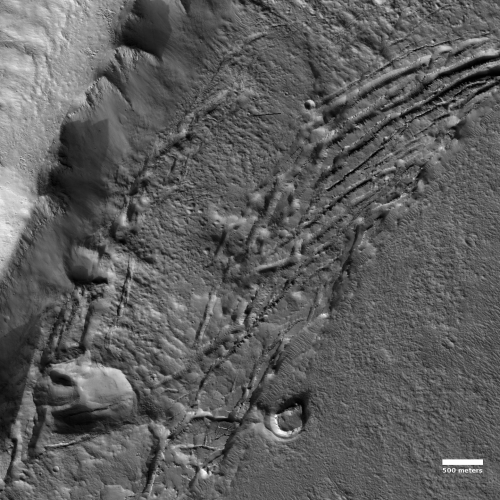
A buried crater on Mars

The overview map to the left indicates the general terrain surrounded today’s cool image. The white rectangle is the area covered by this image, taken on July 4, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. If you look close you can see that this photograph covers the eastern rim of what looks like an ancient and mostly buried crater on Mars. This unnamed crater is about 17 miles across.
» Read more

The overview map to the left indicates the general terrain surrounded today’s cool image. The white rectangle is the area covered by this image, taken on July 4, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. If you look close you can see that this photograph covers the eastern rim of what looks like an ancient and mostly buried crater on Mars. This unnamed crater is about 17 miles across.
» Read more
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
New data: young red dwarf stars are not nice stars for life
New data from both the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Hubble Space Telescope has reinforced earlier data that suggested the strong flares emitted by young red dwarf stars make them inhospitable to the development of life on any planet in the habitable zone.
A new study using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope examined the red dwarf called Barnard’s Star, which is about 10 billion years old, more than twice the current age of the Sun. Red dwarf stars are much cooler and less massive than the Sun, and are expected to live much longer lives because they do not burn through their fuel as fast. Barnard’s Star is one of the closest stars to Earth at a distance of only 6 light-years.
Young red dwarfs, with ages less than a few billion years, are known as strong sources of high-energy radiation, including blasts of ultraviolet light and X-rays. However, scientists know less about how much damaging radiation red dwarfs give off later in their lifetimes.
The new observations concluded that about 25% of the time, Barnard’s Star unleashes scorching flares, which may damage the atmospheres of planets closely orbiting it. While its only known planet does not have habitable temperatures, this study adds to evidence that red dwarfs may present serious challenges for life on their planets.
It is very important to remember that this data makes difficult the formation of life, as we know it. Since we know so little about such processes, as well as the formation processes of solar systems, it is too early to say whether no life can ever form around such stars.
New data from both the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Hubble Space Telescope has reinforced earlier data that suggested the strong flares emitted by young red dwarf stars make them inhospitable to the development of life on any planet in the habitable zone.
A new study using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope examined the red dwarf called Barnard’s Star, which is about 10 billion years old, more than twice the current age of the Sun. Red dwarf stars are much cooler and less massive than the Sun, and are expected to live much longer lives because they do not burn through their fuel as fast. Barnard’s Star is one of the closest stars to Earth at a distance of only 6 light-years.
Young red dwarfs, with ages less than a few billion years, are known as strong sources of high-energy radiation, including blasts of ultraviolet light and X-rays. However, scientists know less about how much damaging radiation red dwarfs give off later in their lifetimes.
The new observations concluded that about 25% of the time, Barnard’s Star unleashes scorching flares, which may damage the atmospheres of planets closely orbiting it. While its only known planet does not have habitable temperatures, this study adds to evidence that red dwarfs may present serious challenges for life on their planets.
It is very important to remember that this data makes difficult the formation of life, as we know it. Since we know so little about such processes, as well as the formation processes of solar systems, it is too early to say whether no life can ever form around such stars.
Scientists confirm another 44 black hole mergers detected by gravitational waves
Scientists have now confirmed that since the first detection of a gravitational wave five years ago they have detected another 44 black hole mergers in the same manner.
A global network of scientists has completed the first major analysis of gravitational wave data, providing exciting insights into some of the most exotic objects in the Universe. “We are announcing the discovery of 44 confirmed black hole mergers, which is a more than a four-fold increase in the number of previously known gravitational-wave signals,” says Shanika Galaudage from Australia’s Monash University, who was part of the research team.
…Their results are described in a trio of papers on the pre-print server arXiv. The first paper describes 39 new detections from the first half of the observing run, primarily of binary black hole systems. This brings the total number of gravitational wave events detected to 47, of which 44 are confidently double black holes, two are confidently double neutron stars, and one is still uncertain.
They think they are detecting more black hole mergers because they are heavier and thus emit bigger and more easily detected waves. They are also finding that the black hole mergers fall into two classes, two holes spinning in the same direction and two holes spinning in opposite or randomly different directions. The former formed together as a binary star system. The latter formed independently and somehow ended up linked up and merging.
Scientists have now confirmed that since the first detection of a gravitational wave five years ago they have detected another 44 black hole mergers in the same manner.
A global network of scientists has completed the first major analysis of gravitational wave data, providing exciting insights into some of the most exotic objects in the Universe. “We are announcing the discovery of 44 confirmed black hole mergers, which is a more than a four-fold increase in the number of previously known gravitational-wave signals,” says Shanika Galaudage from Australia’s Monash University, who was part of the research team.
