Zhurong’s travels during first three weeks on Mars
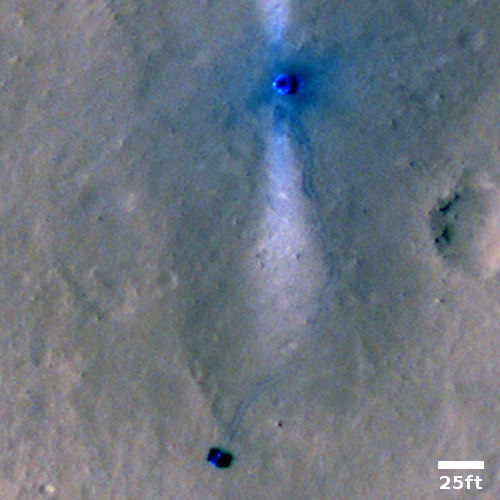
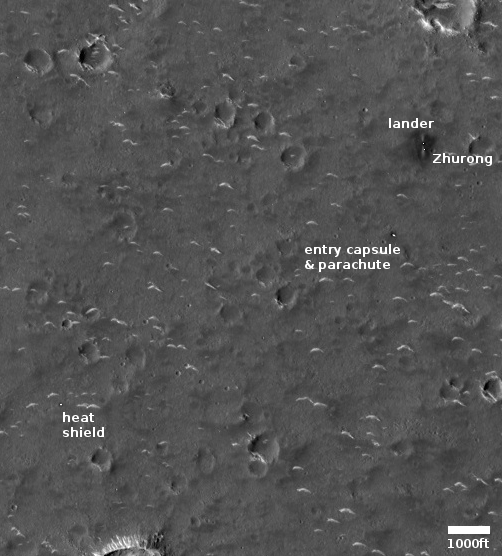
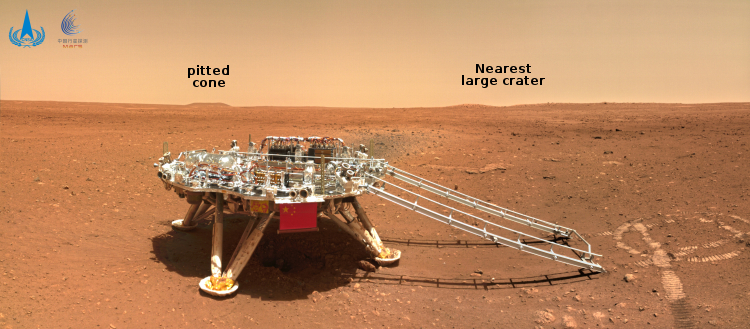
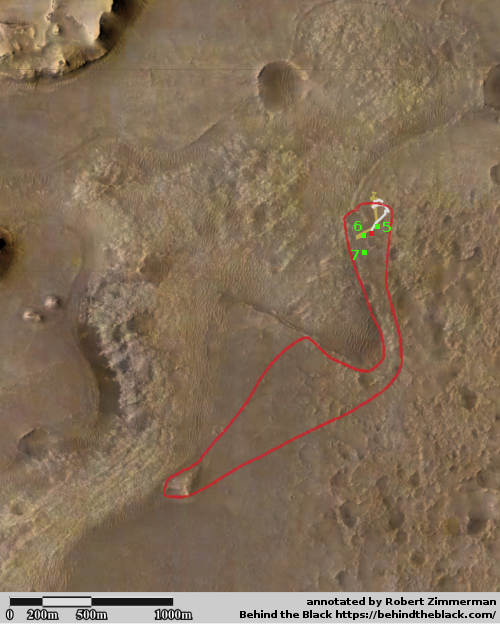
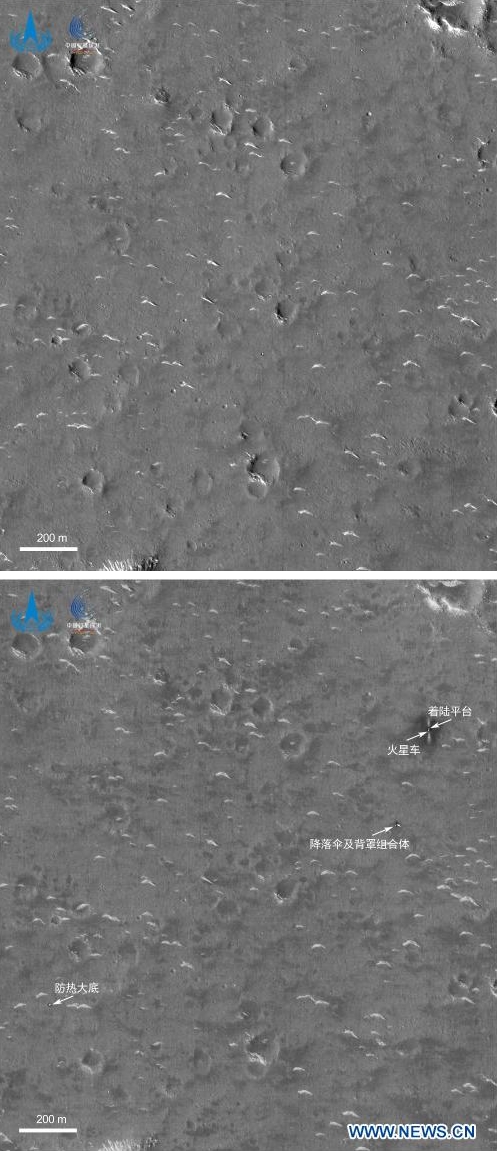
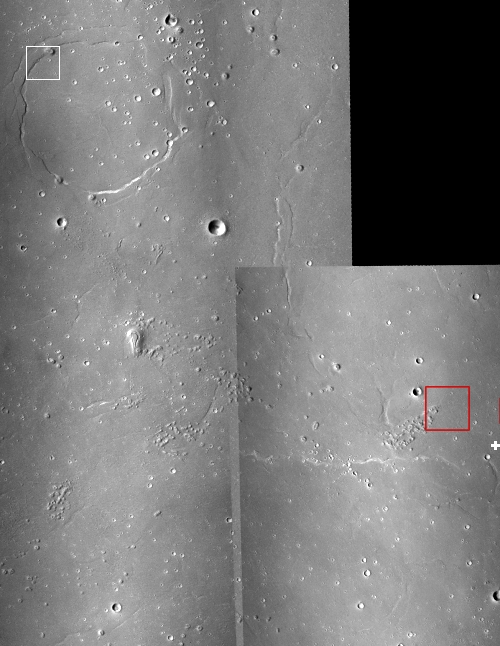
The science team for the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) today released a new image showing the path that China’s rover , Zhurong, has taken from its landing on May 14th through June 11th.
The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is that photo. If you look close you can see the rover’s track skirting the edge of the bright blast mark put on the surface by the lander’s engines during touchdown. Though my scale bar is approximate, it does show that in those four weeks the rover traveled about 150 to 200 feet. However, half of that distance was crossed in the five days from June 6th to June 11th (as shown by the two different MRO images at these links), which means the pace is picking up.
The rover’s nominal three-month mission ends in mid-August, only two months from now. However, none of us should be surprised if the mission gets extended for as long as the rover continues to function.
The science team for the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) today released a new image showing the path that China’s rover , Zhurong, has taken from its landing on May 14th through June 11th.
The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is that photo. If you look close you can see the rover’s track skirting the edge of the bright blast mark put on the surface by the lander’s engines during touchdown. Though my scale bar is approximate, it does show that in those four weeks the rover traveled about 150 to 200 feet. However, half of that distance was crossed in the five days from June 6th to June 11th (as shown by the two different MRO images at these links), which means the pace is picking up.
The rover’s nominal three-month mission ends in mid-August, only two months from now. However, none of us should be surprised if the mission gets extended for as long as the rover continues to function.