Dormant volcanic vent on Mars
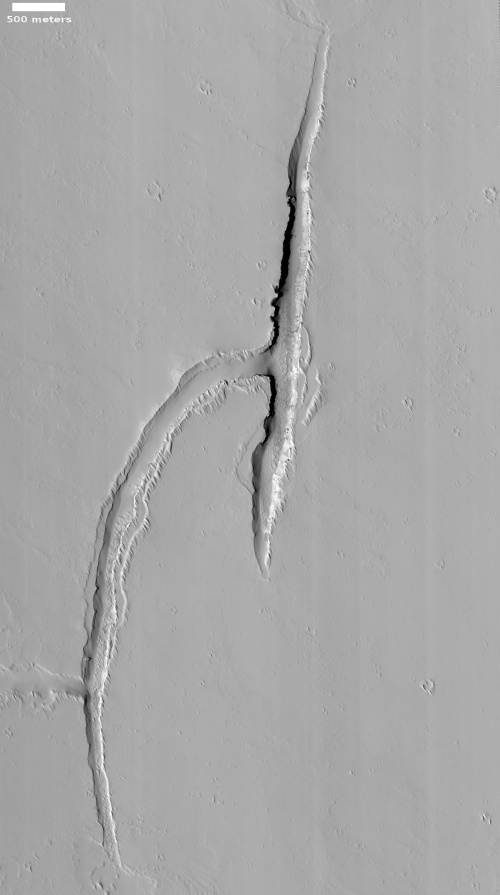
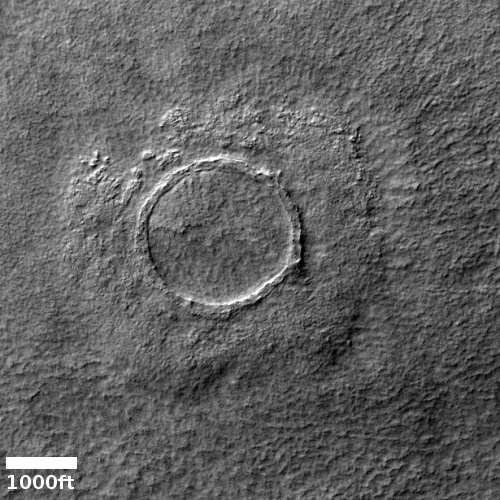
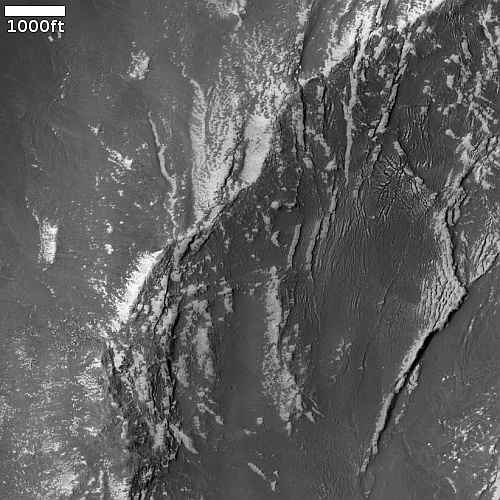
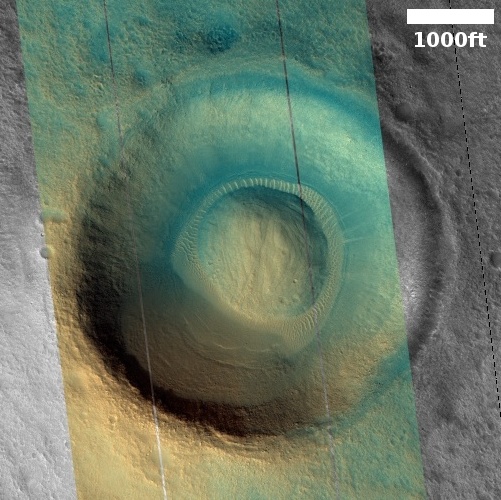
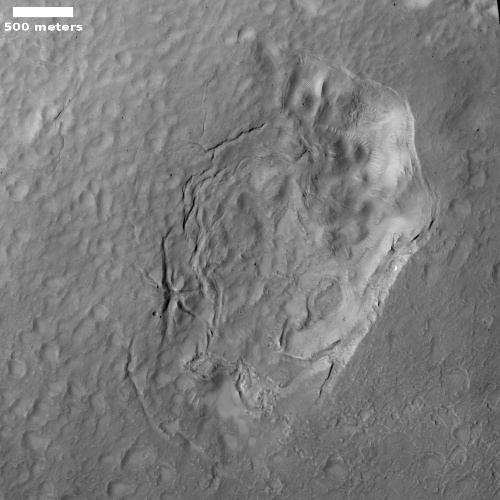
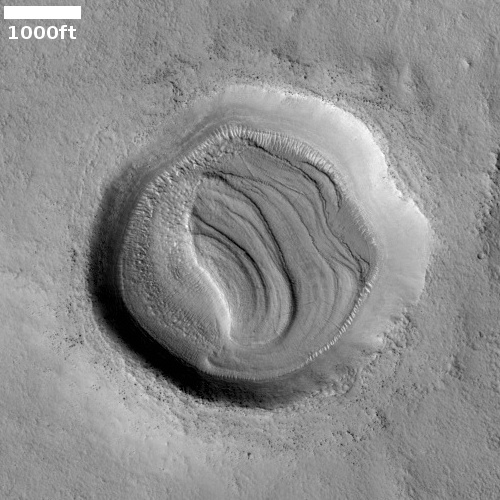
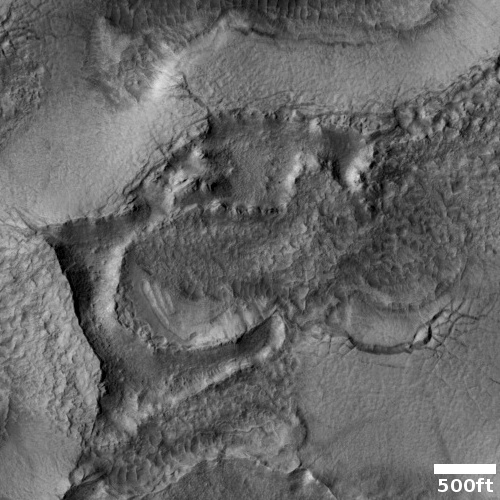