…Their results are described in a trio of papers on the pre-print server arXiv. The first paper describes 39 new detections from the first half of the observing run, primarily of binary black hole systems. This brings the total number of gravitational wave events detected to 47, of which 44 are confidently double black holes, two are confidently double neutron stars, and one is still uncertain.
They think they are detecting more black hole mergers because they are heavier and thus emit bigger and more easily detected waves. They are also finding that the black hole mergers fall into two classes, two holes spinning in the same direction and two holes spinning in opposite or randomly different directions. The former formed together as a binary star system. The latter formed independently and somehow ended up linked up and merging.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
Conscious Choice: The origins of slavery in America and why it matters today and for our future in outer space, is a riveting page-turning story that documents how slavery slowly became pervasive in the southern British colonies of North America, colonies founded by a people and culture that not only did not allow slavery but in every way were hostile to the practice.
Conscious Choice does more however. In telling the tragic history of the Virginia colony and the rise of slavery there, Zimmerman lays out the proper path for creating healthy societies in places like the Moon and Mars.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
U.S. court orders India’s s space agency ISRO to pay $1.2 billion
A U.S. court has ordered Antrix, the commercial arm of India’s space agency ISRO, to pay $1.2 billion to Devas, a private company with operations in both India and the United States, for a contract they canceled arbitrarily in 2011.
This is a very complicated story going back many years. ISRO’s Antrix and Devas had agreements beginning in 2005 to work together to develop commercial satellites, with Antrix building the satellites and Devas commercializing bandwidth. In 2011 the India government cancelled the contracts unilaterally.
On February 25, 2011, Antrix issued a termination notice to Devas, which among other things stated that the policy decision was of the central government, acting in its sovereign capacity is the event of force majeure, which was an occurrence on February 23, 2011, PTI report said. “The scope and duration of the said decision cannot be anticipated. It is likely to be indefinite. It is not possible for Antrix to take any effective step to resume the obligations under the agreement,” Antrix was quoted as saying.
One of the reasons for the cancellation were accusations that payoffs were occurring between officials at both Antrix and Devas to make the deal happen.
Devas has been fighting in numerous courts for years to get compensation for that cancellation.
ISRO can probably ignore this U.S. court decision, except that if it does it will make it very difficult, if not impossible, for ISRO to do any work in partnership with the U.S., such as in the Artemis program. As soon as they try to do so, Devas will slap a lien on that operation, demanding payment.
A U.S. court has ordered Antrix, the commercial arm of India’s space agency ISRO, to pay $1.2 billion to Devas, a private company with operations in both India and the United States, for a contract they canceled arbitrarily in 2011.
This is a very complicated story going back many years. ISRO’s Antrix and Devas had agreements beginning in 2005 to work together to develop commercial satellites, with Antrix building the satellites and Devas commercializing bandwidth. In 2011 the India government cancelled the contracts unilaterally.
On February 25, 2011, Antrix issued a termination notice to Devas, which among other things stated that the policy decision was of the central government, acting in its sovereign capacity is the event of force majeure, which was an occurrence on February 23, 2011, PTI report said. “The scope and duration of the said decision cannot be anticipated. It is likely to be indefinite. It is not possible for Antrix to take any effective step to resume the obligations under the agreement,” Antrix was quoted as saying.
One of the reasons for the cancellation were accusations that payoffs were occurring between officials at both Antrix and Devas to make the deal happen.
Devas has been fighting in numerous courts for years to get compensation for that cancellation.
ISRO can probably ignore this U.S. court decision, except that if it does it will make it very difficult, if not impossible, for ISRO to do any work in partnership with the U.S., such as in the Artemis program. As soon as they try to do so, Devas will slap a lien on that operation, demanding payment.
Russian astronaut: Crack on ISS could be from “external impact”
Russian astronaut, Sergei Ryzhikov, today noted that to him the 1-inch crack causing the leak on ISS appeared to have been caused by an “external impact.”
Speaking with Flight Director of the Russian segment of the ISS Vladimir Solovyov, Russian cosmonaut Sergei Ryzhikov said: “If you take a closer look at the picture, there are changes of color in the middle of the crack.”
“We suspect an external impact,” Ryzhikov said adding that the place of the suspected impact should be examined during the crew’s next spacewalk, which is scheduled for November 18.
This conclusion is different than that expressed yesterday by another Russian astronaut, who suggested the crack was from age and wear and tear of the twenty-year-old Zvezda module.
Either way, an inspection of the exterior point of the crack is essential in order to permanently seal it, and that inspection will tell us one way or the other the cause of the crack.
Russian astronaut, Sergei Ryzhikov, today noted that to him the 1-inch crack causing the leak on ISS appeared to have been caused by an “external impact.”
Speaking with Flight Director of the Russian segment of the ISS Vladimir Solovyov, Russian cosmonaut Sergei Ryzhikov said: “If you take a closer look at the picture, there are changes of color in the middle of the crack.”
“We suspect an external impact,” Ryzhikov said adding that the place of the suspected impact should be examined during the crew’s next spacewalk, which is scheduled for November 18.
This conclusion is different than that expressed yesterday by another Russian astronaut, who suggested the crack was from age and wear and tear of the twenty-year-old Zvezda module.
Either way, an inspection of the exterior point of the crack is essential in order to permanently seal it, and that inspection will tell us one way or the other the cause of the crack.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
Winner of the 2003 Eugene M. Emme Award of the American Astronautical Society.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
War between two Spanish space balloon companies
Capitalism in space: A legal battle is developing between two different Spanish high altitude space balloon companies, one that came first, and a second that is being backed by a venture capitalist who had previously worked at the first.
