May 26, 2021 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
An evening pause: A very well known piece of music from one of the most popular composers of the post-World War II era that you’ve probably never heard of, Leroy Anderson.
Any New Yorker who grew up in the 1960s will immediately recognize it as the theme music used for CBS’s afternoon and late night movie presentations, where they would squeeze two hour movies into 90 minutes slots that were really only about 60 minutes after commercials. (My first impressions as a child of many of Hollywood’s great movies was noticeably distorted because of this.)
Hat tip Diane Zimmerman.
The uncertainty of science: According to a new paper, based on ground-penetrating radar data obtained by China’s Yutu-2 rover on the far side of the Moon, scientists now think that the Moon’s more heavily cratered far side is that way because it actually gets bombarded more frequently than the near side.
From the paper’s abstract:
The Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR) onboard Yutu-2 can transmit electromagnetic pulses to detect the lunar subsurface structure and properties of the regolith. The relative permittivity, loss tangent and TiO2+FeO content of lunar regolith materials at landing site are constrained with LPR data in this paper. The results indicate that the farside may be bombarded more frequently, leading to different regolith accumulation rates on the lunar nearside vs. farside. [emphasis mine]
The data was accumulated during the rover’s first five months on the surface, during those five lunar days. It found that the regolith at the landing site was about 39 feet thick, much thicker than found at the landing site for Yutu-1 on the Moon’s near side. The difference was partly expected because of the nature of the different locations, but combined with other factors the scientists concluded that a higher bombardment rate on the far side would also help explain the difference.
To put it mildly, this conclusion is uncertain. We only have one data point on the far side, and only a few more on the near side. At the same time, the conclusion is somewhat an example of science discovering the obvious. The very first images of the Moon’s far side, taken The Soviet Union’s Luna 3 lunar probe in 1959, showed the surface much more heavily cratered than the near side, with far less areas of smooth mare. Numerous mapping missions since have confirmed that impression.
And it is also intuitive to come to this conclusion. The near side always faces the Earth, which likely acts to intercept many of the type of meteorite hits that reach the Moon’s far side.
This conclusion however is still intuitive, and an honest scientist will not trust it. That this result from Yutu-2 appears to confirms it is therefore nice.
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on March 4, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows an eroded mound that appears to have flows coming off its north and south slopes that fill the surrounding low spots, including half-covering a nearby crater.
The science team for MRO’s high resolution camera chose this picture as their April 28th picture of the day, noting the following:
The objective of this observation is to examine a crater which seems to be in the process of getting covered by flow from a mound. This image, in Protonilus Mensae, may show us characteristics of the covering material: could it be debris-covered glaciers?
Below is a global map of Mars, with this mound’s location in Protonilus Mensae in the northern mid-latitudes indicated by a black cross.
» Read more

Disagree with John Kerry?
No more bank services for you!
They’re coming for you next: The Biden administration, under the leadership of its “climate envoy” John Kerry, is apparently working behind the scenes to force banks to blackball fossil fuel companies from obtaining financial services.
Not surprisingly, the initial news stories from the mainstream press in mid-March describing this effort were written to hide the Biden administration’s goals. For example, Politico described a number of meetings arranged by Kerry and the Biden administration both with climate activist groups as well as financial institutes aimed at making those financial institutions “put your money behind your climate PR,” but the article only hinted at what the goals were.
Kerry has pitched banks on creating a U.S. net-zero banking alliance following the climate commitments from six major Wall Street banks, according to two people familiar with the discussions. Citi, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs all set 2050 net-zero goals and JPMorgan Chase has said its lending would be aligned with the Paris agreement although Kerry and his team are pushing for more specific financial commitments as part of this effort.
Kerry also wants clear near-term actions from banks by 2030, which would align with the Biden administration’s timeline for the new emissions target it intends to submit as part of the Paris Climate Agreement process. [emphasis mine]
Doesn’t meeting “net-zero” goals for climate change sound wonderful? But what does it mean?
» Read more
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to place another sixty Starlink satellites in orbit, bringing that constellation to over 1,700 in orbit.
The first stage was making its second flight, and landed successfully on the drone ship in the Atlantic. Both fairings were reused, with one making a record fifth flight. Though the rocket has not yet deployed the satellites as I write this, it is expected in about a half hour and based on past history, should proceed with no problems. If there is an issue I will report it immediately.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
16 SpaceX
13 China
7 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
2 ULA
The U.S. now leads China 22 to 13 in the national rankings.
