April 26, 2018 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Very brief descriptions, with appropriate links, of current or recent news items.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Using data gathered by the MESSENGER spacecraft while it was in orbit around Mercury, scientists now estimate that the planet’s crust is thinner than previously believed, 16 miles thick rather than 22 miles.
The crust is also as dense as aluminum. It is also the thinnest crust, relative to the planet’s core, of any rocky planet in the solar system.
Mercury’s core is believed to occupy 60 percent of the planet’s entire volume. For comparison, Earth’s core takes up roughly 15 percent of its volume. Why is Mercury’s core so large?
“Maybe it formed closer to a normal planet and maybe a lot of the crust and mantle got stripped away by giant impacts,” Sori said. “Another idea is that maybe, when you’re forming so close to the sun, the solar winds blow away a lot of the rock and you get a large core size very early on. There’s not an answer that everyone agrees to yet.”
There appears to be a great deal of uncertainty to these conclusions, and I would not be surprised if these conclusions change with the arrival of more data.
South Korea’s second largest earthquake has now been linked by two different studies to the injection of water deep below the surface at a new geothermal power plant.
Perched on South Korea’s southeast coast and far from grinding tectonic plates, Pohang is an unlikely spot for a big earthquake. Before the geothermal plant’s two wells were drilled, there had never been an earthquake there of any significance, says Kwanghee Kim, a seismologist at Pusan National University in Busan, South Korea, and lead author of one study. But while Kim was monitoring the aftermath of an unrelated earthquake in 2016, he began to detect rumbles from Pohang. That prompted his lab to deploy eight temporary seismic sensors at the site, which were finally in place on 10 November 2017. He expected any quakes to be small—after all, the largest previous quake tied to enhanced geothermal power, in Basel, Switzerland, was just 3.4 in magnitude.
It took only 5 days to be proved wrong. “The Pohang earthquake was larger than any predicted by existing theories,” Kim says. Although some initial measures placed the source of the quake several kilometers away from the plant, Kim’s network revealed that the earthquake, and several of its foreshocks, all began right below the 4-kilometer-deep well used to inject water into the subsurface to create the plant’s heating reservoir. Indeed, it appears likely that the well’s high-pressure water lubricated an unknown fault in the rock, causing it to slip and triggering the quake, Kim says.
A second paper, by European scientists who used regional seismic data, reinforces the South Korean team’s results, in particular its shallow depth. That study also points out that an earlier 3.1-magnitude earthquake also took place near the well bottom, increasing the odds of a common source. Satellite measures of shifts in the surface after the November 2017 quake support that idea, says Stefan Wiemer, the second study’s lead author and director of the Swiss Seismological Service in Zurich. It’s clear the locked fault was storing energy that was waiting to be released, Wiemer says. “If that fault would have gone next Tuesday or 50 years from now, we’ll never know.”
The article notes that scientists had previously concluded that injecting water underground for geothermal purposes was okay (since it reduced use of fossil fuels) while doing the same for fracking (to obtain and use fossil fuels) was bad.. The data here actually suggests just the reverse, since fracking has never produced an earthquake as large as the 5.5 magnitude Pohang quake.
One of China’s top space engineers said this week at a conference that they are aiming to reuse vertically-landed first stages by 2020 on a new Long March 8 rocket.
At an aerospace industry seminar on Tuesday, leading Chinese carrier rocket designer Long Lehao said that China is expected to realize vertical recycling – similar to the technology employed by US-based firm SpaceX – by 2020 at the earliest on its CZ-8 rockets. This will further lower the price tag of a launch and boost China’s chances of getting international commercial satellite launch orders, the CCTV report said.
Lan Tianyi, founder of Beijing-based Ultimate Blue Nebula Co, a space industry consultancy, said China will become the second rocket power to have this capacity, putting the country ahead of Russia and the EU. However, Lan said that while the aim of recycling rockets is to reduce costs for launch operators, whether this can be achieved remains to be seen.
The recycled rockets developed by SpaceX are reported to have helped the company reduce launch costs by as much as 30 percent, according to media reports.
“There is no way to verify SpaceX’s claim, as it is the only company that owns the technology, and China has to wait for the moment when it has successfully recycled a rocket to see whether the costs can be lowered,” Lan told the Global Times on Thursday.