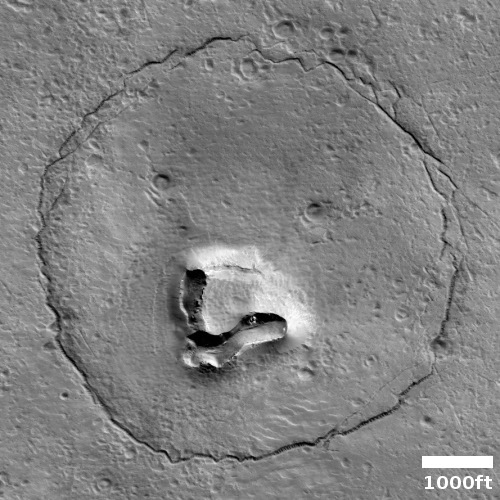
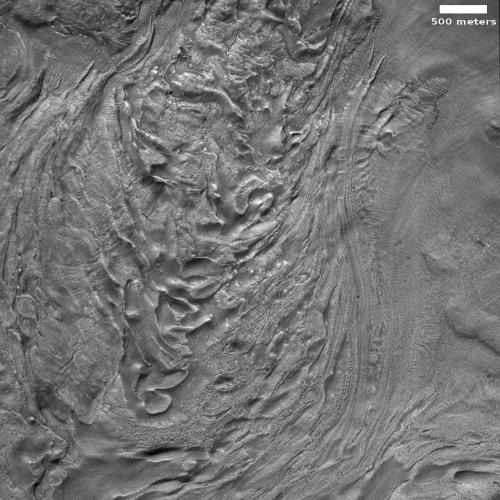
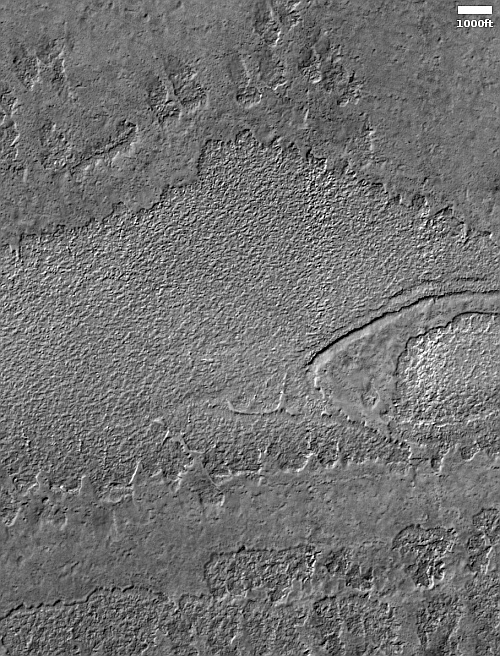
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on November 19, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the science team labels “Intersecting Fissures.”