Capitalism in space? The geosynchronous communications satellite company Viasat has demanded the FCC freeze any further launches of SpaceX’s quickly growing constellation of Starlink satellites.
The company claims a recent modification of SpaceX’s FCC license should not have been granted without a new environmental review of the 4,000+ satellite constellation’s impact.
Viasat is asking the FCC to hit pause on further launches until federal courts can review the legality of the license modification.
Carlsbad, California-based Viasat, which provides broadband services from geostationary orbit (GEO), had petitioned the FCC to conduct an environmental review before granting the license modification as part of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), which currently categorically exempts satellite systems, but says this did not happen despite megaconstellations bringing new considerations for regulators.
Some astronomers had also requested an environmental assessment, worried about how the constellation’s reflectivity affects ground-based telescope observations.
What is really happening here is that Viasat, having discovered its market share is seriously threatened by a competitor, is trying to use the government to squelch that competition. Viasat doesn’t really give a twit about the environmental issues. It is launching its own new three-satellite geosynchronous constellation next year to provide broadband services globally, and Starlink’s success threatens to cut into its profits.
The article also reveals one interesting tidbit about former NASA administrator Jim Bridenstine. During his short three-year tenure heading NASA he aggressively moved to encourage provide competition and private enterprise by transferring the design, construction, and ownership of rockets and spaceships from NASA to the commercial sector.
Now that he is out of the government however he — like most Washington swamp creatures — has discovered his true calling: using his influence to squelch private competition:
In April, former NASA administrator Jim Bridenstine joined Viasat’s board of directors. Bridenstine told SpaceNews in an interview at the time that the threat of megaconstellations to space safety, and the overall space access environment, were among issues on his radar.
Like a ventriloquist’s dummy, Bridenstine upon leaving NASA immediately began mouthing the manufactured concerns of his new patrons at Viasat. To hell with allowing real competition and freedom. It is much more important to manipulate the power of the government to prevent Viasat’s competitors from succeeding. And earn a nice big salary at the same time.
After successfully completing its last ground tests, Roscosmos announced today that it has finally approved the launch on July 15th of its next module for ISS, dubbed Nauka.
Nauka’s long road to space began more than a quarter of a century ago, in 1995, with this year’s launch about fourteen years behind schedule. An engineer who started working on Nauka after graduation at the age of 25 would now be a grizzled veteran of 51 and looking forward to retirement in only a few years.
The module will provide the Russian half of ISS a second restroom, greater oxygen and water recycling capacity, and room for a third resident, all necessary additions for the planned two commercial tourist launches Russia has scheduled for the fall.
Capitalism in space: Axiom has announced that retired NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson will command its second commercial manned flight.
Whitson was the first woman to command the International Space Station and the oldest woman to fly in space (57, in 2017). She holds the U.S. record for most cumulative time in space (665 days) as well as the world record for most spacewalks by a woman (10).
Joining her will be 65-year-old John Shoffner, an airplane pilot and a champion car racer.
No word yet on when this flight will take place, but expect them to aim for next year, as soon as possible after Axiom’s first ISS commercial flight in January. Scheduling will also depend on NASA, which is presently working out an ISS scheduling policy to manage the increasing number of private missions being offered.
The flight will likely use a SpaceX Dragon capsule, which means there is room for two more passengers. It is possible that those seats will be filled with the winners of Discovery Channel’s proposed reality show, but they also might be filled by actor Tom Cruise and a movie director, both of whom have expressed interest in filming scenes of a movie on ISS.
In a just published paper scientists reveal how they think they have identified the oldest rocks on the rubble pile asteroid Ryugu, and found them to be distributed across the entire face of the asteroid.
These boulders are light enough that they would float on water.
Ryugu is thought to have initially formed as a fluffy planetesimal that coalesced from accumulated dust in the early Solar System, and subsequently underwent processes such as thermal evolution and compression. This parent body was then later destroyed in a collision and fragments of this reaccumulated into the asteroid. However, planetesimals have never been seen, so whether they really existed or what they may have looked like is one of the biggest challenges in understanding the planet formation process. The boulders discovered in this research are thought to be a material that most strongly retains the appearance of the fluffy planetesimals that triggered the birth of the planets in the Solar System.