Jose Mariano Lopez Urdiales, an MIT-trained aeronautics engineer who founded Zero 2 Infinity 11 years ago, says Kemel Kharbachi, the now CEO of EOS X Space, worked closely with the company to raise a €1m investment for Zero 2 Infinity. But the funding deal never happened.
Instead, Kharbachi, whose previous experience has focused on tourism and catering, has emerged to build his own rival space balloon business.
It does appear, from the details outlined in the article, that Kharbachi essentially stole the concept and designs from Zero 2 Infinity in order to form his own company.
As these Spanish companies fight it out, a third company in America, Space Perspectives, hopes to begin flying tourists on its stratospheric balloon, dubbed Neptune, by ’24.
Capitalism in space: A legal battle is developing between two different Spanish high altitude space balloon companies, one that came first, and a second that is being backed by a venture capitalist who had previously worked at the first.
Jose Mariano Lopez Urdiales, an MIT-trained aeronautics engineer who founded Zero 2 Infinity 11 years ago, says Kemel Kharbachi, the now CEO of EOS X Space, worked closely with the company to raise a €1m investment for Zero 2 Infinity. But the funding deal never happened.
Instead, Kharbachi, whose previous experience has focused on tourism and catering, has emerged to build his own rival space balloon business.
It does appear, from the details outlined in the article, that Kharbachi essentially stole the concept and designs from Zero 2 Infinity in order to form his own company.
As these Spanish companies fight it out, a third company in America, Space Perspectives, hopes to begin flying tourists on its stratospheric balloon, dubbed Neptune, by ’24.
October 28, 2020 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Jay Proctor – Apples Peaches Pumpkin Pie
ESA maps out first launch schedule for new rockets
Capitalism in space? The European Space Agency (ESA) today laid out the development roadmap that will lead to the launch of two new rockets, the Vega-C being built by the Italian company Avio, and the Ariane 6 being built by ArianeGroup.
The Vega-C is a more powerful version of the Vega rocket, aimed at capturing the smaller satellite market. It maiden flight is now scheduled for June ’21.
The Ariane 6 is aimed at replacing the Ariane 5, Europe’s big workhorse rocket, but to do so at a lower cost. Its maiden flight is now set for the second quarter of ’22, a significant delay from the previously announced target date in ’21, which itself was a delay from the original late ’20 launch date.
Ariane 6 however has not succeeded in cutting costs enough to match its competitor SpaceX, and thus it continues to have trouble attracting customers, even among ESA’s partner nations that it is meant to serve. These issues have led to rumors that ESA is already looking to either significantly upgrade Ariane 6 (before it even flies), or replace it entirely wit a new re usable rocket.
Capitalism in space? The European Space Agency (ESA) today laid out the development roadmap that will lead to the launch of two new rockets, the Vega-C being built by the Italian company Avio, and the Ariane 6 being built by ArianeGroup.
The Vega-C is a more powerful version of the Vega rocket, aimed at capturing the smaller satellite market. It maiden flight is now scheduled for June ’21.
The Ariane 6 is aimed at replacing the Ariane 5, Europe’s big workhorse rocket, but to do so at a lower cost. Its maiden flight is now set for the second quarter of ’22, a significant delay from the previously announced target date in ’21, which itself was a delay from the original late ’20 launch date.
Ariane 6 however has not succeeded in cutting costs enough to match its competitor SpaceX, and thus it continues to have trouble attracting customers, even among ESA’s partner nations that it is meant to serve. These issues have led to rumors that ESA is already looking to either significantly upgrade Ariane 6 (before it even flies), or replace it entirely wit a new re usable rocket.
OSIRIS-REx completes storage of Bennu sample
OSIRIS-REx has now completed placing its sample from the asteroid Bennu in the Sample Return Capsule that will bring it back to Earth.
On the afternoon of Oct. 28, following the backout check, the mission team sent commands to disconnect the two mechanical parts on the TAGSAM arm that connect the sampler head to the arm. The spacecraft first cut the tube that carried the nitrogen gas that stirred up the sample through the TAGSAM head during sample collection, and then separated the collector head from the TAGSAM arm itself.
That evening, the spacecraft completed the final step of the sample stowage process –closing the SRC. To secure the capsule, the spacecraft closed the lid and then fastened two internal latches. As of late Oct. 28, the sample of Bennu is safely stored and ready for its journey to Earth.
Because they decided it was better to store the sample immediately and not risk losing it, they were unable to do the spin test that would told them how much sample they obtained. For this reason we will not know the amount until the sample capsule is opened here on Earth, after its return on September 24, ’23.
UPDATE: You can watch if short movie of the Sample Return Capsule closing here.
OSIRIS-REx has now completed placing its sample from the asteroid Bennu in the Sample Return Capsule that will bring it back to Earth.
On the afternoon of Oct. 28, following the backout check, the mission team sent commands to disconnect the two mechanical parts on the TAGSAM arm that connect the sampler head to the arm. The spacecraft first cut the tube that carried the nitrogen gas that stirred up the sample through the TAGSAM head during sample collection, and then separated the collector head from the TAGSAM arm itself.
That evening, the spacecraft completed the final step of the sample stowage process –closing the SRC. To secure the capsule, the spacecraft closed the lid and then fastened two internal latches. As of late Oct. 28, the sample of Bennu is safely stored and ready for its journey to Earth.
Because they decided it was better to store the sample immediately and not risk losing it, they were unable to do the spin test that would told them how much sample they obtained. For this reason we will not know the amount until the sample capsule is opened here on Earth, after its return on September 24, ’23.
