Curiosity’s upcoming travel route
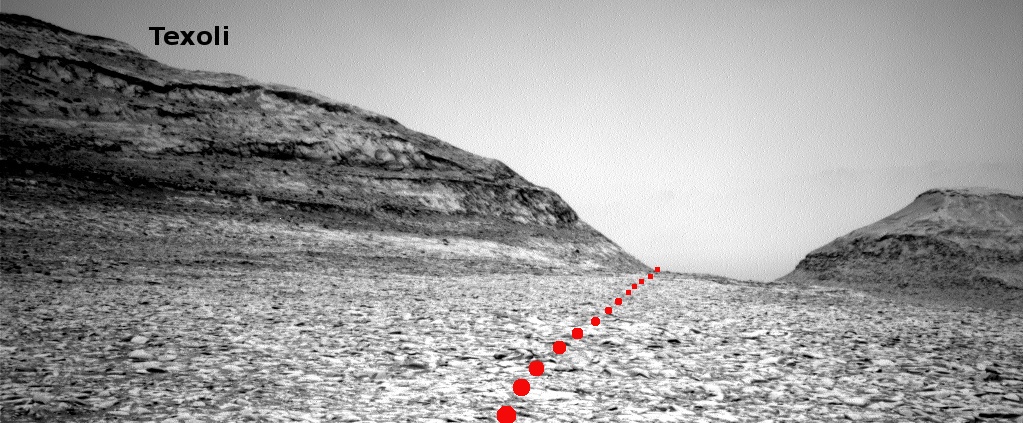
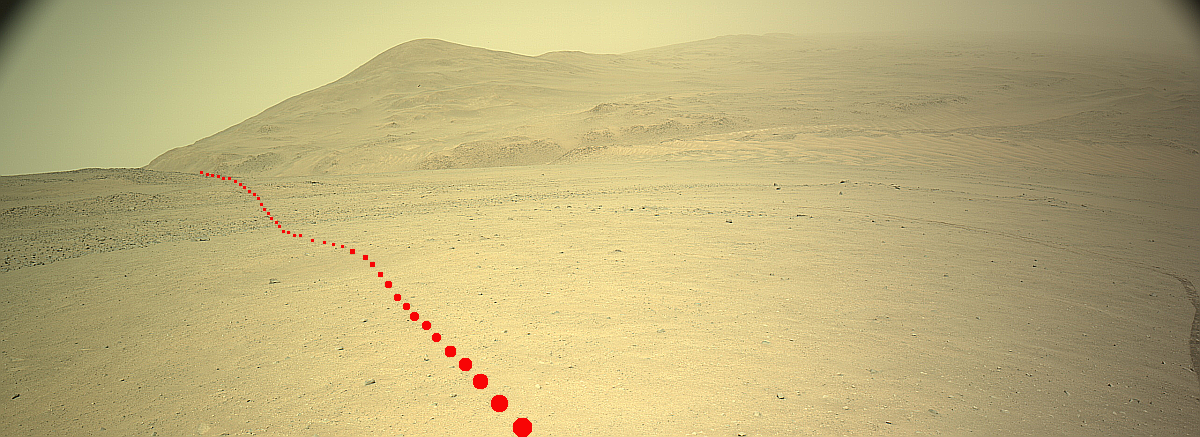
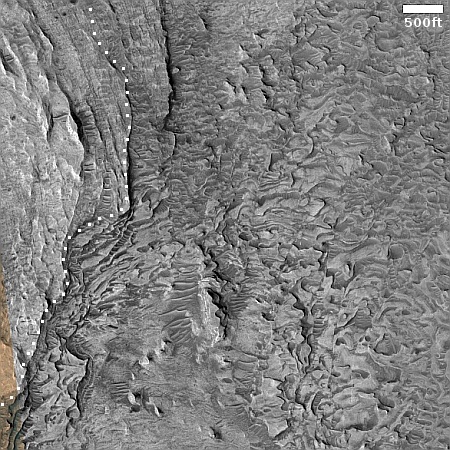
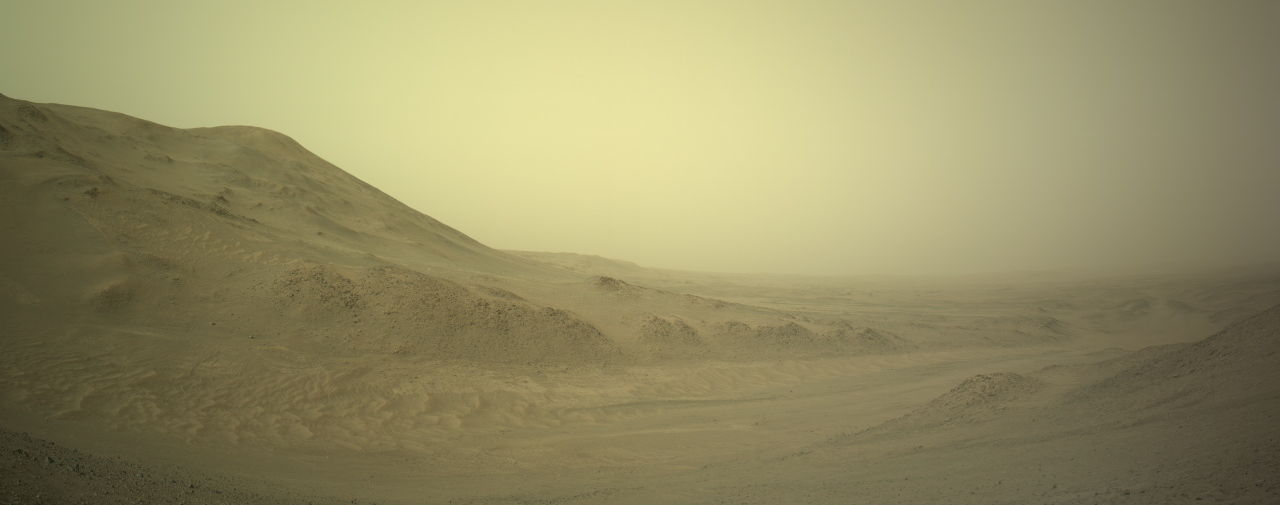
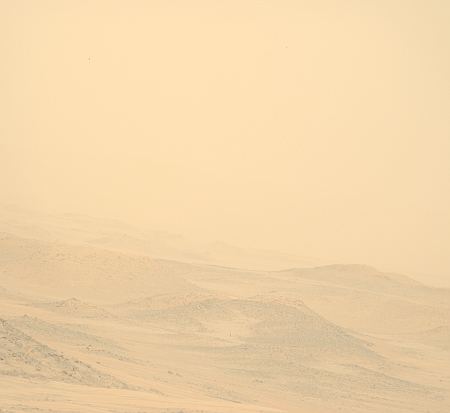
Cool image time! The panorama above, cropped and annotated to post here, was taken on October 6, 2024 by the right navigation camera on the Mars rover Curiosity. It looks south, down the slopes of Mount Sharp and across Gale Crater, the distant crater rim barely visible through the dusty air twenty to thirty miles away.
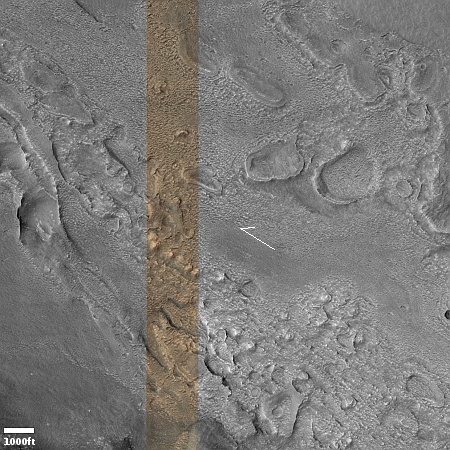
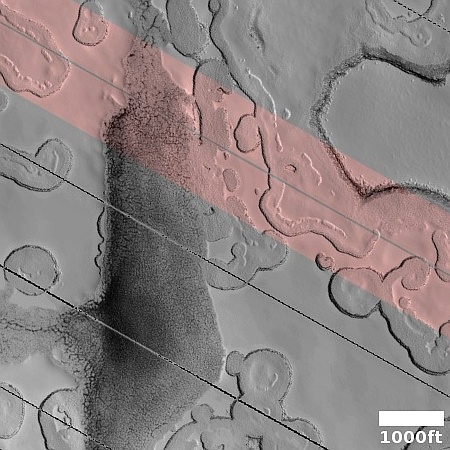
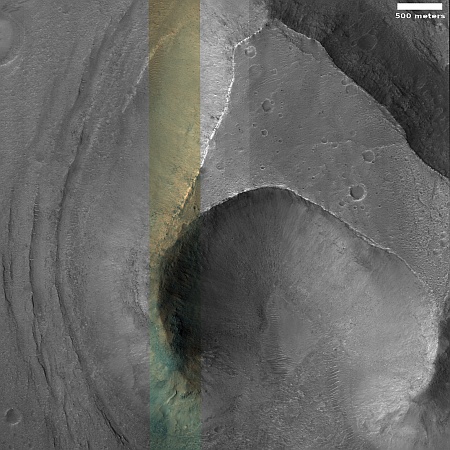
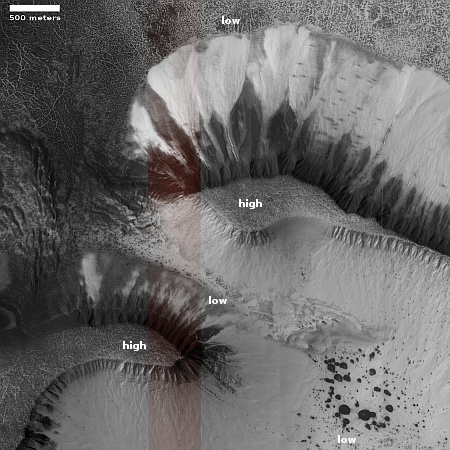
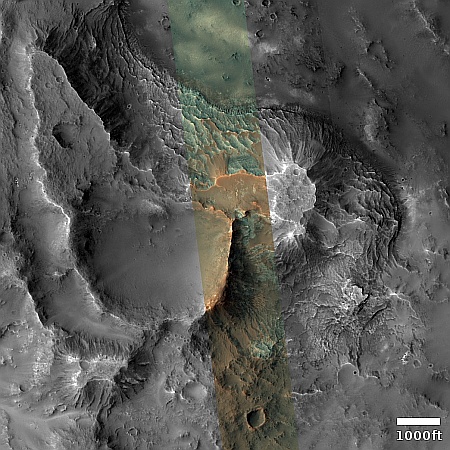
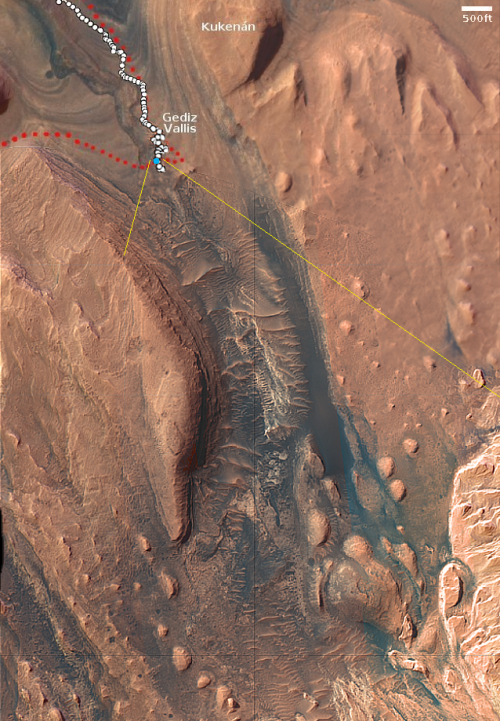
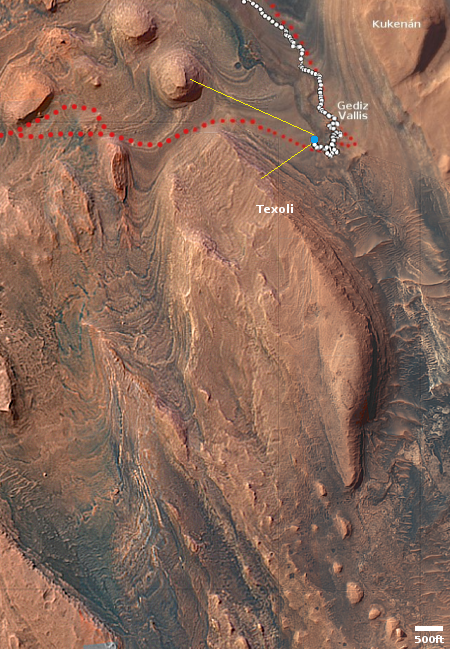