Right now, the politics in China are extremely favorable for space development, with so many top posts occupied by former space managers. Thus, it seems reasonable to believe that the country is investing the cash necessary to develop rocket stages that can land vertically. If they do it, they will put themselves in a strong position for future space colonization, because such technology is essential for landing spacecraft on other worlds. Right now, only the U.S. has done this repeatedly and successfully.
The first summit in more than a decade between the leaders of North and South Korea began today.
The two leaders are meeting at Peace House, south of the demarcation line in the border truce village of Panmunjom.
Kim is the first North Korean leader to step foot in South Korea since the 1950-53 Korean War, and the two leaders are expected to discuss issues relating to peace and denuclearisation of the Korean peninsula.
The two leaders smiled and shook hands after which Kim gestured to Moon to cross over to North Korea briefly, which they did for a few steps, then returned to the South, holding hands.
Though no one should trust much of what Kim says or does, this summit is certainly a testament to the foreign policy of Donald Trump. During the Obama administration, all we had from North Korea were nuclear tests and threats of war, with the U.S. weakly responding with typically empty diplomatic statements of “serious concern.”
Now Kim is signing the guest register in South Korea like so: “New history starts now; age of peace, from the starting point of history.” Trump forced his allies, most specifically China, to put pressure on him, and it has apparently had a positive effect.
Embedded below the fold.
» Read more
A search by a Twitter user of the Rosetta archive from its visit to Comet 67P/C-G has produced a very short movie of the comet’s surface.
The bright dots travelling from the top of the frame to the bottom, which look something like snow, are in fact background stars. They have that apparent motion as the spacecraft moves and the comet rotates. The more rapidly moving streaks are thought to be dust particles illuminated by the Sun. There also appear to be a few streaking cosmic rays.
Take a look. The twelve second movie gives a flavor of what it would be like to walk that comet’s surface.
China’s Long March 11 rocket today launched five Earth observation satellites.
The rocket appears designed to compete with some of the smallsat rockets being developed by private companies in the U.S. and elsewhere.
The Long March-11 (Chang Zheng-11) is a small solid-fueled quick-reaction launch vehicle developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT) with the goal to provide an easy to operate quick-reaction launch vehicle, that can remain in storage for long period and to provide a reliable launch on short notice.
LM-11 is a four stage solid-fueled launch vehicle equipped with a reaction control system on the fourth stage. The vehicle has a length of 20.8 meters, 2.0 meters in diameter and a liftoff mass of 58,000 kg. At launch it develops 120.000 kg/f, launching a 350 kg cargo into a 700 km SSO. The CZ-11 can use two types of fairing with 1.6 meters or 2.0 meters.
LM-11’s first launch took place on September 25, 2015, when successfully orbited the Pujiang-1 and the three Tianwang small sats from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center.
Update: I had initially left off Russia’s Rokot launch of a new European Earth observation satellite late yesterday. The standings below have therefore been updated.
The leaders in the 2018 launch standings:
12 China
8 SpaceX
5 Russia
4 ULA
Europe, India, and Japan are all tied at 3. The U.S. and China are now tied at 12 in the national standings.
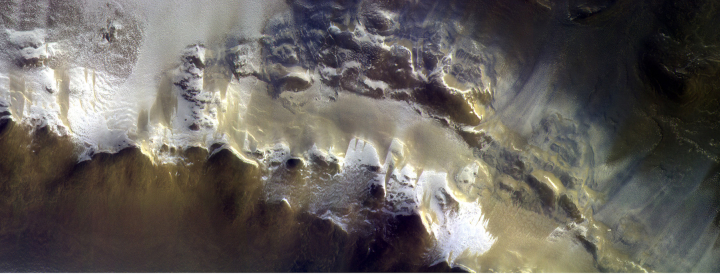
Europe’s Trace Gas Orbiter has released its first image after reaching its planned science orbit.
The image is posted above, reduced in resolution to show here. It shows a portion of the rim of Korolev Crater, a rare large crater located in the vast northern plains of Mars. Because it is so far north, it has ice on the rim which looks almost like glacial flows in this image.
Fascist California: UC-San Diego now requires anyone applying for a teaching job to submit a statement demonstrating their commitment to “diversity,” including proving that their research, in whatever field, “highlights inequalities.”
“All candidates applying for faculty appointments at UC San Diego are required to submit a personal statement on their contributions to diversity. The purpose of the statement is to identify candidates who have the professional skills, experience, and/or willingness to engage in activities that will advance our campus diversity and equity goals.
