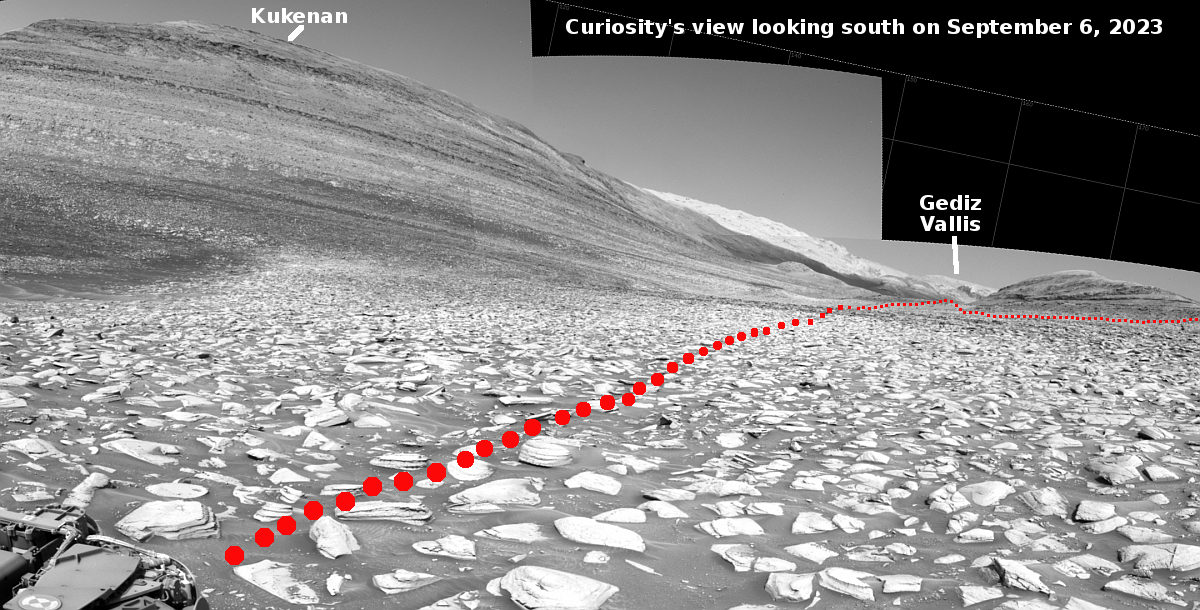
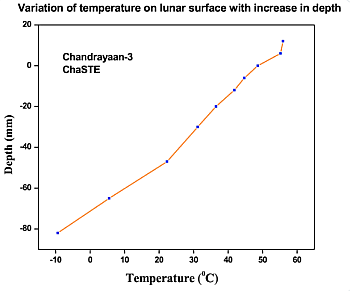
Weird rocks on Mars

For original images, go here and here.
Time for two cool images, this time from both of the American rovers on Mars.
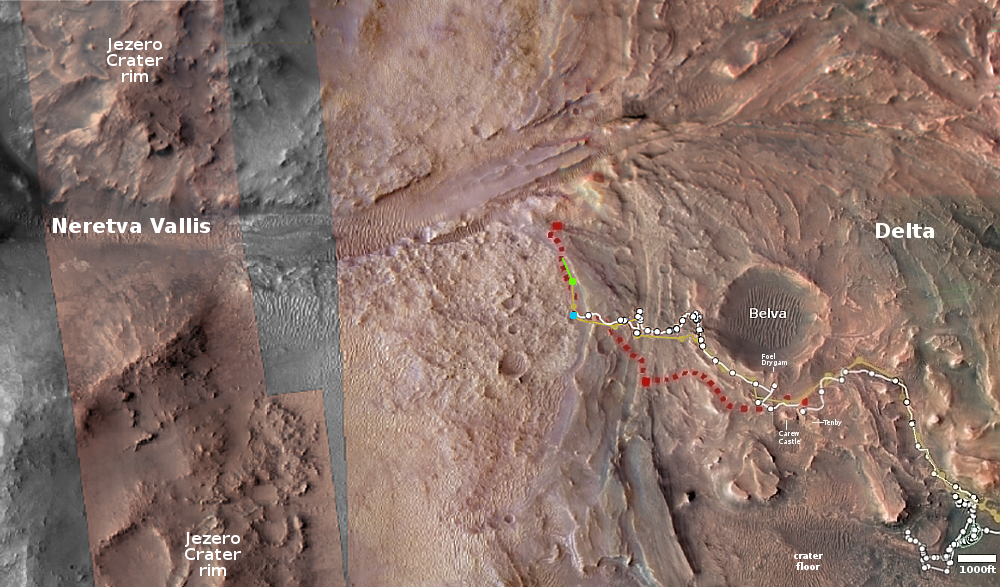
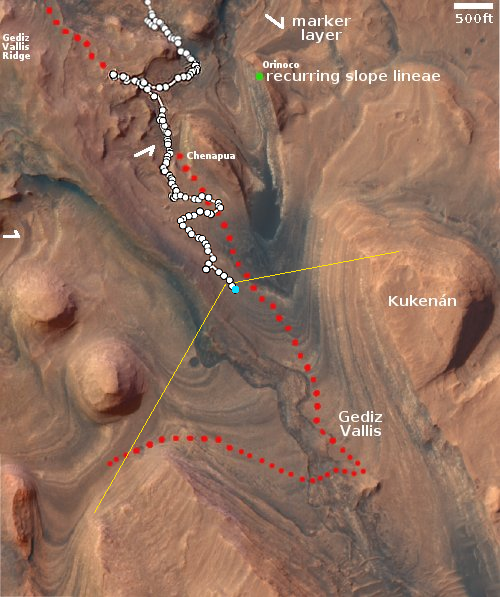
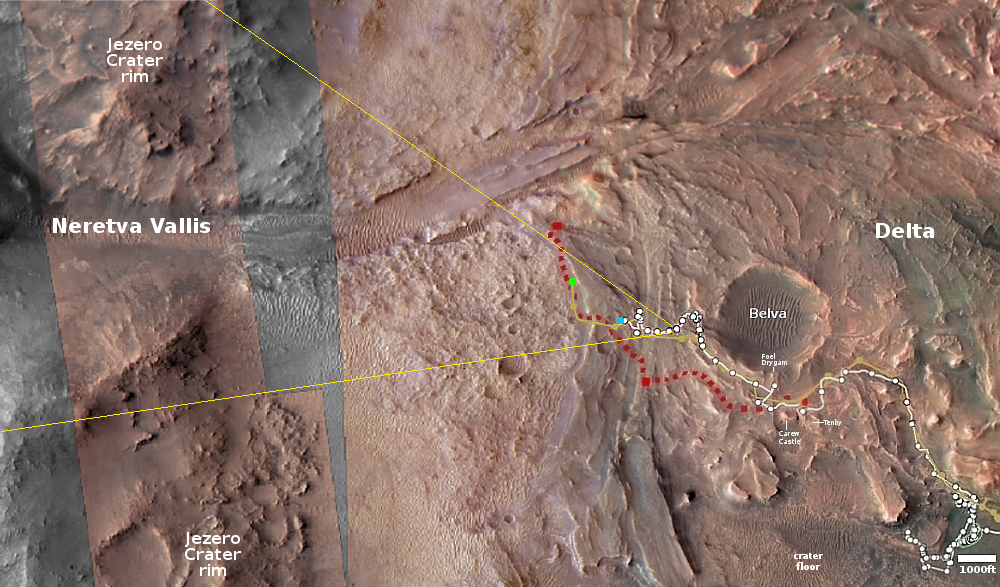
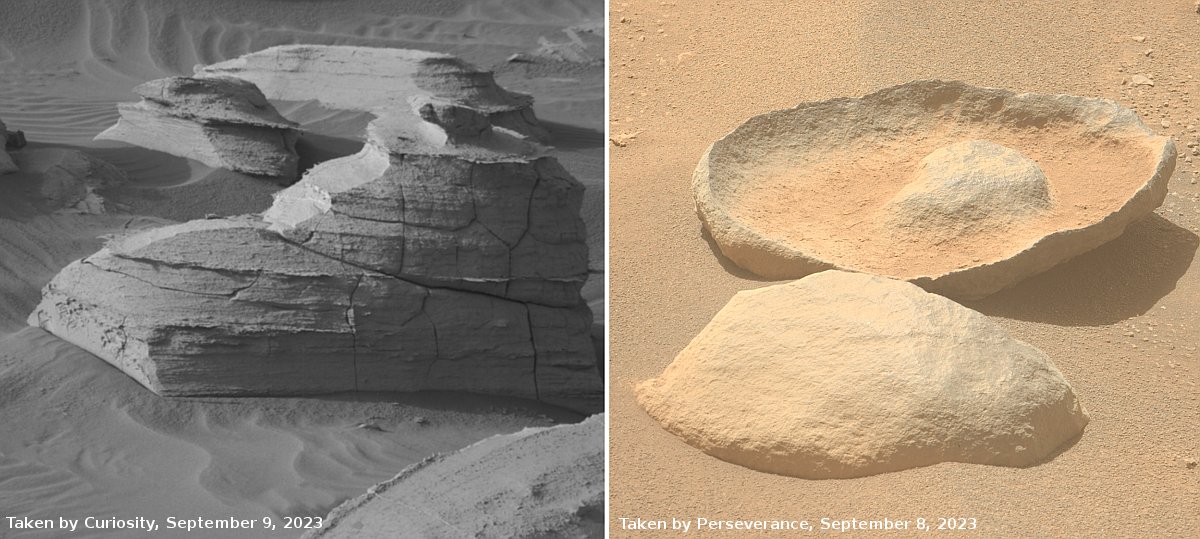
The left picture above was taken on September 9, 2023 by the high resolution mast camera on Curiosity. It shows what appears to be a many-layered but rounded rock which appears typical of the many boulders that cover the terrain through which Curiosity is presently traveling. In the past the layered rocks that Curiosity has observed lower on the flanks of Mount Sharp have not been rounded. Instead, the delicate layers have often extended outward at the rock’s edges, almost like paper or threads. For some reason, the layers in the rocks here have been eroded smooth, suggesting they were once covered by flowing water or ice, able to round the rough edges in a way that Mars’ thin atmosphere can’t.
What is puzzling is the location, higher on Mount Sharp. One would expect the reverse, with such erosion more typical lower on the mountain and uneroded delicate layers more common higher on the mountain.
