The sunspot decline continues
NOAA’s monthly update of the solar cycle was released today, showing the Sun’s sunspot activity in March. It is annotated and posted below.
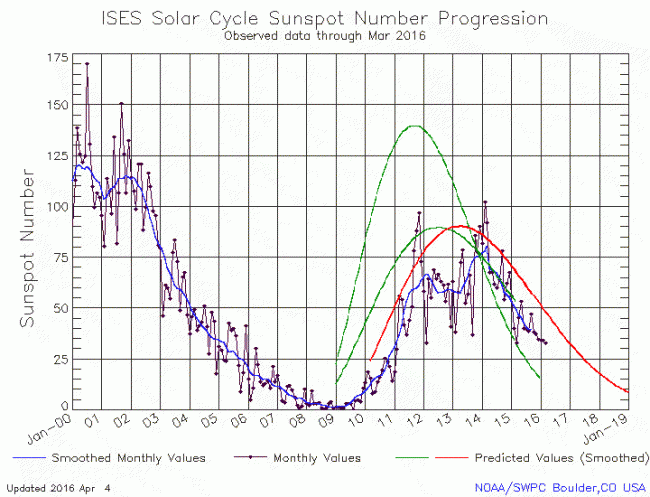
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.
For the fourth month in a row the change in the graph is so small you almost need a magnifying glass to see it. Despite this, the decline remains remarkably steady, tracking precisely the decline predicted by the low prediction of the 2007 predictions (indicated by the smaller green line curve).
Recently the number of sunspots has dropped enough that I suspect we are not far the moment when we will once again begin to see days where the Sun is blank of sunspots, a situation last seen in 2010 near the end of the previous solar minimum. When that happens, it will herald the beginning of the next solar minimum.
NOAA’s monthly update of the solar cycle was released today, showing the Sun’s sunspot activity in March. It is annotated and posted below.

The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.
For the fourth month in a row the change in the graph is so small you almost need a magnifying glass to see it. Despite this, the decline remains remarkably steady, tracking precisely the decline predicted by the low prediction of the 2007 predictions (indicated by the smaller green line curve).
Recently the number of sunspots has dropped enough that I suspect we are not far the moment when we will once again begin to see days where the Sun is blank of sunspots, a situation last seen in 2010 near the end of the previous solar minimum. When that happens, it will herald the beginning of the next solar minimum.