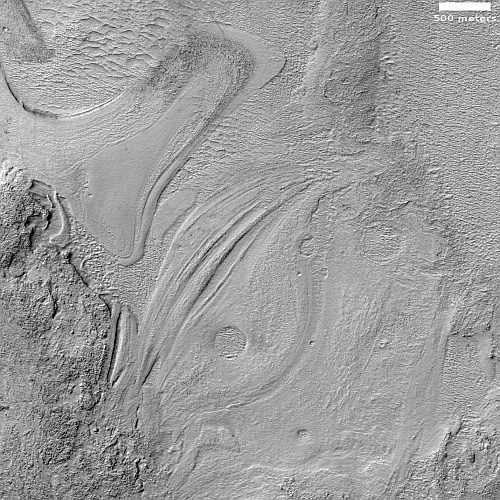
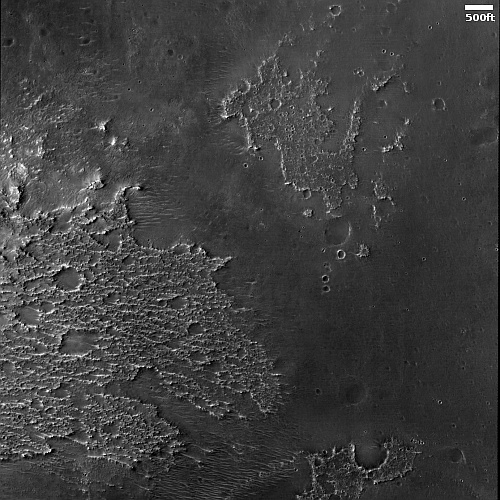
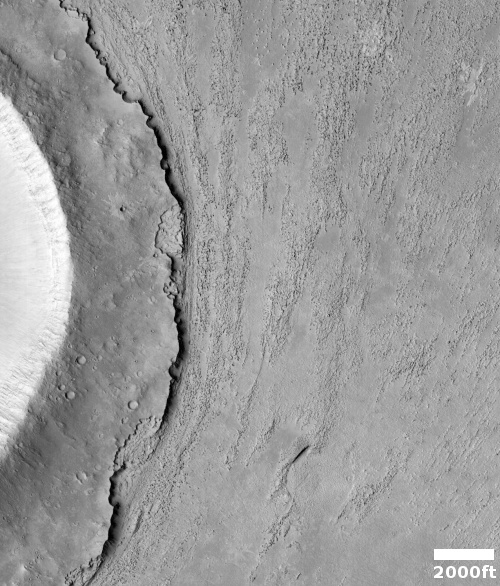
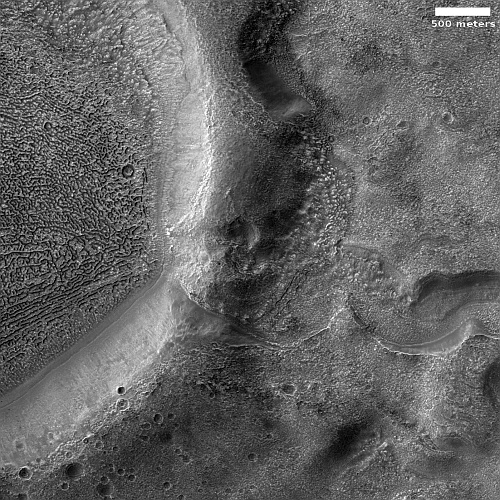
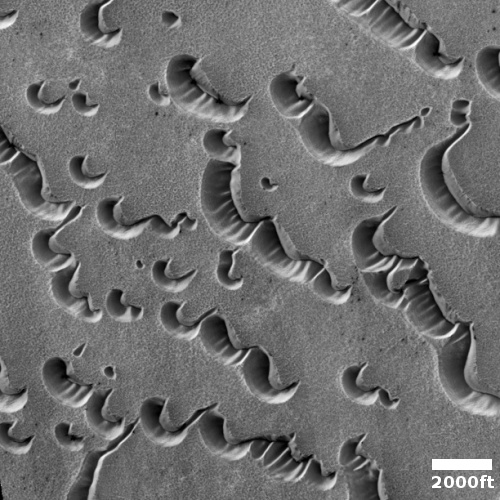
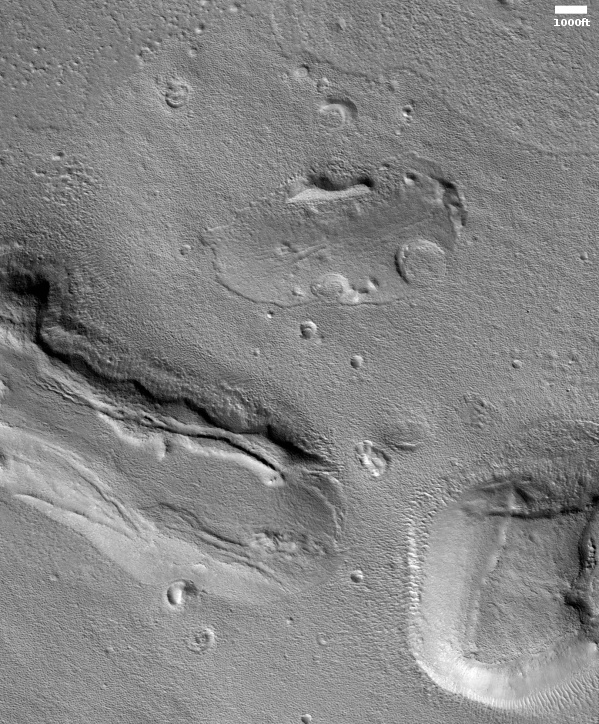
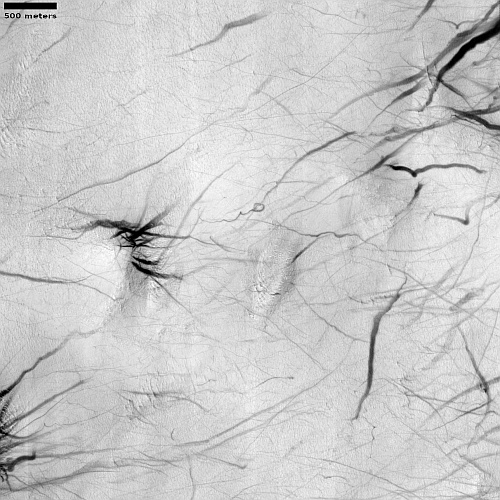
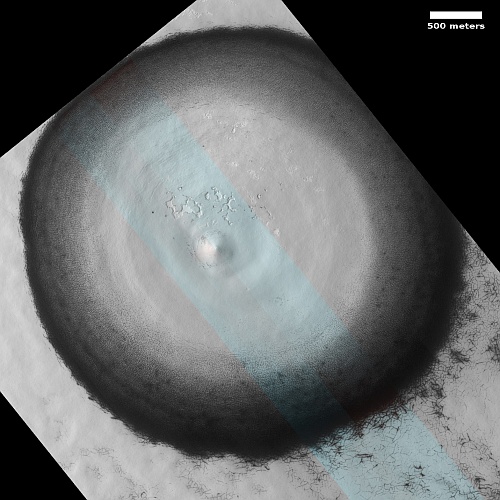
These fissures stand out distinctly on this terrain. If you look at an MRO context camera image, showing a wider view, you can see that the surrounding plain is relatively featureless, with few craters. Except for some strange and inexplicable dark streaks close by to the east, some mottled but flat terrain to the north, and a long but very faint similar east-west fissure to the south, this runelike fissure is the only major topological feature for miles around.