“In accordance with APM 210-1-d, ‘these contributions to diversity and equal opportunity can take a variety of forms including efforts to advance equitable access to education, public service that addresses the needs of California’s diverse population, or research in a scholar’s area of expertise that highlights inequalities.’”
In other words, the university will police the research of all faculty, and require them to only do research that serves the university’s leftist political ends. And I say that confidently, because I have no doubt that these rules have nothing to do with equal justice before the law or with preventing racial prejudice or discrimination. No, these requirements are there to guarantee that the only people UC-San Diego hires are leftist ideologues.
The House yesterday passed a new law to reform the commercial space licensing rules.
Essentially, the bill shifts a majority of commercial space regulation to the Department of Commerce, and matches somewhat closely the recommendations being put forth by the Trump administration.
The bill appears to be almost identical to the version I analyzed in great detail in an op-ed for The Federalist last year. It has the same positives and negatives. While it definitely aims at simplifying the licensing process for space (abolishing such agencies as NOAA’s Office of Commercial Remote Sensing Regulatory Affairs that recently tried to claim it had the right to license all photograph of Earth from space.), it does not appear to completely make Commerce that “one-stop shop” for all licensing, allowing the FAA and FCC to retain their space licensing responsibilities. Moreover, it appears, as I noted in my op-ed, to avoid the more essential legal problems, such as the Outer Space Treaty, that hamper private space today and will hamper private space even more in the future.
Regardless, it does appear that the turf war over licensing between Commerce and the FAA is over. Though the law still must get through the Senate, it does appear that Commerce has mostly won. It will get the majority of this bureaucratic bauble. What that bureaucracy will do with it, however, is the real question.
The yellow water found in Russian section of ISS earlier this week was caused by the ordinary crust deposits that formed on the inside of a water-heating unit, what the Russians have labeled a “samovar” and we would probably call a teapot.
Limescale crust inside a ‘samovar’ whose service life had expired was the cause for the appearance of yellow water admixtures in the Russian segment of the International Space Station (ISS), First Deputy CEO for Space Systems’ Flight Operation and Tests at Energia Rocket and Space Corporation Vladimir Solovyov told TASS on Tuesday. “A household cause is behind the emergence of the yellow admixtures in the water. Routine limescale crust had formed in the water-heating unit, which had reached the end of its service life. There is nothing terrible in that as we are regularly confronted with such things on Earth. The problem is solved quite easily, we will just promptly replace this unit, which cosmonauts normally call ‘samovar’ with a reserve one,” Solovyov explained.
Anyone who has used a teapot to boil water for years will eventually have to replace it because of the development of a crust on its inside surface. This is what has happened here. It appears the Russian article today was in response to panicked news reports earlier in the week about the appearance of the yellow water and the need for the Russians to use water from the American segment while they pinned down the cause, a procedure that is quite routine.
The Trump administration is considering reinstating the fee system to purchase Landsat images that existed prior to 2008.
Not surprisingly, the Nature article is completely hostile to this idea. The quote below gives a flavor.
Since the USGS made the data freely available, the rate at which users download it has jumped 100-fold. The images have enabled groundbreaking studies of changes in forests, surface water, and cities, among other topics. Searching Google Scholar for “Landsat” turns up nearly 100,000 papers published since 2008.
A USGS survey of Landsat users released in 2013 found that the free distribution of Landsat imagery generates more than US$2 billion of economic benefit annually — dwarfing the programme’s current annual budget of roughly $80 million. More than half of the nearly 13,500 survey respondents were academics, and the majority lived outside the United States. [emphasis mine]
Why should scientists, a majority of which are not even Americans, have a free ride?
Link here. The article provides practically no information about the legislation or its chances of passing. Instead, it focuses on the past history behind ULA’s use of the Russian RD-180 rocket engine in its Atlas 5 rocket as well as the recent efforts to replace it.
Thus, I have no idea if this legislation signals a real threat to future ULA launches or not. Moreover, the article tries to make it sound that the U.S. is entirely reliant on this rocket engine, something that is simply not true.
Nonetheless, this story underscores again the need for ULA to find a different engine to power its rockets. They shouldn’t be dependent on a rocket engiine built by a foreign power that has political motives that sometimes conflict with those of the United States.
India’s space agency ISRO yesterday recalled its largest ever communications satellite, GSAT-11, from French Guiana, where it was being prepared for a May Ariane 5 launch, citing a need to check the satellite’s systems.