Additionally, the data from all the scientific instruments onboard Hayabusa2 that were used to examine the surface of Ryugu revealed that fragments of material similar to those of the ultra-high porosity boulders are globally distributed over the asteroid surface, and may have been collected in the sample taken by Hayabusa2. If highly primitive material with the ultra-high porosity discovered here is also found in the collected samples, it will both clarify the formation and evolutional history of Ryugu’s parent body, and also provide evidence of planetesimal formation in the early stage of the Solar System formation process.
There is no word yet from the scientists studying the Hayabusa-2 samples on what they have found. This paper gives them an idea of what could be the most important type of rock to look for.

No first amendment on Facebook.
The new dark age of silencing: It isn’t really news to post an article describing the effort at Facebook to silence and squelch conservative thought. I along with many others have already done so repeatedly, with the worst and most blatant banning beginning with the wave of censorship that these big social media sites initiated just after January 6th. Nor has Facebook eased up in subsequent months. For example, in April Facebook blackballed a mother for daring to criticize the radical Marxist and racist policies of her school board.
Since then, Facebook has shut down a pro-Israel Christian site with 77 million followers and blocked the viewing of reviews of a climate book by former Obama science advisor Steve Koonin that raised doubts about the theory of human-caused climate change.
In the former case, it appears that Facebook allowed itself to be influenced by a orchestrated attack by radical Islamic organizations, which posted more than a million comments of complaint to the site in an effort to get it canceled. Facebook of course complied.
In the latter case Facebook took on faith the complaints made by pro-global warming websites, which claimed that the book was false simply because it disagreed with those pro-global warming sites. None of them actually cited any incorrect facts put forth by the reviewed book. And even if they had found errors and falsehoods, the right answer to bad speech is never censorship, but an educated response.
Facebook claims that this censorship campaign is not really aimed at any particular political point of view, but is instead designed to reduce the overall political content on Facebook. And yet, their own description of their effort illustrates its partisan nature:
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on May 21, 2021 by Curiosity’s chemistry camera (ChemCam), normally designed to look at high resolution close-up imagery of nearby objects.
However, it can also be used as what the science team call “a long distance spyglass.” The image to the right is an example, looking at what I think are the distant but steadily approaching big cliffs on the western wall of the canyon Gediz Vallis. Make sure you look close at the shadowed cliff-face, probably several hundred feet high. It is filled with huge rock faces reminiscent of the most stark rock cliffs on the mountains of Earth.
The two images below provide the context, which makes the image even more quite breath-taking.
» Read more
Link here. Up to now the word “astronaut” has generally been applied to anyone who has flown in space, though its use for the previous space tourists has generally seemed inappropriate.
The arrival this fall of regularly and frequent commercial flights carrying private passengers into space raises the question: What do we call these individuals? Some, such as the companies Axiom and Blue Origin, want to call them astronauts. Others, such as previous space tourists Richard Garriott and former senator and now NASA administrator Bill Nelson, think that word should be reserved for the professionals. Think for example of aviation. You don’t get wings by simply flying on a commercial jet. You have to fly a plane yourself, and do it solo to earn that designation.
In truth, the most likely thing that will happen in the future is that no future space traveler will be called an astronaut. As the article notes correctly,
It might be necessary to retire the term altogether once hundreds if not thousands reach space, noted Fordham University history professor Asif Siddiqi, the author of several space books. “Are we going to call each and every one of them astronauts?”
The term is going to become historical, referring not to those who have reached space, but to those early pioneers to made it possible for everyone else. It carries too much special meaning to assign it to every Tom, Dick, or Harry who simply bought a ticket. It signifies a person who did something special and at great risk, and deserves a special honor because of it.
Neil Armstrong and Yuri Gagarin were astronauts. It seems wrong to call every commercial passenger who follows the same.
Capitalism in space? Senator Bernie Sanders (Socialist/Democrat-Vermont) has submitted a new amendment to the new NASA authorization bill, now being debated in the Senate, that eliminates the earlier changes added by senator Maria Cantwell (D-Washington) that required NASA to award a contract to a second company for building its manned lunar lander.
This earlier amendment, submitted by Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-Wash.), modified NASA’s Artemis Program. Cantwell’s amendment, in part, called for $10.03 billion in additional funding for NASA to carry out the Human Landing System program. This legislation was filed as Blue Origin and Jeff Bezos were urging Congress to add $10 billion to NASA’s budget—enough money to fully fund the development of a second Human Landing System. It was passed 11 days ago without any debate by the US Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation.
Sanders’ terse amendment seeks to excise the Cantwell language that provides additional funding for a Human Landing System.