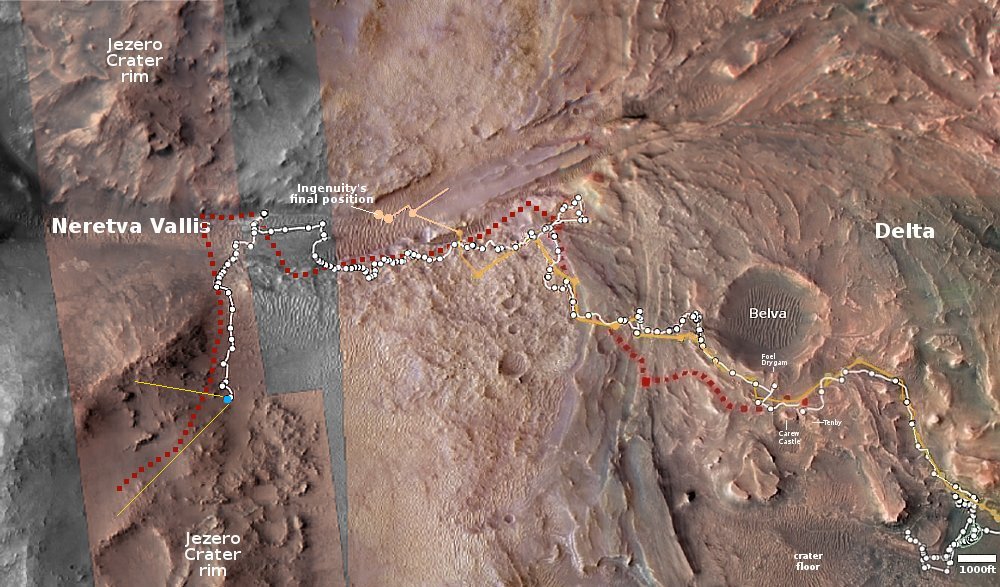
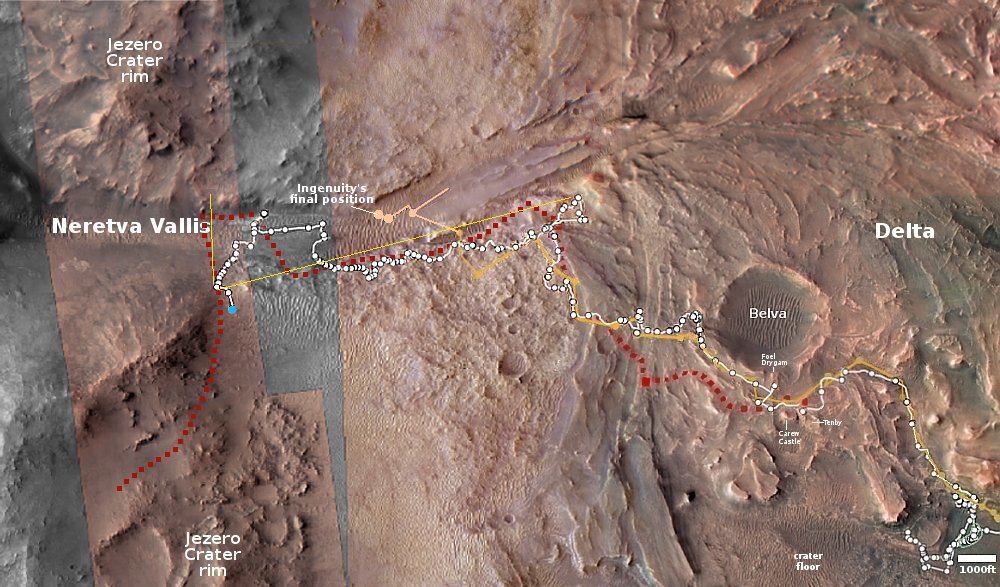
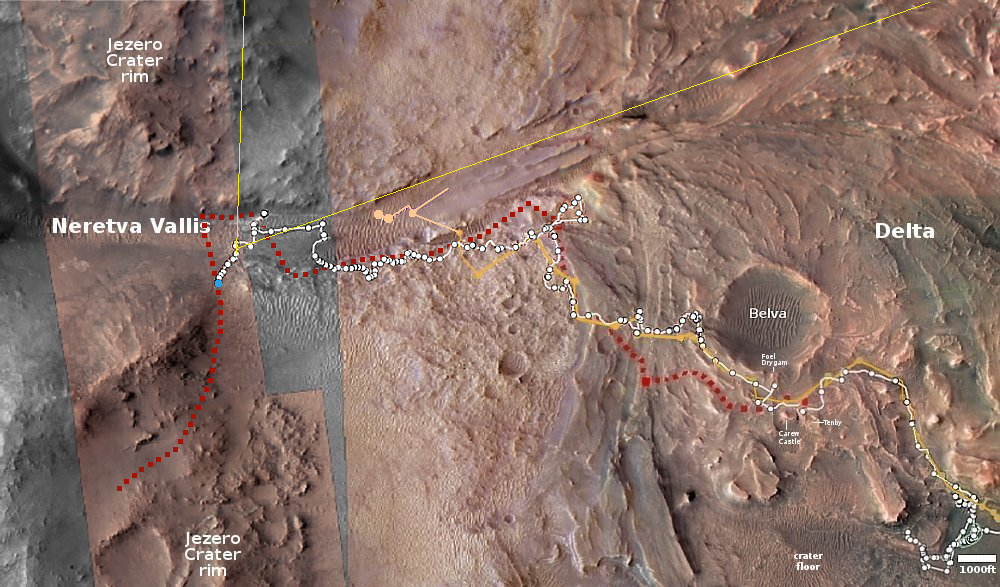
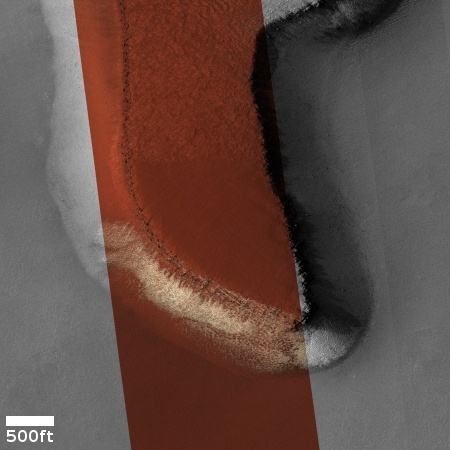
The overview map to the right provide the context. The blue dot marks Curiosity’s present position. The yellow lines the approximate area covered by the panorama. The red dotted line indicates the rover’s planned route, with the white dotted line the path it has recently traveled.
As you can see, the rover has moved up onto a higher terrace surrounding the Texoli butte, and will now travel downhill a bit to skirt around its northern nose. From there, the science team plans to send the rover westward, traversing along the contour lines on the side of Mount Sharp. Along the way it will lose more elevation, but eventually, after passing several parallel north-south trending canyons, it will finally turn south into one canyon to resume its climb up the mountain.