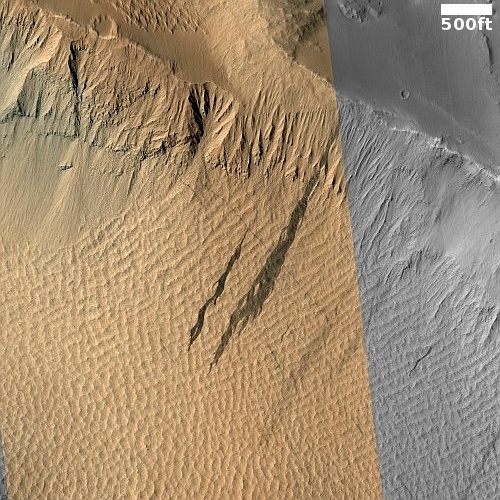
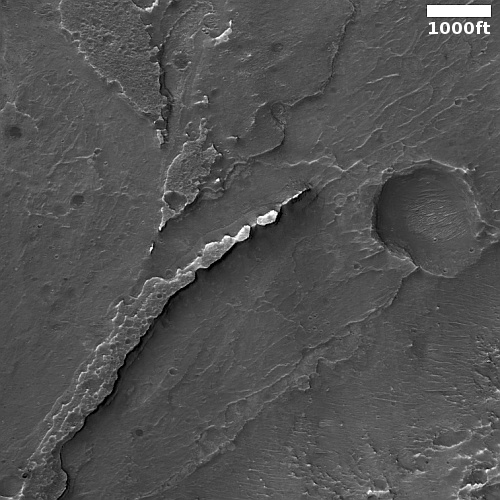
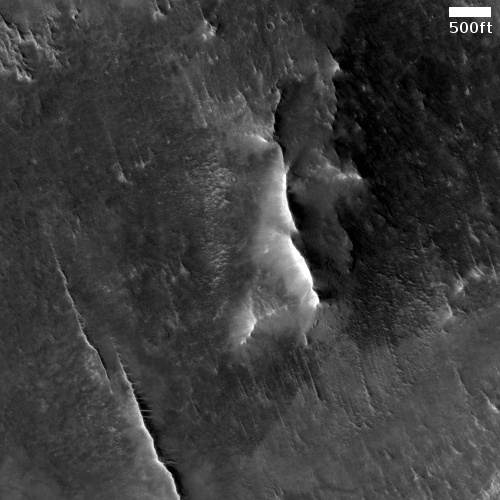
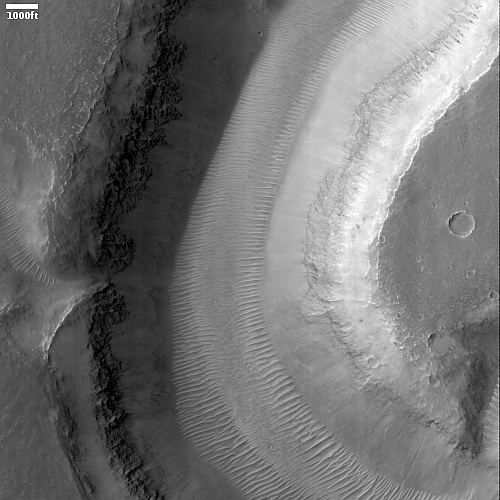
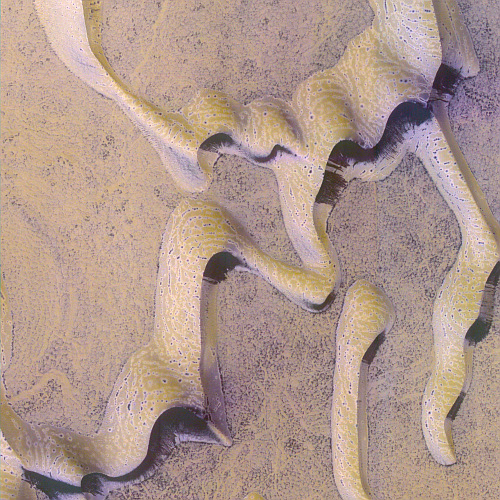
That context camera image also shows that this fissure sits on top of a very faint bulge, with hints that material had flowed downhill from the fissure’s western and southern outlets. Located very close to the equator, it is unlikely that any of those flow features are glacial, and in fact they do not have that appearance in the context camera picture. Instead, they have the look of Martian lava, fast-moving and far less viscous than Earth-lava, and thus able to cover large areas much more quickly.
