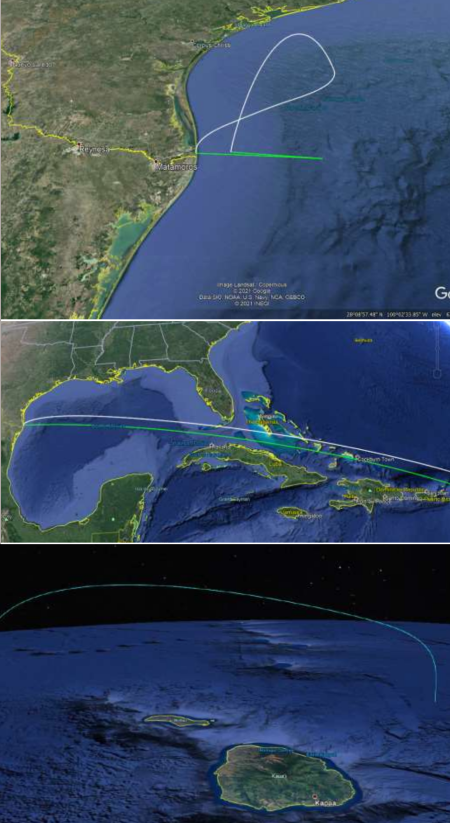
SpaceX launches 52 Starlink + 2 customer satellites
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully launched another 52 Starlink satellites along with two smallsat satellites.
They have put just under 1,700 Starlink satellites into orbit. The first stage completed its 8th launch, and the fourth in 2021, according to the SpaceX announcer. Let me repeat that: That’s four launches of the first stage in less than five months. The fairing halves were also flying on their second flight.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
15 SpaceX
12 China
7 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 20 to 12 in the national rankings.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully launched another 52 Starlink satellites along with two smallsat satellites.
They have put just under 1,700 Starlink satellites into orbit. The first stage completed its 8th launch, and the fourth in 2021, according to the SpaceX announcer. Let me repeat that: That’s four launches of the first stage in less than five months. The fairing halves were also flying on their second flight.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
15 SpaceX
12 China
7 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 20 to 12 in the national rankings.