UPDATE: You can watch if short movie of the Sample Return Capsule closing here.
Twelve graphs prove masks are useless against COVID-19
Link here. The graphs, covering many more regions, countries, and states then the similar graphs I have posted previously, show that masks have zero effect on preventing the spread of the Wuhan virus. In some places infections rose after mask mandates were imposed. In others they declined. And the pattern showed little difference between places with or without mask mandates. As the author notes quite correctly,
Masks are not merely a small inconvenience. They have inadvertently become a key impediment to returning to a more normal life, a desirable goal for those seeking to twist the pandemic for political and electoral purposes.
Masks dehumanize us, and ironically serve as a constant reminder that we should be afraid. People can now be spotted wearing masks while camping by themselves in the woods or on a solo sailing trip. They have become a cruel device on young children everywhere, kindergarten students covered by masks and isolated by Plexiglas, struggling to understand the social expressions of their peers. Face coverings are causing real harm to the American psyche, provide little to no medical benefit, and distract us from more important health policy issues.
The mask dogma had many cracks in it from the start. For one, the U.S. surgeon general and the Centers for Disease Control both previously said that “masks are NOT effective in preventing [the] general public from catching coronavirus,” so they were already starting with a credibility deficit. Furthermore, many officials have been frequently caught without masks when they think the cameras are off them. Dr. Anthony Fauci, for example, has been caught doing this multiple times.
Take a look at the article and the graphs. They will make you feel really silly and stupid when you next put that mask on.
I say, throw the mask away. I don’t wear one, and won’t. I won’t bow to the scare tactics of politicians and incompetent and lying health officials. I have also found I pretty much can go anywhere I want without that mask. Almost no one questions me, and the few times someone has, I simply tell them I don’t wear for medical reasons, and they back off, leaving me alone.
If more people did as I do, so that those more timid began to see more people maskless and free, more people would be willing to do that same. We might actually begin to see people’s faces again, and live in a manner humans were meant to live.
Link here. The graphs, covering many more regions, countries, and states then the similar graphs I have posted previously, show that masks have zero effect on preventing the spread of the Wuhan virus. In some places infections rose after mask mandates were imposed. In others they declined. And the pattern showed little difference between places with or without mask mandates. As the author notes quite correctly,
Masks are not merely a small inconvenience. They have inadvertently become a key impediment to returning to a more normal life, a desirable goal for those seeking to twist the pandemic for political and electoral purposes.
Masks dehumanize us, and ironically serve as a constant reminder that we should be afraid. People can now be spotted wearing masks while camping by themselves in the woods or on a solo sailing trip. They have become a cruel device on young children everywhere, kindergarten students covered by masks and isolated by Plexiglas, struggling to understand the social expressions of their peers. Face coverings are causing real harm to the American psyche, provide little to no medical benefit, and distract us from more important health policy issues.
The mask dogma had many cracks in it from the start. For one, the U.S. surgeon general and the Centers for Disease Control both previously said that “masks are NOT effective in preventing [the] general public from catching coronavirus,” so they were already starting with a credibility deficit. Furthermore, many officials have been frequently caught without masks when they think the cameras are off them. Dr. Anthony Fauci, for example, has been caught doing this multiple times.
Take a look at the article and the graphs. They will make you feel really silly and stupid when you next put that mask on.
I say, throw the mask away. I don’t wear one, and won’t. I won’t bow to the scare tactics of politicians and incompetent and lying health officials. I have also found I pretty much can go anywhere I want without that mask. Almost no one questions me, and the few times someone has, I simply tell them I don’t wear for medical reasons, and they back off, leaving me alone.
If more people did as I do, so that those more timid began to see more people maskless and free, more people would be willing to do that same. We might actually begin to see people’s faces again, and live in a manner humans were meant to live.
Meteor over Alaska sets off volcano sensors
A bright fireball meteor that passed over western Alaska on October 15th caused enough disturbance in the atmosphere to set off volcano sensors throughout the region.
The event, which took place on October 15, triggered six of the sensors’ alarms at a new monitoring station on the Kenai Peninsula. The sensors are built to detect low-frequency sound waves in the atmosphere during volcanic activity, but in this case they picked up waves coming from the meteor that had streaked across the sky around 360 miles away.
In a Facebook post, the USGS said the meteor also triggered an alarm at Mount Spurr—a large, active volcano that sits around 80 miles from Anchorage that last erupted in 1992. However, as other monitoring systems also picked up on the waves, “it quickly became clear that this was not activity at Mount Spur,” the post said.
It is ironic, but those sensors, designed to monitor volcano eruptions, have likely also provided scientists some worthwhile data on asteroids.
Hat tip Commander Cobra of Task Force Gryphon
A bright fireball meteor that passed over western Alaska on October 15th caused enough disturbance in the atmosphere to set off volcano sensors throughout the region.
The event, which took place on October 15, triggered six of the sensors’ alarms at a new monitoring station on the Kenai Peninsula. The sensors are built to detect low-frequency sound waves in the atmosphere during volcanic activity, but in this case they picked up waves coming from the meteor that had streaked across the sky around 360 miles away.
In a Facebook post, the USGS said the meteor also triggered an alarm at Mount Spurr—a large, active volcano that sits around 80 miles from Anchorage that last erupted in 1992. However, as other monitoring systems also picked up on the waves, “it quickly became clear that this was not activity at Mount Spur,” the post said.
