Curiosity looking back
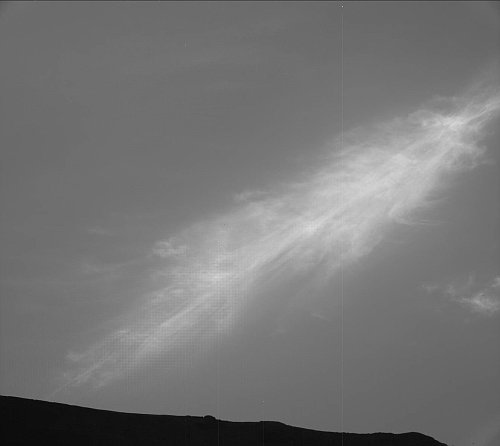
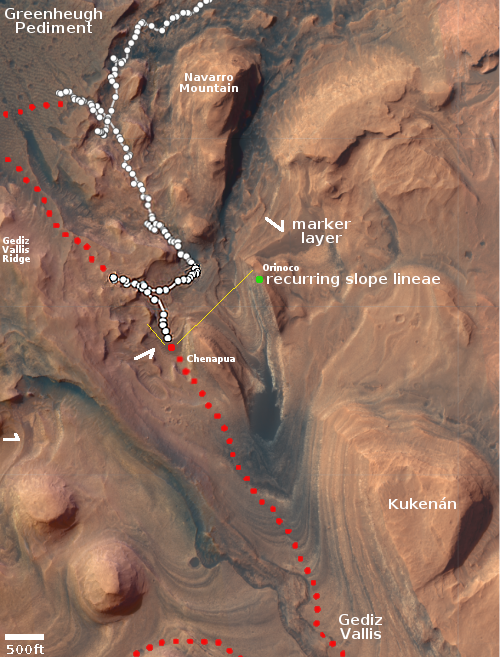
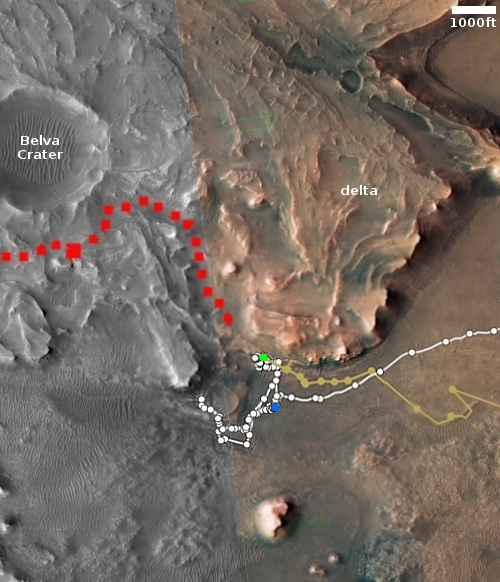
Curiosity is now about halfway across the flat marker band terrain it faced last week, and as part of its routine, used its right navigation camera on January 28, 2023 to create a 360 degree panorama mosaic of the Mount Sharp foothills that now surround it. The panorama above, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, focuses on the part of that mosaic looking behind Curiosity.
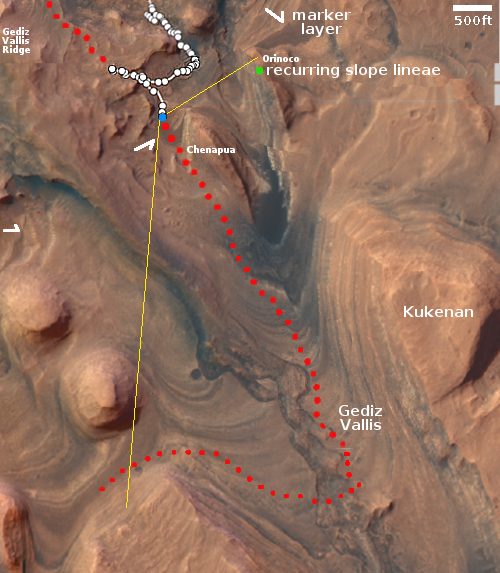
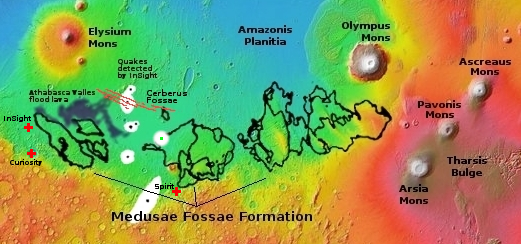
You can see the rover’s recent tracks as it crossed this part of the marker band. In the far distance can be seen in the haze the rim of Gale Crater, approximately 20 to 40 miles away. The yellow lines in the overview map to the right show the approximate area covered by this section of the panorama. It is possible the peak of Navarro Mountain is peeking up in the center of this panorama, but more likely it is no longer visible, blocked by the smaller but closer hills.
As Curiosity is now inside the foothills of Mount Sharp, the floor of Gale Crater is no longer easily seen. The rover needs to be at a high lookout point, something that will likely not occur in its travels for many months if not years to come.
The Curiosity pictures I am featuring this morning are cool, and they are also the only real news in the space field at this moment. As is usual on Monday, it takes few hours for the news at the beginning of the week to make itself known.
Curiosity is now about halfway across the flat marker band terrain it faced last week, and as part of its routine, used its right navigation camera on January 28, 2023 to create a 360 degree panorama mosaic of the Mount Sharp foothills that now surround it. The panorama above, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, focuses on the part of that mosaic looking behind Curiosity.
You can see the rover’s recent tracks as it crossed this part of the marker band. In the far distance can be seen in the haze the rim of Gale Crater, approximately 20 to 40 miles away. The yellow lines in the overview map to the right show the approximate area covered by this section of the panorama. It is possible the peak of Navarro Mountain is peeking up in the center of this panorama, but more likely it is no longer visible, blocked by the smaller but closer hills.
As Curiosity is now inside the foothills of Mount Sharp, the floor of Gale Crater is no longer easily seen. The rover needs to be at a high lookout point, something that will likely not occur in its travels for many months if not years to come.
The Curiosity pictures I am featuring this morning are cool, and they are also the only real news in the space field at this moment. As is usual on Monday, it takes few hours for the news at the beginning of the week to make itself known.