Trump budget proposal
The Trump administration today released its overall rough budget plan for 2018. This is not a detailed budget, but an summary of their plan, indicating where they wish to cut and where they wish to increase budgets. The proposal is also not complete, making no mention of the administration’s budget plans for many departments, such as the National Science Foundation.
Science research in the federal government is significantly impacted, but not as badly as most of the articles you will read in the mainstream anti-Trump, Democratic Party press. A few examples:
- Science: NIH, DOE Office of Science face deep cuts in Trump’s first budget
- Science: A grim budget day for U.S. science: analysis and reaction to Trump’s plan
- Nature: US science agencies face deep cuts in Trump budget
- Washington Post: NASA budget would cut Earth science and education
- Washington Post: Federal health department would face a nearly 18 percent cut
I must note that not all the news stories are blindly hostile to this budget proposal:
- Washington Post: Trump would increase Energy Department funds to manage nuclear stockpile
- SpacePolicyOnLine: Trump Budget Request Kills ARM, Supports SLS/Orion and Public Private Partnerships
- USA Today: Trump’s NASA budget preserves Mars mission, cuts Earth science, asteroid trip, education
Of all the science agencies, NASA probably came off with the least change. The budget cuts only about 5% from the agency’s Earth science budget, while cutting some specific Earth science missions. The budget also supports SLS/Orion, though it finally puts the nail in the coffin of the asteroid redirect mission, an Obama proposal that has never garnered any interest from anyone else.
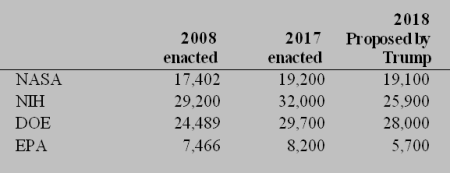
The key to understanding all these budget cuts is to see them in context, to compare the 2018 proposed budgets with the budgets these agencies received in the past. The table on the right gives some of this context (numbers shown are in millions) for several of the science agencies most effected by the proposal. The proposal is not detailed enough to pin down the changes for many other science agencies, but from this table it is clear that the Trump administration is not calling for the end of science, and is proposing some reasonable cost cutting, something that has been rare in government for many years.
What will be missed by most of the press about this Trump budget proposal is that it is not trying to trim the size of the federal government. While it cuts spending in many departments, those cuts are entirely aimed at providing room to raise the budget of the Defense Department by $54 billion. While I can applaud the desire of the Trump administration to be revenue neutral, the stark fact remains that by remaining revenue neutral Trump still leaves us with a gigantic annual federal deficit. They have made no effort to balance the overall budget.
Worse, this proposal would repeal the Budget Control Act of 2011, which imposed sequestration to the federal budget and has actually done the most in the past half century to bring that budget under control. Once this act is repealed, it will allow the spenders in Congress (of which the Republicans are as guilty as the Democrats) to open the floodgates once again. This will not be good.
Let me add one good aspect of the Trump budget. It proposes to eliminate a whole range of government political agencies that accomplish nothing but provide pork or to propagandize the Democratic Party’s positions:
The Budget also proposes to eliminate funding for other independent agencies, including: the African Development Foundation; the Appalachian Regional Commission; the Chemical Safety Board; the Corporation for National and Community Service; the Corporation for Public Broadcasting; the Delta Regional Authority; the Denali Commission; the Institute of Museum and Library Services; the Inter-American Foundation; the U.S. Trade and Development Agency; the Legal Services Corporation; the National Endowment for the Arts; the National Endowment for the Humanities; the Neighborhood Reinvestment Corporation; the Northern Border Regional Commission; the Overseas Private Investment Corporation; the United States Institute of Peace; the United States Interagency Council on Homelessness; and the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Getting these eliminated will at least be a start to cleaning up the mess in Washington.