It is ironic, but those sensors, designed to monitor volcano eruptions, have likely also provided scientists some worthwhile data on asteroids.
Hat tip Commander Cobra of Task Force Gryphon
Hayabusa-2’s impactor shook Ryugu
When Hayabusa-2 fired an impactor into the asteroid Ryugu in order to access subsurface material in a sample grab, it apparently shook the asteroid, shifting boulders and rocks as far as 130 feet away.
The artificial impactor disturbed boulders within a 30m radius from the center of the impact crater- providing important insight into asteroids’ resurfacing processes.
Professor ARAKAWA Masahiko (Graduate School of Science, Kobe University, Japan) and members of the Hayabusa2 mission discovered more than 200 boulders ranging from 30cm to 6m in size, which either newly appeared or moved as a result of the artificial impact crater created by Japanese spacecraft Hayabusa2’s Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI) on April 5th, 2019. Some boulders were disturbed even in areas as far as 40m from the crater center. The researchers also discovered that the seismic shaking area, in which the surface boulders were shaken and moved an order of cm by the impact, extended about 30m from the crater center. Hayabusa2 recovered a surface sample at the north point of the SCI crater (TD2), and the thickness of ejecta deposits at this site were estimated to be between 1.0mm to 1.8cm using a Digital Elevation Map (DEM).
This data makes all the more important for OSIRIS-REx to get post-sample-grab images of its Nightingale site, if at all possible.
When Hayabusa-2 fired an impactor into the asteroid Ryugu in order to access subsurface material in a sample grab, it apparently shook the asteroid, shifting boulders and rocks as far as 130 feet away.
The artificial impactor disturbed boulders within a 30m radius from the center of the impact crater- providing important insight into asteroids’ resurfacing processes.
Professor ARAKAWA Masahiko (Graduate School of Science, Kobe University, Japan) and members of the Hayabusa2 mission discovered more than 200 boulders ranging from 30cm to 6m in size, which either newly appeared or moved as a result of the artificial impact crater created by Japanese spacecraft Hayabusa2’s Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI) on April 5th, 2019. Some boulders were disturbed even in areas as far as 40m from the crater center. The researchers also discovered that the seismic shaking area, in which the surface boulders were shaken and moved an order of cm by the impact, extended about 30m from the crater center. Hayabusa2 recovered a surface sample at the north point of the SCI crater (TD2), and the thickness of ejecta deposits at this site were estimated to be between 1.0mm to 1.8cm using a Digital Elevation Map (DEM).
This data makes all the more important for OSIRIS-REx to get post-sample-grab images of its Nightingale site, if at all possible.
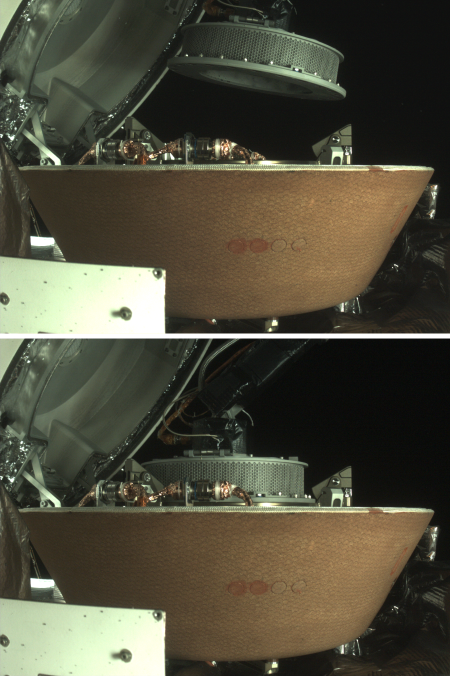
OSIRIS-REx engineers successfully place sample collector in return capsule
OSIRIS-REx engineers have successfully placed the sample collector head holding the material captured from the asteroid Bennu in the return capsule that will bring it back to Earth.
Yesterday, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission successfully placed the spacecraft’s sample collector head into its Sample Return Capsule (SRC). The first image shows the collector head hovering over the SRC after the Touch-And-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism (TAGSAM) arm moved it into the proper position for capture. The second image shows the collector head secured onto the capture ring in the SRC. Both images were captured by the StowCam camera.
Today, after the head was seated into the SRC’s capture ring, the spacecraft performed a “backout check,” which commanded the TAGSAM arm to back out of the capsule. This maneuver is designed to tug on the collector head and ensure that the latches – which keep the collector head in place – are well secured. Following the test, the mission team received telemetry confirming that the head is properly secured in the SRC.
The next step will be to seal the capsule for return to Earth. However, based on the two images above, the sample is now relatively secure, as the opening where material could escape is now held face down in the capsule.
The spacecraft will head back to Earth in March ’21, with the sample capsule landing on Earth on September 24, 2023. I do not know whether it will be possible in the next six months to get new images of the Nightingale touch-and-go site, but have emailed Erin Morton, head of the communications for the science team, and asked. I will update this post when I hear back from her.
OSIRIS-REx engineers have successfully placed the sample collector head holding the material captured from the asteroid Bennu in the return capsule that will bring it back to Earth.
Yesterday, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission successfully placed the spacecraft’s sample collector head into its Sample Return Capsule (SRC). The first image shows the collector head hovering over the SRC after the Touch-And-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism (TAGSAM) arm moved it into the proper position for capture. The second image shows the collector head secured onto the capture ring in the SRC. Both images were captured by the StowCam camera.