Though no specific reason was given for the recall, which will postpone the satellite’s launch indefinitely, it likely is related to the March failure in orbit of India’s GSAT-6A satellite.
ISRO lost communication contact with its GSAT-6A communication satellite soon after it was put into orbit on March 29.
ISRO suspects the failure of the power systems in the satellite for the loss of communication link. “The satellites are powered by solar panels that charge the onboard batteries. The batteries are fully charged when the satellite is loaded on to the rocket. Even if there is a problem with the solar panel, then the battery power should have kicked in. Here the entire power system of the satellite seems to have failed,” one space expert told IANS earlier.
According to experts, the power system could have failed due to some short circuiting or arcing resulting in what is known in the space terminology ‘loss of lock’ or loss of contact with the ground station.
The head of ISRO is a well-trained engineer who has worked in the trenches. I suspect he decided the problems with GSAT-6A demanded a more detailed systems check on GSAT-11 prior to launch. And even if it wasn’t his specific decision, the willingness to make such a decision I think indicates a great deal of maturity in the present culture at ISRO. It might be embarrassing to make such a recall, but it is far better to do so beforehand than after an unrecoverable failure in space. That they are willing to face this embarrassment to avoid a future failure is something laudable.
The science team for the space telescope Gaia, designed to map the positions of billions of stars, have released the probe’s second catalog, producing a 3D map of 1.7 billion stars in the Milky Way
The new data release, which covers the period between 25 July 2014 and 23 May 2016, pins down the positions of nearly 1.7 billion stars, and with a much greater precision. For some of the brightest stars in the survey, the level of precision equates to Earth-bound observers being able to spot a Euro coin lying on the surface of the Moon.
With these accurate measurements it is possible to separate the parallax of stars – an apparent shift on the sky caused by Earth’s yearly orbit around the Sun – from their true movements through the Galaxy. The new catalogue lists the parallax and velocity across the sky, or proper motion, for more than 1.3 billion stars. From the most accurate parallax measurements, about ten per cent of the total, astronomers can directly estimate distances to individual stars.
The catalog provides much more information than this. For example:
As well as positions, the data include brightness information of all surveyed stars and colour measurements of nearly all, plus information on how the brightness and colour of half a million variable stars change over time. It also contains the velocities along the line of sight of a subset of seven million stars, the surface temperatures of about a hundred million and the effect of interstellar dust on 87 million.
Gaia also observes objects in our Solar System: the second data release comprises the positions of more than 14 000 known asteroids, which allows precise determination of their orbits. A much larger asteroid sample will be compiled in Gaia’s future releases.
Further afield, Gaia closed in on the positions of half a million distant quasars, bright galaxies powered by the activity of the supermassive black holes at their cores. These sources are used to define a reference frame for the celestial coordinates of all objects in the Gaia catalogue, something that is routinely done in radio waves but now for the first time is also available at optical wavelengths.
I guarantee that many theories about specific strange stars, such as the plethora of different types of variable stars, are going to change drastically with this new and precise information. At the article they describe just one example relating to white dwarf stars.
Russia has agreed to replace Angola’s first satellite, lost shortly after launch, and have the replacement paid for by both insurance and Russia.
The minister confirmed that payment for the production of the second satellite would come from the insurance reimbursement for the lost AngoSat-1 satellite worth 121 million US dollars. The rest of the cost will be paid by the Russian side. The overall sum of the project amounts to 320 million US dollars.
The AngoSat-1 telecommunications satellite was launched by a Zenit-2SB carried rocket with a Fregat booster on December 26, 2017 from the Baikonur space center in Kazakhstan. Contact with the satellite was lost on the following day after the separation from the upper stage.
Essentially, this is another example of a Russian launch failure, as it appears the Russians have accepted blame for the failure.
The coming dark age: Penn State has pulled all support for three outdoor clubs, two that have existed for 70 and 100 years respectively, because a risk analysis suggested they were simply too risky.
These organizations have a long history attached to Penn State.
Nittany Grotto has been a resource that introduced students to caving with regularly scheduled Wednesday trips for 70 years, while the Outing Club is nearing the century mark in bringing students together hiking, backpacking, kayaking and enjoying the outdoors in whatever capacity possible.
“Losing affiliation with the university as a recognized student organization or club sport at Penn State means losing all privileges granted to a student organization,” Outing Club president Christina Platt said via email. “These privileges include the ability to reserve rooms to meet on campus, to be protected with $1,000,000 liability insurance, to use ASA to manage club funds, to fundraise through special university funding opportunities (such as stadium cleanup), to recruit at the Involvement Fair, and to use the university name on merchandise.”