While Sanders’ amendment probably makes more sense based on the money that Congress has actually appropriated for this task, he didn’t do it for that reason. More likely he did it as a petty attack on Jeff Bezos, whose company Blue Origin was likely expected to win that second contract.
Nothing is settled yet of course. The bill still has to pass the Senate and also be approved by the House, then signed by the president. Much will change before then.
Regardless, isn’t nice how NASA’s modern space effort is so well designed by our senators and congressmen? What would we do without them?
Link here. The article not only provides a thorough review of the company’s most recent test flight and what it did and did not accomplish, it takes a look backward to reevaluate Virgin Galactic’s history, including the many engineering problems in the past few years that have slowed development and risked lives.
The most shocking aspect of this story is this fact:
The fact that VSS Unity was broken was never disclosed to Social Capital shareholders who approved the merger, or to investors who bought the stock after the merged companies went public under Virgin Galactic’s name on the New York Stock Exchange on Oct. 28, 2019.
The source who revealed the near-fatal February 2019 flight to Parabolic Arc questioned whether withholding that information from shareholders was legal under securities laws. A number of law firms have launched investigations into Virgin Galactic recently. Their primary focus seems to be the steep drop in the company’s stock price earlier this year. (It has rebounded sharply since the flight test.) But, perhaps they will carefully review the company’s public disclosures regarding the condition of VSS Unity.
In reviewing the building competition between Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin to fly the first commercial passengers, the article also confirms many of the same observations I have made about both companies.
Read it all. It shines light beyond the pr blather that you will get from most modern media as they rewrite press releases.
The auditors of the Windham, New Hampshire, local vote have determined that folded ballots caused many of the false totals produced by the computer tabulators.
Auditors said they found “experimental confirmation that if the contest is undervoted, a fold through a vote target can create a vote.”
“Something we strongly suspect at this juncture, based on various evidence, is that in some cases, fold lines are being interpreted by the scanners as valid votes,” Mark Lindeman, who is part of the audit team, told WMUR.
Harri Hursti, another auditor, wrote on Twitter that testing proved folded ballots were misinterpreted by machines. “Test decks proved that foldings across a vote targets is misinterpreted as additional phantom votes or subtracts votes due to false overvotes,” he wrote in a post.
Their testing however has shown that folded ballots are not the only cause of the untrustworthy tabulations.
Another machine was found to have “an even more dramatic problem” by the auditors, who said that only 28 percent of the votes for Republican candidates were counted.
The machines were apparently provided by a company called AccuVote, but the “machines’ intellectual property is owned by Dominion Voting Systems.”
The results here prove that these tabulator machines are totally untrustworthy, and should be junked entirely, with the state having a legitimate case for suing the companies involved for failure to deliver.
At the least. The research so far has found that the bulk of the errors routinely seem to penalize Republicans. If further research reveals that this partisan slant is not an accident, then criminal charges might very well be in order.
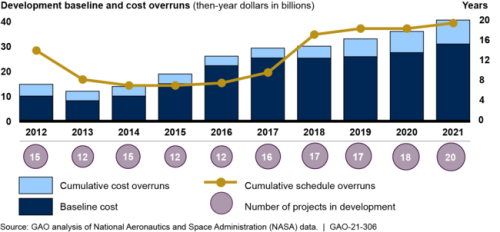
The annual Government Accountability Office’s (GAO) report on major NASA-led programs has found that the cost overruns and scheduling problems it has documented now for years continued in 2020.
You can obtain the report here. The graph to the left, from the report, summarizes the data quite succinctly.
The cumulative cost overrun of 20 major programs in development, defined as those with total costs of at least $250 million, grew to more than $9.6 billion in the report. Three programs — the James Webb Space Telescope, Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System — account for $8 billion of that total, including $4.4 billion for JWST alone.
SLS and the Exploration Ground Systems program accounted for effectively all of the $1.1 billion in overruns in 2020. … SLS alone accounted for nearly $990 million in cost increases. About two-thirds of that increase came from NASA adopting a GAO recommendation to lower the original baseline cost estimate for SLS to properly account for work that had been shifted to later phases of the program.
The report also documented almost 20 years of cumulative delays, with Webb leading the way with delays of more than seven years. The new report added 37 more months of delays during the last year.
The report, and NASA, laid the blame for many of the more recent delays and cost overruns on last year’s COVID epidemic, but if so those delays were imposed by choice, not necessity, considering how both China and SpaceX moved forward without any delays during the same time period. In reporting on NASA for the last three decades I have found it willing to initiate long delays at the drop of a hat, sometimes for reasons, such as a storm that causes some minor damage, that do not justify either the delay or its length. The COVID panic was just another example of this.