Today, after the head was seated into the SRC’s capture ring, the spacecraft performed a “backout check,” which commanded the TAGSAM arm to back out of the capsule. This maneuver is designed to tug on the collector head and ensure that the latches – which keep the collector head in place – are well secured. Following the test, the mission team received telemetry confirming that the head is properly secured in the SRC.
The next step will be to seal the capsule for return to Earth. However, based on the two images above, the sample is now relatively secure, as the opening where material could escape is now held face down in the capsule.
The spacecraft will head back to Earth in March ’21, with the sample capsule landing on Earth on September 24, 2023. I do not know whether it will be possible in the next six months to get new images of the Nightingale touch-and-go site, but have emailed Erin Morton, head of the communications for the science team, and asked. I will update this post when I hear back from her.
Russian astronaut: ISS crack could be result of Zvezda module’s age
A Russian astronaut just returned from ISS admitted during a press conference that the recently located crack on the 20-year-old Zvezda module that was the source of the long-term slow leak could be the result of the module’s age.
“Twenty years are actually an absolute record for all space stations now. And we see now that something is changing and something requires greater [attention]. Again, if we go back to the leak, the hull is already beginning to give cracks and scratches somewhere, that is, we see the limits [of the ISS structure’s service life],” [cosmonaut Ivan Vagner] said.
The crack has been sealed temporarily, with a more permanent seal put in place after the nearby docking port is cleared and the hatches closed and out of the way.
If Russian astronauts are noticing wear and tear in Zvezda that is bad enough to cause “cracks”, this raises some very serious issues for ISS’s future, as replacing that module on ISS will be complicated and expensive, and at this point no one has even begun planning such an replacement.
A Russian astronaut just returned from ISS admitted during a press conference that the recently located crack on the 20-year-old Zvezda module that was the source of the long-term slow leak could be the result of the module’s age.
“Twenty years are actually an absolute record for all space stations now. And we see now that something is changing and something requires greater [attention]. Again, if we go back to the leak, the hull is already beginning to give cracks and scratches somewhere, that is, we see the limits [of the ISS structure’s service life],” [cosmonaut Ivan Vagner] said.
The crack has been sealed temporarily, with a more permanent seal put in place after the nearby docking port is cleared and the hatches closed and out of the way.
If Russian astronauts are noticing wear and tear in Zvezda that is bad enough to cause “cracks”, this raises some very serious issues for ISS’s future, as replacing that module on ISS will be complicated and expensive, and at this point no one has even begun planning such an replacement.
Is this the planned landing site of China’s Mars rover?
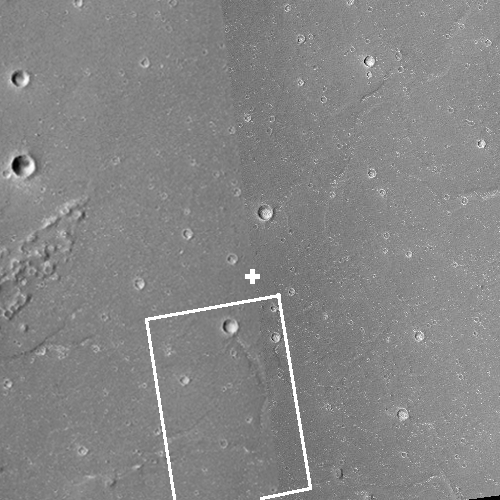

According to this Space News article, a report in the Chinese press, since revised to remove the information, had provided precise coordinates on Mars for the prime candidate landing site for China’s Tianwen-1 rover.
[I]nformation published in an article (in Chinese) in the official China Space News publication following launch in July provides a specific primary landing site. The article reported landing coordinates of 110.318 degrees east longitude and 24.748 degrees north latitude, within the southern portion of Utopia Planitia. Online versions of the article have since been edited to remove the coordinates; however, these remain published by sources citing the article.
The mosaic on the right, made up of two images taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s (MRO) context camera (found here and here) shows this location with the white cross. The white box is the area covered by the only image taken of this area by MRO’s high resolution camera.
As these photos show, this location, in a part of Mars’ northern lowland plains dubbed Utopia Planitia, is generally smooth and flat, making for a relatively safe landing site. At the same time, it has craters and some ridges and hills that could pose issues.
That the coordinates were removed from the Chinese press story suggests that this might be the prime site, but until Tianwen-1 gets into Mars orbit and begins scouting the site with its own high resolution images, they want to reserve judgement. The spacecraft arrives in orbit in February ’21, and they presently plan to land the rover in May. That gives them three months to scout this location as well as a secondary landing site on the other side of Mars, in the Chryse Planitia northern lowlands [pdf], the same region where Viking 1 and Mars Pathfinder landed.
Once they have done this they will be able to refine the location more precisely.

According to this Space News article, a report in the Chinese press, since revised to remove the information, had provided precise coordinates on Mars for the prime candidate landing site for China’s Tianwen-1 rover.
[I]nformation published in an article (in Chinese) in the official China Space News publication following launch in July provides a specific primary landing site. The article reported landing coordinates of 110.318 degrees east longitude and 24.748 degrees north latitude, within the southern portion of Utopia Planitia. Online versions of the article have since been edited to remove the coordinates; however, these remain published by sources citing the article.
The mosaic on the right, made up of two images taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s (MRO) context camera (found here and here) shows this location with the white cross. The white box is the area covered by the only image taken of this area by MRO’s high resolution camera.
As these photos show, this location, in a part of Mars’ northern lowland plains dubbed Utopia Planitia, is generally smooth and flat, making for a relatively safe landing site. At the same time, it has craters and some ridges and hills that could pose issues.
