SpaceX successfully launches another sixty Starlink satellites
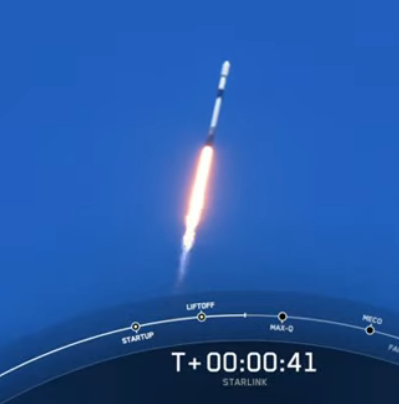
SpaceX this morning successfully launched another 60 Starlink satellites, bringing the total number in orbit to more than 1,500.
The first stage, on its seventh flight, successfully landed on the drone ship. During SpaceX’s live stream they noted that every launch by the company this year has used a previously flown first stage. Both fairings on this flight were also reused.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
10 SpaceX
7 China
5 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 14 to 7 in the national rankings.
I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream below the fold. Because of the clear weather this was a particularly beautiful launch. The video during the landing of the first stage was especially spectacular, with the camera on the booster showing the entire landing.
» Read more

SpaceX this morning successfully launched another 60 Starlink satellites, bringing the total number in orbit to more than 1,500.
The first stage, on its seventh flight, successfully landed on the drone ship. During SpaceX’s live stream they noted that every launch by the company this year has used a previously flown first stage. Both fairings on this flight were also reused.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
10 SpaceX
7 China
5 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 14 to 7 in the national rankings.
I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream below the fold. Because of the clear weather this was a particularly beautiful launch. The video during the landing of the first stage was especially spectacular, with the camera on the booster showing the entire landing.
» Read more