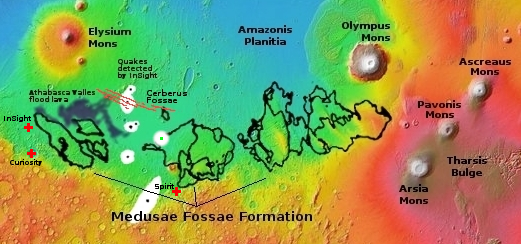
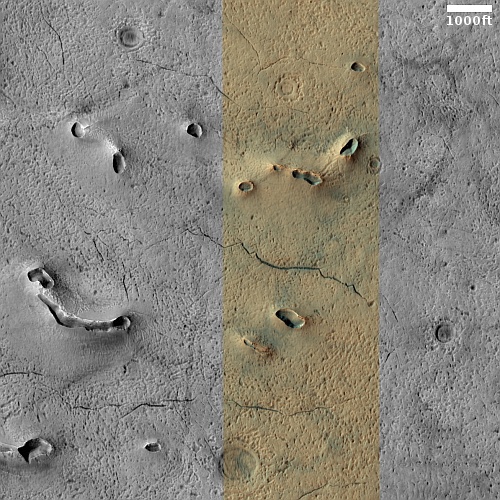
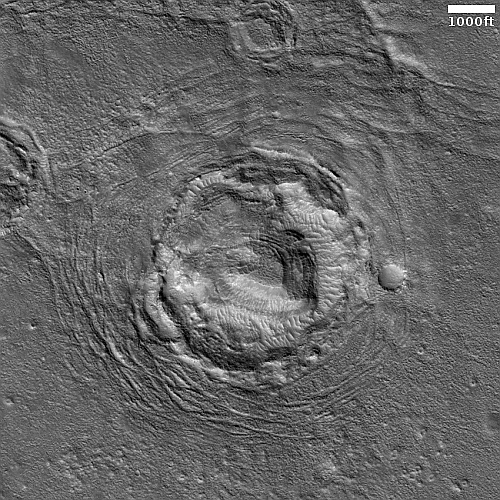
Thus, all the evidence says that this feature is a dormant volcanic vent, sitting on a flood lava plain. And the overview map below cements this conclusion.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on November 19, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the science team labels “Intersecting Fissures.”
These fissures stand out distinctly on this terrain. If you look at an MRO context camera image, showing a wider view, you can see that the surrounding plain is relatively featureless, with few craters. Except for some strange and inexplicable dark streaks close by to the east, some mottled but flat terrain to the north, and a long but very faint similar east-west fissure to the south, this runelike fissure is the only major topological feature for miles around.
That context camera image also shows that this fissure sits on top of a very faint bulge, with hints that material had flowed downhill from the fissure’s western and southern outlets. Located very close to the equator, it is unlikely that any of those flow features are glacial, and in fact they do not have that appearance in the context camera picture. Instead, they have the look of Martian lava, fast-moving and far less viscous than Earth-lava, and thus able to cover large areas much more quickly.
Thus, all the evidence says that this feature is a dormant volcanic vent, sitting on a flood lava plain. And the overview map below cements this conclusion.
» Read more