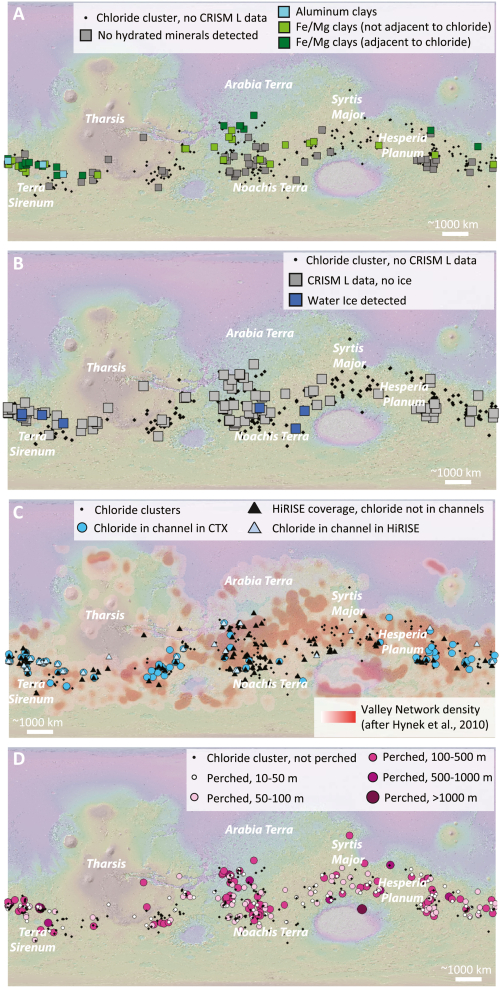
Israel, overrun with Covid, proves the vaccines have failed and must be abandoned
Link here. The analysis is data driven, extensive, and thorough. It shows that with each COVID shot and booster the effectiveness against the Wuhan virus goes down, and in fact eventually reduces a person’s immunity against the virus. Key quote:
Israel is first, always.
Other highly vaccinated and boosted countries are a few weeks behind, and their boosted patients may still have some partial protection against severe disease and death. (People who received two doses last winter or spring probably have none at this point, if the data out of Scotland and the United Kingdom are to be believed.)
But that won’t last. The Israeli experience this month could not be clearer. A third dose does not provide long-term protection. When it fails, the boomerang effect is severe. Hospitals come under even more pressure than they would in a “natural” Covid wave, because the vaccine failure is highly synchronized – everyone becomes exposed at once.
And so – insanity upon insanity – the Israelis are offering a fourth dose.
Why would anyone believe at this point that a fourth dose will help for more than a couple of weeks? Not months, weeks. The trend line was obvious even BEFORE Omicron arrived; and Omicron drives vaccine efficacy down even more quickly. In countries with good data, vaccinated people actually are more likely to be infected than the unvaccinated.
Further, a fourth dose is likely to have MORE severe side effects – remember, the second and third doses produce notably increasing levels of heart inflammation in men, and mRNA therapeutics were repurposed as vaccines because of problems with toxicity after repeated dosing. [emphasis mine]
I am beginning to believe the reason so many lovers of the COVID shots want to force everyone else to get them is because they realize the facts above, either consciously or unconsciously. They are terrified of the consequences for themselves, and thus resent those who are not in the same boat. Rather than face their mistakes and admit error, they instead want no one to escape. Everyone has got to get the shots, so that everyone is equally in danger.
Link here. The analysis is data driven, extensive, and thorough. It shows that with each COVID shot and booster the effectiveness against the Wuhan virus goes down, and in fact eventually reduces a person’s immunity against the virus. Key quote:
Israel is first, always.
Other highly vaccinated and boosted countries are a few weeks behind, and their boosted patients may still have some partial protection against severe disease and death. (People who received two doses last winter or spring probably have none at this point, if the data out of Scotland and the United Kingdom are to be believed.)
But that won’t last. The Israeli experience this month could not be clearer. A third dose does not provide long-term protection. When it fails, the boomerang effect is severe. Hospitals come under even more pressure than they would in a “natural” Covid wave, because the vaccine failure is highly synchronized – everyone becomes exposed at once.
And so – insanity upon insanity – the Israelis are offering a fourth dose.
Why would anyone believe at this point that a fourth dose will help for more than a couple of weeks? Not months, weeks. The trend line was obvious even BEFORE Omicron arrived; and Omicron drives vaccine efficacy down even more quickly. In countries with good data, vaccinated people actually are more likely to be infected than the unvaccinated.
Further, a fourth dose is likely to have MORE severe side effects – remember, the second and third doses produce notably increasing levels of heart inflammation in men, and mRNA therapeutics were repurposed as vaccines because of problems with toxicity after repeated dosing. [emphasis mine]
I am beginning to believe the reason so many lovers of the COVID shots want to force everyone else to get them is because they realize the facts above, either consciously or unconsciously. They are terrified of the consequences for themselves, and thus resent those who are not in the same boat. Rather than face their mistakes and admit error, they instead want no one to escape. Everyone has got to get the shots, so that everyone is equally in danger.