SpaceX to upgrade 2nd Kennedy launchpad for manned launches
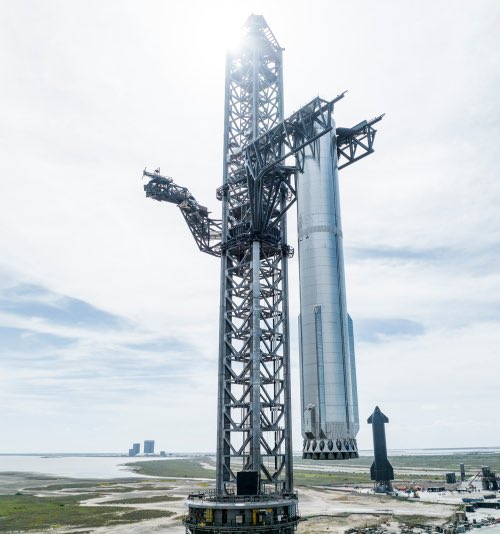
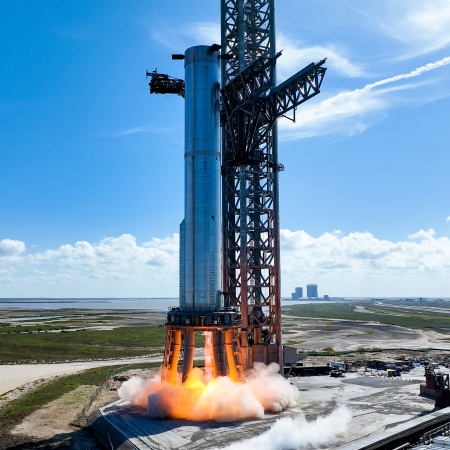
In order to create some increased redundancy, SpaceX and NASA have agreed to upgrade the company’s second launchpad at Cape Canaveral, LC-40, so that both it and pad LC-39A can launch manned Dragon capsules.
This plan grew out of concern by NASA that the new Starship orbital launchpad was too close to LC-39A, and could possibly damage it during a launch. Should that happen, and no back-up launchpad was available, the agency would have no way to get astronauts up to ISS, since Boeing’s Starliner is not yet operational. Because of that concern, NASA made it clear that no Starship launches could occur in Florida until this issue was resolved.
The solution? Make LC-40 a manned launchpad too.
Nothing is known about the nature of the modifications that LC-40 will require. But more likely than not, NASA will require SpaceX to develop something similar to Pad 39A’s facilities. That would involve building a new crew access tower, crew access arm, escape system (39A uses baskets and ziplines), and an on-site bunker for astronauts.
It is also likely that no Starship launches at Kennedy will occur until this work is done and a manned launch from LC-40 takes place. Though this could delay Starship somewhat, I expect not significantly. Before SpaceX is ready to launch operationally in Florida, it still has to do a lot of testing and development of Starship/Superheavy in Boca Chica, work that could take several years. I also suspect that it will get the launchpad work done relatively quickly, especially if NASA agrees to pay for it.
In order to create some increased redundancy, SpaceX and NASA have agreed to upgrade the company’s second launchpad at Cape Canaveral, LC-40, so that both it and pad LC-39A can launch manned Dragon capsules.
This plan grew out of concern by NASA that the new Starship orbital launchpad was too close to LC-39A, and could possibly damage it during a launch. Should that happen, and no back-up launchpad was available, the agency would have no way to get astronauts up to ISS, since Boeing’s Starliner is not yet operational. Because of that concern, NASA made it clear that no Starship launches could occur in Florida until this issue was resolved.
The solution? Make LC-40 a manned launchpad too.
Nothing is known about the nature of the modifications that LC-40 will require. But more likely than not, NASA will require SpaceX to develop something similar to Pad 39A’s facilities. That would involve building a new crew access tower, crew access arm, escape system (39A uses baskets and ziplines), and an on-site bunker for astronauts.
It is also likely that no Starship launches at Kennedy will occur until this work is done and a manned launch from LC-40 takes place. Though this could delay Starship somewhat, I expect not significantly. Before SpaceX is ready to launch operationally in Florida, it still has to do a lot of testing and development of Starship/Superheavy in Boca Chica, work that could take several years. I also suspect that it will get the launchpad work done relatively quickly, especially if NASA agrees to pay for it.