To review the rover’s journey, Curiosity during its dozen years on Mars has traveled just over 20 miles and climbed about 2,500 feet. The peak of Mount Sharp however is still about 26 miles away and about 16,000 feet higher. Getting there will probably take at least three more decades, which is possible since the rover uses a nuclear power source similar to that used by the two Voyager interplanetary probes, now functioning in space for almost a half century.
In fact, it would not surprise me if the first human Mars colonies are established while Curiosity is still working, and that in its later years it sends its data to that colony directly (via an orbiting relay satellite), rather than beaming it back to Earth.
Cool image time! The panorama above, cropped and annotated to post here, was taken on October 6, 2024 by the right navigation camera on the Mars rover Curiosity. It looks south, down the slopes of Mount Sharp and across Gale Crater, the distant crater rim barely visible through the dusty air twenty to thirty miles away.
The overview map to the right provide the context. The blue dot marks Curiosity’s present position. The yellow lines the approximate area covered by the panorama. The red dotted line indicates the rover’s planned route, with the white dotted line the path it has recently traveled.
As you can see, the rover has moved up onto a higher terrace surrounding the Texoli butte, and will now travel downhill a bit to skirt around its northern nose. From there, the science team plans to send the rover westward, traversing along the contour lines on the side of Mount Sharp. Along the way it will lose more elevation, but eventually, after passing several parallel north-south trending canyons, it will finally turn south into one canyon to resume its climb up the mountain.
To review the rover’s journey, Curiosity during its dozen years on Mars has traveled just over 20 miles and climbed about 2,500 feet. The peak of Mount Sharp however is still about 26 miles away and about 16,000 feet higher. Getting there will probably take at least three more decades, which is possible since the rover uses a nuclear power source similar to that used by the two Voyager interplanetary probes, now functioning in space for almost a half century.
In fact, it would not surprise me if the first human Mars colonies are established while Curiosity is still working, and that in its later years it sends its data to that colony directly (via an orbiting relay satellite), rather than beaming it back to Earth.