Burning witches: What the Lake Washington Institute of
Technology wants to do to anyone who expresses an
original and independent thought
They’re coming for you next: Because a tenured professor, Elisa Parrett, made a four minute statement objecting to the segregated-by-race training class the Lake Washington Institute of Technology was mandating for its teachers, the school instigated a nine month investigation resulting in a reprimand and rules forbidding her to speak on such topics again.
The investigation included the hiring of a private investigator, numerous interviews, public humiliation, and wild unsubstantiated claims that her remarks caused widespread trauma. The school removed her from her teaching duties, and worse, doubled down on its insistence that future sessions will be segregated by race. From the university’s president Amy Morrison:
» Read more
Capitalism in space: Sierra Space, the newly created space division of Sierra Nevada, announced last week that it has signed an agreement with Redwire, formerly known as Made in Space, to establish manufacturing facilities on its LIFE private space station.
The press release is vague about details, being mostly a sales pitch for encouraging other in-space manufacturing companies to consider partnering with Sierra. This in turn suggests the agreement is nothing more that a statement by Redwire that should Sierra’s station launch, it will then be willing to launch its 3D printing technology to it.
Nonetheless, this agreement lends weight to Sierra’s station proposal, which while plausible still remains somewhat vague as there is no indication on when the company plans to launch it.

The new colonial movement: According to China’s state-run press, the Zhurong rover has successfully rolled off its lander and reached the Martian surface.
The image to the right was taken by the rover’s rear hazard avoidance camera, and shows the lander and the deployment ramps behind Zhurong.
At this moment China has released no other images of the Martian surface, nor have they revealed if they have a precise idea of where the lander actually put down on Mars. This latter information is essential for them to plan the rover’s travels over its 90-day nominal mission.
Nonetheless, it appears Zhurong is functioning perfectly. If all goes right, it will not only complete that 90-day mission but continue on for considerably longer, as have other similar small rovers on both Mars and the Moon.
Capitalism in space: More than a decade later than initially promised, Virgin Galactic today finally made its first successful manned flight from Spaceport America in New Mexico.
The flight apparently reached 55 miles altitude before returning to Earth.
This was the first flight of VSS Unity since December 12, 2020, when the flight was aborted just one second after separating from its carrier airplane, WhiteKnightTwo, when a computer disconnected unexpectedly. Further delays followed:
The problems didn’t stop there, as in early May, a new issue crept up as a post-flight inspection of VMS Eve called for further engineering analysis to assess a known problem in the tail of the vehicle which was to be addressed during the next scheduled maintenance period. The company says that they have completed the analysis and determined that the structures are healthy and cleared Eve for flight.
Their plans are to do one more test flight, and then a “commercial” flight carrying company founder Richard Branson. Following that they will begin selling and flying tourists.
It appears however that they will have lost the race to fly the first suborbital tourist in space, as it appears that Blue Origin’s July 20th commercial flight will happen first.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Auditors today completed a hand recount of the votes in the town of Windham, New Hampshire and concluded that the count proves the machine tabulators are unreliable and do not produce trustworthy totals.
Hand recount finished & #’s very closely match the hand recount #’s done on Nov 12. Windham voting machine election results are confirmed to be unreliable. @WAuditors still investigating causes & contributing factors.
None of the local results are changed because of these new results, but the audit was done because a hand recount done in November showed serious discrepancies, with the hand count consistently finding more votes for Republicans compared to what was tabulated by the machines.
On Election Night, Republicans swept all four of Windham’s state representative seats. One Democrat, Kristi St. Laurent, fell short by just 24 votes and requested a recount.
But during the recount, the margin between St. Laurent and the Republican candidates changed significantly. The vote totals for all of the Republican candidates in the race increased by about 300, while St. Laurent’s vote count decreased by nearly 100.
While the outcome of the race didn’t change — the four Republican victories from Election Day were upheld at the recount — the change in vote totals raised serious questions for many from both parties.
The audit has now confirmed what the hand count has suggested. Both matched closely, but differed significantly from the machine totals, the numbers of which apparently penalized Republican candidates consistently.
They are now beginning an investigation into what caused the discrepancies. I would say above all the town should dump these machines and replace them with something that can be trusted, even if it means we go back to primitive times and hand count all elections.