More here, which notes the following:
Two other outdoor recreation clubs — the spelunking Nittany Grotto Caving Club and the Nittany Divers SCUBA Club — also have been directed to end trip offerings.
“Safety is a legitimate concern, but it wasn’t an open dialogue,” Waltz said. Christina Platt, the Outing Club’s incoming president, said, “I can hardly blame Penn State for protecting itself against further litigation after a number of high-profile scandals in the past decade.” Student safety is the school’s primary focus, university spokeswoman Lisa Powers said in a statement.
Penn State conducted a “proactive risk assessment” not based on any previous participant injuries, according to Powers. She said Outing Club activities were rated high risk because they take place in remote environments with poor cell service and distance from emergency services.
I guess students must only be allowed in a safe space where nothing bad can ever happen to them, and they can therefore avoid the horror of experiencing life to its fullest.
I am heading to the Grand Canyon today for another four day cave expedition. I will return late Tuesday. There is a chance I will be able to post later today, on the way there, as well as on Tuesday on the way back. If not, I will resume posting Tuesday evening.
Can we believe it? In anticipation of the upcoming summits with both South Korea and President Trump, North Korea today announced that it has suspended both its nuclear and missile programs.
The new policy, which sets the table for further negotiations when the summits begin, was announced by leader Kim Jong Un at a meeting of the North Korean ruling party’s Central Committee on Friday and reported by the North’s state-run media early Saturday.
Kim justified the suspension to his party by saying that the situation around North Korea has been rapidly changing “in favor of the Korean revolution” since he announced last year his country had completed its nuclear forces. He said North Korea has reached the level where it no longer needs to conduct underground testing or test-launching of ICBMs.
I think the real reason he announced this is that he knows that if he continues the program, he shall be increasingly isolated. Trump’s pressure on China forced that nation to put the screws on Kim, and as a result he really has no choice but announce the suspension of these programs.
What we really don’t know is if this announcement can be taken seriously. Its public framing, justified under the lie that the programs were completed, makes me very suspicious that he is lying about everything. We shall see how Trump takes it in the coming months..
Fascist California: Two stories today illustrate forcefully the fascist political atmosphere in the state of California. And both are in support of the totalitarian homosexual agenda.
In the first story, the California Assembly has passed a bill that would ban any book, publication, or activity that is aimed at helping someone who wishes to stop their attraction to the same sex. As noted in the article,
“The State of California has no right to deny its residents the resources to help them find happiness or to shut down counselors, schools, and religious organizations that provide those services,” California Family Council president Jonathan Keller said of the vote. “Every person experiencing unwanted same-sex attraction or gender dysphoria must be allowed to pursue help in achieving their desired goals and outcomes.”
The bill is unprecedented for another reason, too: by classifying the subject under prohibited “goods,” which critics say means it would go so far as to ban the sale of books endorsing the practice, as well as other forms of constitutionally-protected speech. “At its core, AB 2943 outlaws speech,” Alliance Defending Freedom’s (ADF) legal analysis of the bill reads. It says that licensed counseling, religious conferences, book sales, and paid speaking engagements could all potentially face legal penalties for promoting ways to reverse unwanted attractions or for expressing traditional Christian teachings on sexuality.
In the second story, the Orange County school district is telling parents that they have no right to opt their children out of its pro-gay sex education classes, even though the law that established these homosexual-friendly classes expressly states that “parents [have] the ability to opt-out of this education and … that the “pupil” shall not be punished academically in any way if they don’t participate.”
To those in power in California, the concept of freedom is essentially dead. They are going to make you do as they demand, no matter what. And you will have no right to dissent.
A new study has found that 95% of all ocean pollution comes from only 10 rivers worldwide, and of those 8 are in Asia.
Dr Schmidt pooled data from dozens of research articles and calculated the amount in rivers was linked to the ‘mismanagement of plastic waste in their watersheds.’ He said: ‘The 10 top-ranked rivers transport 88-95 per cent of the global load into the sea.’
The study follows a recent report that pointed the finger at China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam for spewing out most of the plastic waste that enters the seas. The Yangtze has been estimated in previous research to dump some 727 million pounds of plastic into the sea each year. The Ganges River in India is responsible for even more – about 1.2 billion pounds. A combination of the Xi, Dong and Zhujiang Rivers (233 million lbs per year) in China as well as four Indonesian rivers: the Brantas (85 million lbs annually), Solo (71 million pounds per year), Serayu (37 million lbs per year) and Progo (28 million lbs per year), are all large contributors.