That the coordinates were removed from the Chinese press story suggests that this might be the prime site, but until Tianwen-1 gets into Mars orbit and begins scouting the site with its own high resolution images, they want to reserve judgement. The spacecraft arrives in orbit in February ’21, and they presently plan to land the rover in May. That gives them three months to scout this location as well as a secondary landing site on the other side of Mars, in the Chryse Planitia northern lowlands [pdf], the same region where Viking 1 and Mars Pathfinder landed.
Once they have done this they will be able to refine the location more precisely.
SpaceX finds clogged valves in several Merlin engines
Capitalism in space: SpaceX has discovered that the problem that caused a recent launch abort of a GPS satellite was a coating that clogged valves in several newer Merlin engines.
Hans Koenigsmann, vice president of build and flight reliability at SpaceX, said teams initially weren’t able to figure out why two of nine engines triggered early-start sensors on Oct. 2, which forced computers to automatically scrub seconds before liftoff. After the engines were removed and shipped to Texas for testing, the anomaly surfaced again when sensors detected higher-than-expected engine chamber pressures.
The cause: a minuscule, almost undetectable amount of “masking lacquer,” which is used to protect engine components and surfaces during the production process. The lacquer is almost like a bright red nail polish. “We found a relief valve – a little line that goes to the relief valve – blocked in the gas generator,” Koenigsmann told reporters Wednesday. “That little red substance was blocking a relief valve that caused it to function a little bit earlier than it was supposed to.”
The gas generators are almost like little rocket engines themselves – they’re used to power a pump that then feeds propellants into the main engine chamber. But the blockage caused certain processes to begin too early.
Once the lacquer was removed the engines functioned perfectly.
The issue was also found in two engines on the new booster that was going to launch astronauts to ISS, which explains why that mission was delayed. The company is swapping out the engines, and is still targeting November 14th for that launch. In addition, NASA wants it to fly at least two missions beforehand to demonstrate the problem is fixed. One will be that GPS satellite, on November 4th. The other could be one of three different payloads on SpaceX’s busy schedule.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX has discovered that the problem that caused a recent launch abort of a GPS satellite was a coating that clogged valves in several newer Merlin engines.
Hans Koenigsmann, vice president of build and flight reliability at SpaceX, said teams initially weren’t able to figure out why two of nine engines triggered early-start sensors on Oct. 2, which forced computers to automatically scrub seconds before liftoff. After the engines were removed and shipped to Texas for testing, the anomaly surfaced again when sensors detected higher-than-expected engine chamber pressures.
The cause: a minuscule, almost undetectable amount of “masking lacquer,” which is used to protect engine components and surfaces during the production process. The lacquer is almost like a bright red nail polish. “We found a relief valve – a little line that goes to the relief valve – blocked in the gas generator,” Koenigsmann told reporters Wednesday. “That little red substance was blocking a relief valve that caused it to function a little bit earlier than it was supposed to.”
The gas generators are almost like little rocket engines themselves – they’re used to power a pump that then feeds propellants into the main engine chamber. But the blockage caused certain processes to begin too early.
Once the lacquer was removed the engines functioned perfectly.
The issue was also found in two engines on the new booster that was going to launch astronauts to ISS, which explains why that mission was delayed. The company is swapping out the engines, and is still targeting November 14th for that launch. In addition, NASA wants it to fly at least two missions beforehand to demonstrate the problem is fixed. One will be that GPS satellite, on November 4th. The other could be one of three different payloads on SpaceX’s busy schedule.
Rocket Lab successfully launches 10 smallsats
Capitalism in space: Rocket Lab today successfully placed ten smallsats into orbit using its Electron rocket, launched from New Zealand.
This was their second successful launch for the company since their launch failure on July 4th. Their next launch should be their first from the U.S., from Wallops Island, Virginia.
The leaders in the 2020 launch race:
27 China
18 SpaceX
12 Russia
4 ULA
4 Europe (Arianespace)
4 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 29 to 27 in the national rankings.
Capitalism in space: Rocket Lab today successfully placed ten smallsats into orbit using its Electron rocket, launched from New Zealand.
This was their second successful launch for the company since their launch failure on July 4th. Their next launch should be their first from the U.S., from Wallops Island, Virginia.
The leaders in the 2020 launch race:
27 China
18 SpaceX
12 Russia
4 ULA
4 Europe (Arianespace)
4 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 29 to 27 in the national rankings.
Bazooka Charlie – WW2s Strangest Tank Buster
An evening pause: Today this man would likely be forbidden from doing this, regardless of its practicality. Modern military rules would be horrified at his independent action.
Hat tip lazarus long.
More evidence the number of COVID-19 deaths is greatly exaggerated
The video report below notes that, according to CDC published data, almost all deaths now listed as COVID-19 deaths were actually caused by other factors.
Specifically, of the approximately 220,000 COVID-19 deaths listed so far, almost 94% were likely not caused exclusively by COVID-19, but by other chronic illnesses. While many of these other maladies, such as a variety of respiratory illnesses, probably worked closely in conjunction with the coronavirus to kill the patient, other illnesses were clearly the real cause of death. For example, the CDC says the 51,000 of today’s 218,000 COVID-19 deaths were caused by heart attacks or heart failure, not COVID-19.
If we subtract these coronary deaths, we are left with about 167,000 COVID-19 deaths. The CDC notes that of these, 88,000 were probably caused not by the coronavirus but by the flu and pneumonia. Hospitals listed them as COVID-19 deaths because the CARES act passed by Congress in the spring gives those hospitals a 20% bonus if they claim the death was COVID-19. This fact might also explain the almost complete lack of flu deaths this year, as listed by hospitals.