The right picture above was taken on September 8, 2023 by one of the high resolution mast cameras on the rover Perseverance in Jezero Crater, about 5,000 miles to west of Curiosity. It shows a rock whose shape is so strange it is hard to fathom a geological process that would result in this form. Possibly the rock was a surface layer on a larger round boulder, and the normal freeze-thaw cycle of Mars caused it crack off as one piece. The lump in the middle however makes this explanation questionable.
Also puzzling is the curved shape. On Mars almost no geological layers have been found that are curved. They are generally flat and horizontal, reflecting the lack of tectonic processes that on Earth often twist and squash layers.

For original images, go here and here.
Time for two cool images, this time from both of the American rovers on Mars.
The left picture above was taken on September 9, 2023 by the high resolution mast camera on Curiosity. It shows what appears to be a many-layered but rounded rock which appears typical of the many boulders that cover the terrain through which Curiosity is presently traveling. In the past the layered rocks that Curiosity has observed lower on the flanks of Mount Sharp have not been rounded. Instead, the delicate layers have often extended outward at the rock’s edges, almost like paper or threads. For some reason, the layers in the rocks here have been eroded smooth, suggesting they were once covered by flowing water or ice, able to round the rough edges in a way that Mars’ thin atmosphere can’t.
What is puzzling is the location, higher on Mount Sharp. One would expect the reverse, with such erosion more typical lower on the mountain and uneroded delicate layers more common higher on the mountain.
The right picture above was taken on September 8, 2023 by one of the high resolution mast cameras on the rover Perseverance in Jezero Crater, about 5,000 miles to west of Curiosity. It shows a rock whose shape is so strange it is hard to fathom a geological process that would result in this form. Possibly the rock was a surface layer on a larger round boulder, and the normal freeze-thaw cycle of Mars caused it crack off as one piece. The lump in the middle however makes this explanation questionable.
Also puzzling is the curved shape. On Mars almost no geological layers have been found that are curved. They are generally flat and horizontal, reflecting the lack of tectonic processes that on Earth often twist and squash layers.