The article also notes this:
More than half of the plastic waste that flows into the oceans comes from just five countries: China, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam and Sri Lanka. The only industrialized western country on the list of top 20 plastic polluters is the United States at No. 20.
The U.S. and Europe are not mismanaging their collected waste, so the plastic trash coming from those countries is due to litter, researchers said.
While China is responsible for 2.4 million tons of plastic that makes its way into the ocean, nearly 28 percent of the world total, the United States contributes just 77,000 tons, which is less than one percent, according to the study published in the journal Science.
So, the next time you see a wild-eyed leftwing environmentalist trying to blame western civilization, capitalism, and the U.S. for the world’s pollution, please remember this study. It is the free nations of the world that have nimbly reacted well to the problems of pollution, not communist dictatorships like China or Vietnam.
I should add that the record of democracies here is not perfect by far. The rivers of India are a big contributor to this pollution. That country needs to deal with this problem also.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Link here. According to the CEO, Bob Smith, they are making good progress on developing their BE-4 rocket engine, and also expect to test fly New Shepard again in a few weeks.
In both cases, he admits that development has taken longer than expected. For example, in discussing New Shepard, he said the following:
Smith said Blue Origin is still planning to start flying people on its New Shepard suborbital spaceship by the end of the year, after further uncrewed tests. “We would have loved to have flown more, earlier, but the design incorporation didn’t go as quickly as we’d like it to,” Smith said.
I have no idea what he means by “design incorporation.” The bottom line however is that they have had issues that slowed things down.
The article provides a lot more details. Overall, while he says nothing that contradicts earlier reports, he provides a good summary of the company’s status.
Link here. The story details the new supercomputer simulation work attempting to model the internal processes inside a dying star that cause it to explode as a supernova.
For more than half a century, physicists have suspected that the heat produced by elusive particles called neutrinos, created in the core of a star, could generate a blast that radiates more energy in a single second than the Sun will in its lifetime. But they have had trouble proving that hypothesis. The detonation process is so complex — incorporating general relativity, fluid dynamics, nuclear and other physics — that computers have struggled to mimic the mechanism in silico. And that poses a problem. “If you can’t reproduce it,” Janka says, “that means you don’t understand it.”
Now, improvements in raw computing power, along with efforts to capture the stellar physics in acute detail, have enabled substantial progress. Janka’s simulation marked the first time that physicists had been able to get a realistic 3D model of the most common type of supernova to explode. Just months later, a competing group based at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee repeated the feat with a heavier, more complex star. The field is now buzzing, with more than half a dozen teams currently working on exploding stars in 3D.
They have apparently solved one problem, figuring out how the neutrino blast wave gets enough energy to blast free from the star’s core. A close read of the article indicates that, while progress has been made, they still have many gaps of their understanding.
We’re here to help you! An effort at the Arizona state legislature to protect student free speech rights has produced a bill that expressly voids the First Amendment of the Bill of Rights.
The original bill language read:
“A university or community college shall not restrict a student’s right to speak, including verbal speech, holding a sign or distributing fliers or other materials, in a public forum.”
Combined with subsequent language in the bill describing the way universities can implement reasonable time, place, and manner restrictions, the original provision was perfectly appropriate. However, after emerging from conference committee, that language now reads:
“A university or community college may restrict a student’s right to speak, including verbal speech, holding a sign or distributing fliers or other materials, in a public forum.” [Emphasis in original]
You really can’t make this stuff up. The article at the link notes that, based on the Arizona legislature’s track record, the change is likely the result of a “drafting error.” Bah. Either this group of lawyers and politicians in Arizona are complete fools, don’t know how to read or write, or they really do intend to shut down free speech.
After an eight month delay, caused partly by the refusal of any Democrats to vote for a Trump nominee, Congressman Jim Bridenstine (R-Oklahoma) was today confirmed as NASA’s administrator.
The vote passed 50-49, and only finally occurred because Senator Marco Rubio (R-Florida) decided to stop opposing Bridenstine.
I don’t think this nomination will matter much. The people who are really in charge of the U.S. space effort don’t work for NASA, and in fact are not even in the government. They also have enough financial power that they probably can force NASA to do what they want, over the long run. Bridenstine will I think carry water for them.
