, orbiting the Sun in the same orbit as the Earth but 60 degrees ahead of us.
In December 2020, 2020 XL5 was spotted by astronomers with the Pan-STARRS 1 survey telescope in Hawaii and added to the International Astronomical Union’s Minor Planet Center database. Amateur astronomer Tony Dunn went on to calculate the object’s trajectory using NASA’s publicly-available JPL-Horizon’s software and found that it orbits L4, the fourth Earth-sun Lagrange point, a gravitationally balanced region around our planet and star. 2010 TK7, the first-confirmed Earth Trojan asteroid, is also at L4.
The confirmation that it is definitely a Trojan was then made using both new observations as well as a review of archival images, allowing the astronomers to not only refine the asteroid’s orbit, but determine that it is a C-type asteroid, dark with lots of carbon. The data also suggests that in about 4,000 years, 2020 XL5 will drift from its Trojan point.
There are certainly more such asteroids, but detecting them is difficult from Earth because they can only be seen in twilight.