Space Force awards SpaceX and ULA new launch contracts worth $2.5 billion
Space Force yesterday awarded both SpaceX and ULA new launch contracts worth $2.5 billion and totaling 21 launches over the next two to three years.
The final batch of assignments were split almost evenly, according to Col. Doug Pentecost, the deputy program executive officer of the Space Force’s Space Systems Command. ULA received 11 missions, valued at $1.3 billion, and SpaceX received 10 missions, valued at $1.23 billion.
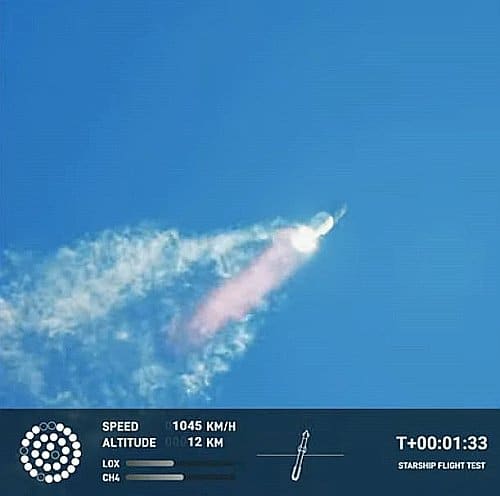
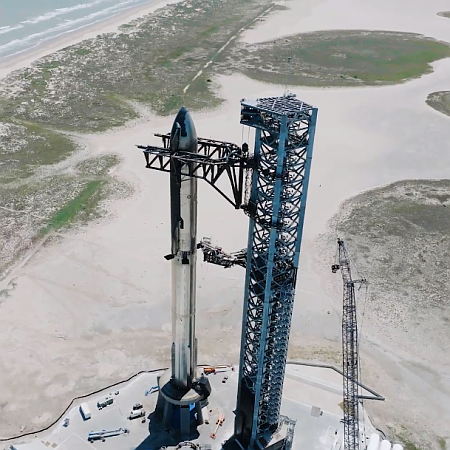
Space Systems Command said the missions are scheduled to launch over the next two to three years. ULA, a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin, will use its soon-to-debut Vulcan rocket for the 11 missions, while SpaceX will fly seven missions with its Falcon 9 rocket and three missions with its Falcon Heavy rocket.
For SpaceX this award is no surprise. The ULA contract is more puzzling. Supposedly the Space Force was not going to award any launch contracts for ULA’s new Vulcan rocket until it successfully launched twice and was certified by the military as operational. Yet, it has now awarded ULA this contract for Vulcan launches. Has the military awarded the contract on a contingency basis? What happens if Vulcan has a failure on one of its first two launches?
The Space Force’s present arrangement limits bidding for launches to just these two companies. If Vulcan fails will it open bidding to other companies, or will it transfer launches to SpaceX?
Space Force yesterday awarded both SpaceX and ULA new launch contracts worth $2.5 billion and totaling 21 launches over the next two to three years.
The final batch of assignments were split almost evenly, according to Col. Doug Pentecost, the deputy program executive officer of the Space Force’s Space Systems Command. ULA received 11 missions, valued at $1.3 billion, and SpaceX received 10 missions, valued at $1.23 billion.
Space Systems Command said the missions are scheduled to launch over the next two to three years. ULA, a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin, will use its soon-to-debut Vulcan rocket for the 11 missions, while SpaceX will fly seven missions with its Falcon 9 rocket and three missions with its Falcon Heavy rocket.
For SpaceX this award is no surprise. The ULA contract is more puzzling. Supposedly the Space Force was not going to award any launch contracts for ULA’s new Vulcan rocket until it successfully launched twice and was certified by the military as operational. Yet, it has now awarded ULA this contract for Vulcan launches. Has the military awarded the contract on a contingency basis? What happens if Vulcan has a failure on one of its first two launches?
The Space Force’s present arrangement limits bidding for launches to just these two companies. If Vulcan fails will it open bidding to other companies, or will it transfer launches to SpaceX?