While Robert Mueller desperately searches (without success) for some crime he can pin on Donald Trump, an actual criminal referral has been issued by the inspector general of the Justice Department (an Obama appointee) against fired FBI official Andrew McCabe.
The Justice Department’s internal watchdog has sent a criminal referral for fired FBI official Andrew McCabe to the U.S. attorney’s office in Washington. The move follows a recent DOJ inspector general report that found McCabe leaked a self-serving story to the press and later lied about it to then-Director James Comey and federal investigators, prompting Attorney General Jeff Sessions to fire him on March 16.
A source confirmed to Fox News that the referral was sent.
This story follows yesterday’s where almost a dozen members of Congress called for criminal investigations by the Justice Department against Hillary Clinton, James Comey, Andrew McCabe, and a number of other FBI officials involved in abusing their positions of power to spy on the presidential campaign of their political opponents. It appears that the some people in Washington are finally getting up the nerve to actually consider prosecuting these violators of the Constitution and the rule of law.
As I said yesterday, in a sane world the entire journalist world would go nuts covering the recommendation that a former Secretary of State and presidential candidate as well as the fired head of the FBI both be investigated for criminal activity. In the past this story would garner giant screaming headlines and wall-to-wall coverage. We no longer live in a sane world however.
In a speech at a space conference this week, Commerce Secretary Wilbur Ross outlined the Trump administration’s plans to streamline the commercial space regulatory bureaucracy, noting that the absurd interference with normal operations by bureaucrats must stop.
He made specific reference to NOAA’s demand that it have the right to license all photography in space.
“This is silly and it will stop,” Ross told an audience of space industry executives, policymakers and military officers at the Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado, backing the view of SpaceX and other rocket companies that the cameras on its rockets aren’t the equivalent of satellites dedicated to Earth views.
He then noted that the regulatory framework is going to be consolidated into an “Office of Space Commerce” under his direct supervision, though the FCC (licensing radio spectrum) and the FAA (licensing rocket launches) will retain their responsibilities.
Will this streamline anything or save the taxpayer any money? Doesn’t look that way to me, as it seems to be adding a new layer of bureaucrats to the process without eliminating any existing departments. And then there is this additional quote from the article:
The question for space executives, who have clamored for more responsive government when it comes to licenses for launches and satellite operation, is whether increased funding will accompany the shifting responsibilities.
Speeding up bureaucracy means hiring more people, and projects like space traffic management demand investment in the technology to detect and track objects in orbit. While the Trump administration had adopted lofty rhetoric around its support for space business, it’s not yet clear that the White House has the needed clout to win congressional support—and federal dollars—for its proposals.
While it is a good thing that the Trump administration has apparently told the NOAA bureaucrats to take a flying leap, it appears they have also decided that building a new layer of bureaucracy to regulate space is a good thing. This is most unfortunate.
The extensive maneuvers in space of China’s SJ-17 satellite, launched in December 2016 on the maiden flight of China’s Long March 5 rocket, have satellite trackers and defense officials intrigued and concerned.
Now China, as far as we know, hasn’t done anything nefarious with this satellite. But it has approached to within “a couple of hundred meters” to an apparently dead Chinese communications satellite recently parked in the so-called graveyard orbit. That is incredibly close by space standards. (Also, that comsat may or may not actually be a dead satellite.) And, as space geeks can tell from the above chart, it has executed “proximity operations” with at least four Chinese satellites.
What does all this mean? Are the Chinese testing space war maneuvers to allow them to get close an enemy satellite to move it or disable it? Since the maneuvers to service a satellite — giving it new fuel or trying tor repair it, for example — are virtually indistinguishable from an offensive maneuver, we don’t know. We do know that Strategic Command’s Gen. John Hyten has made it clear China and Russia are building weapons that include satellites, lasers and other ground-to-space weapons. Russia has deployed three Kosmos satellites that appear designed to approach other nations satellites and destroy them. China has launched Shiyan satellites, reportedly able to use a grappling arm to move satellites.
SJ-17 could be testing anti-satellite capabilities, where either it approaches close enough to a target so that when it explodes it takes the target with it, or it grabs that satellite to take it over. Or it could be testing robot orbital maneuvering for the purpose of future satellite servicing missions.
In either case, China is demonstrating that its future satellites will have very sophisticated maneuvering systems, capable of doing any number of things in orbit.