A butte on Mars
Cool image time! Because the Martian geology inside the enclosed stone valley beyond Maria Gordon notch is so complex and exposed, the Curiosity science team is spending a lot of time there. As noted in their January 7th update:
[W]e are marvelling at the landscape in front of us, which is very diverse, both in the rover workspace and in the walls around us. It’s a feast for our stratigraphers (those who research the succession in which rocks were deposited and deduce the geologic history of the area from this). We are all looking forward to the story they will piece together when they’ve had a bit of time to think!
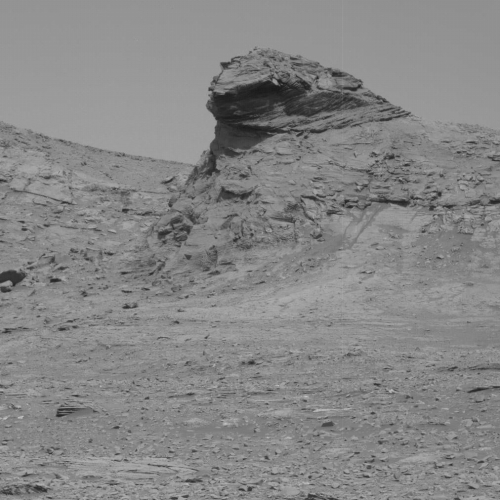
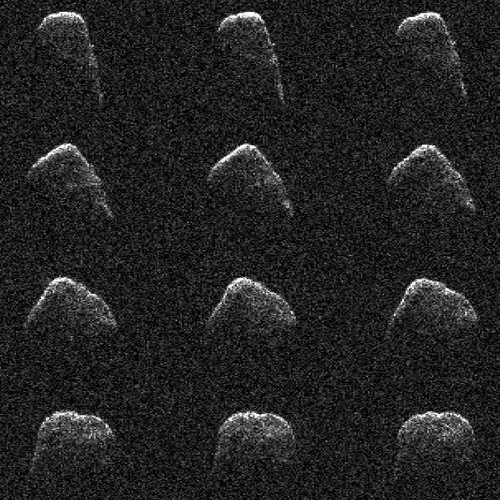
The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken by the rover’s high resolution camera on December 18th, soon after it entered this stone valley and was part of scan covering both this butte as well as a nearby cliff. I had previously featured a close-up of the top of this butte and its incredible overhang on December 20, 2021. This image however shows the whole butte, which I estimate to be about 30 to 40 feet high is about 10 feet high.
Not only does the butte illustrate well the alien nature of this stark and barren Martian terrain, so does all the terrain surrounding it. The surface everywhere is nothing but pavement stones of all sizes. Once again, there is no life, something you practically never see on Earth.
Cool image time! Because the Martian geology inside the enclosed stone valley beyond Maria Gordon notch is so complex and exposed, the Curiosity science team is spending a lot of time there. As noted in their January 7th update:
[W]e are marvelling at the landscape in front of us, which is very diverse, both in the rover workspace and in the walls around us. It’s a feast for our stratigraphers (those who research the succession in which rocks were deposited and deduce the geologic history of the area from this). We are all looking forward to the story they will piece together when they’ve had a bit of time to think!
The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken by the rover’s high resolution camera on December 18th, soon after it entered this stone valley and was part of scan covering both this butte as well as a nearby cliff. I had previously featured a close-up of the top of this butte and its incredible overhang on December 20, 2021. This image however shows the whole butte, which I estimate to be about 30 to 40 feet high is about 10 feet high.
Not only does the butte illustrate well the alien nature of this stark and barren Martian terrain, so does all the terrain surrounding it. The surface everywhere is nothing but pavement stones of all sizes. Once again, there is no life, something you practically never see on Earth.