Today’s cool image, to the right and cropped to post here, was taken on April 18, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Released today by MRO’s science team, it shows the rover Curiosity sitting on top of the 20-foot high rock outcrop the scientists have dubbed Mt. Mercou. The 16,400 foot high Mt. Sharp is to the south, with the rim of Gale Crater about 30 miles to the north.
I have annotated the image to show the rover’s route both before and after the moment when this picture was taken. As the caption at the link notes, the rover is currently working its way up Mt. Mercou, a route that was not initially in their plans, as shown by the wider MRO view below.
» Read more

Burning witches: What St. John’s university wished it could do
to a Jewish professor.
They’re coming for you next: Hannah Berliner Fischthal, a professor at St. John’s University in New York and the daughter of Holocaust survivors, was immediately fired because she read aloud in her literature class a selection from Mark Twain’s anti-slavery book, Pudd’nhead Wilson, that included the “N-word”.
On March 3 she was called into a meeting with HR about her use of the N-word in class, the subsequent discussion of it and a comment she allegedly made about a Black student’s hair. Fischthal said she only made a remark about a student’s head being wrapped up during class and it had nothing to do with her hair.
She said she was also criticized for mentioning her family’s experience in the Holocaust during class.
On March 5 she was suspended pending an investigation she had violated the university’s policy against bias. On April 29 she was fired.
The school had been alerted to her terrible crime of reading accurately from an accurate book portraying the actual culture of the pre-Civil War south by at least one of her students, who apparently was so weak-minded that even hearing this word that-shall-not-be-named was ““unnecessary and very painful.” It didn’t matter to this brainless student that the book was written to condemn slavery and bigotry. All that mattered is that a word of six letters was spoken aloud and she or he was forced to hear it.
» Read more
The European Space Agency is proposing in this decade to build a constellation of communications and GPS-type satellites, dubbed Moonlight, to orbit the Moon.
ESA is asking two industrial consortia in Europe to define what an integrated sat-nav and telecoms system at the Moon would look like.
It’ll include a constellation of at least three, but probably more, positioning-and-relay satellites to give global coverage, and will likely include some surface beacons, too, to augment the accuracy of the navigation signals.
“The target we have at the moment is that the constellation would be able to allow for an accuracy of 100m and probably better. We think we are able to get to 30m in the first instance,” explained Paul Verhoef, the director of ESA’s navigation department.
The two consortiums are the UK’s Surrey Satellite and Italy’s Telespazio.
It also appears the ESA is proposing making this system available to all lunar exploration missions, whether they be part of the U.S.’s Artemis program or China’s lunar plans. If so, it is commercially smart, as they will have plenty of customers to buy their services.
Because the development of ULA’s new Vulcan rocket is behind schedule, the Space Force has agreed to allow the company to replace it with an Atlas 5 rocket on a ’22 launch.
That mission, known as USSF-51, was awarded to ULA in August 2020 and is scheduled to launch in late 2022. The company had bid its newly developed Vulcan to fly that mission but the vehicle is not going to be ready on time. As a result, the Space Force agreed to allow ULA to launch USSF-51 on the company’s legacy vehicle the Atlas 5.
…Switching vehicles financially penalizes ULA. According to the company, the Atlas 5 is more expensive than Vulcan. Phase 2 provisions allow ULA to change vehicles but at no cost penalty to the government.
This story however is important because of what it tells us about the state of Blue Origin’s BE-4 rocket engine, required by both Vulcan and Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket.
At this moment ULA is saying that the first launch of Vulcan is still scheduled for late this year, launching Astrobotic’s Peregrine lander to the Moon. However, for that launch to happen the rocket requires working BE-4 rocket engines for its first stage. In January Blue Origin announced it had finally completed a full throttle test of that engine after problems lasting several years, and would soon be delivering flight-worthy engines to ULA.
It is now late May, and the article at the link revealed this very significant and somewhat shocking detail buried in the text:
Blue Origin in 2020 delivered pathfinder engines for ground tests but has yet to provide a flight-qualified engine for Vulcan’s first flight. A spokeswoman for Blue Origin said May 20 the company is “on track to deliver BE-4 engines this year.” [emphasis mine]
It seems completely impossible for ULA to launch that lunar lander on Vulcan this year if it does not yet have any flight-worthy engines on hand to incorporate and test in the rocket. Worse, it appears that Blue Origin might not deliver those engines for months yet.
This story thus suggests that we will not see launches of either ULA’s new Vulcan rocket or Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket for a considerable time.