Based on this data, it appears that the coronavirus probably caused about 79,000 deaths, on top of the 88,000 flu and pneumonia deaths this year. These Wuhan virus deaths are probably excess deaths this year, but with an average age of 78 the deaths are still occurring almost exclusively among the aged sick, rather than the general population. For everyone else, COVID-19 remains relatively harmless, like the flu.
Interestingly, the CDC recently reported that in 2020 the total number of excess deaths is presently estimated at 300,000. Most significantly, the CDC also stated that
» Read more
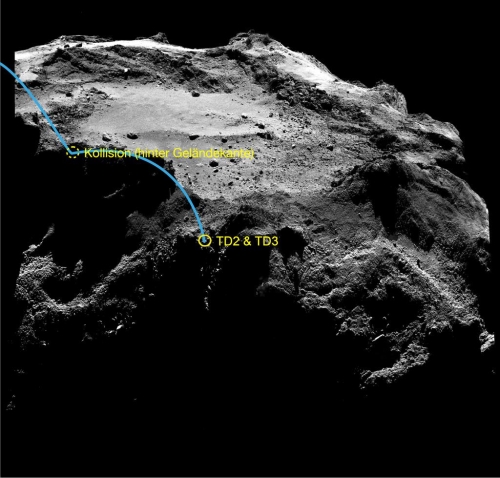
Scientists finally map Philae’s full route to its final landing site on Comet 67/C-G

Click for full resolution image.
Using archival data from Rosetta, scientists have finally been able to map out the full route and all impact points made by the lander Philae on its journey to land on the Comet 67P/C-G in November 2014.
All that was known previously was the location of the first contact, that there had been another impact following the rebound, and the location of the final landing site where Philae came to rest after two hours and where it was found towards the end of the Rosetta mission in 2016 . “Now we finally know the exact place where Philae touched down on the comet for the second time. This will allow us to fully reconstruct the lander’s trajectory and derive important scientific results from the telemetry data as well as measurements from some of the instruments operating during the landing process,” explains Jean-Baptiste Vincent from the DLR Institute of Planetary Research, who was involved in the research published today.
…Analysis of the data revealed that Philae had spent almost two full minutes – not unusual in this very low gravity environment – at the second surface contact point, making at least four different surface contacts as the lander ‘ploughed’ through the rugged landscape. A particularly remarkable imprint, which became visible in the images, was made when the top of Philae sank 25 centimetres into the ice at the side of an open crevice, leaving visible traces of the sample drill and the lander’s top. The peaks in the magnetic field data resulting from the boom movement show that Philae took three seconds to make this particular ‘dent’.
This new data about this particular impact has helped the scientists determine a great deal about the comet’s make-up and density, finding that it is extremely fluffy.
The parameters of surface contact showed that this ancient, 4.5-billion-year-old mixture of ice and dust is extraordinarily soft – it is fluffier than the froth on a cappuccino, the foam in a bathtub or the whitecaps of waves meeting the coast.
They also found that the interior has many voids comprising 75% of the interior, with the “boulders” between having the density of Styrofoam.

Click for full resolution image.
Using archival data from Rosetta, scientists have finally been able to map out the full route and all impact points made by the lander Philae on its journey to land on the Comet 67P/C-G in November 2014.
All that was known previously was the location of the first contact, that there had been another impact following the rebound, and the location of the final landing site where Philae came to rest after two hours and where it was found towards the end of the Rosetta mission in 2016 . “Now we finally know the exact place where Philae touched down on the comet for the second time. This will allow us to fully reconstruct the lander’s trajectory and derive important scientific results from the telemetry data as well as measurements from some of the instruments operating during the landing process,” explains Jean-Baptiste Vincent from the DLR Institute of Planetary Research, who was involved in the research published today.
…Analysis of the data revealed that Philae had spent almost two full minutes – not unusual in this very low gravity environment – at the second surface contact point, making at least four different surface contacts as the lander ‘ploughed’ through the rugged landscape. A particularly remarkable imprint, which became visible in the images, was made when the top of Philae sank 25 centimetres into the ice at the side of an open crevice, leaving visible traces of the sample drill and the lander’s top. The peaks in the magnetic field data resulting from the boom movement show that Philae took three seconds to make this particular ‘dent’.
This new data about this particular impact has helped the scientists determine a great deal about the comet’s make-up and density, finding that it is extremely fluffy.
The parameters of surface contact showed that this ancient, 4.5-billion-year-old mixture of ice and dust is extraordinarily soft – it is fluffier than the froth on a cappuccino, the foam in a bathtub or the whitecaps of waves meeting the coast.
They also found that the interior has many voids comprising 75% of the interior, with the “boulders” between having the density of Styrofoam.
Bringing life to the slumping lifeless slopes of Mars
To me, the cool image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, helps illustrate the most significant difference between Mars and Earth, its obvious lack of life. This lack fundamentally changes the nature of erosion on the Red Planet.
On Earth life covers practically every square foot of the surface, and that life probably does more than anything to reshape the surface, and it does it far more quickly than any geological or meteorological process. For example, even if we are in the most lifeless area of the Sahara Desert, with no plant life, the dunes will still be reshaped and changed simply by the passage of any animal, whether it be a lizard, camel, or human driving a jeep.
On Mars, there is no visible life, and this lack means that any changes we see are solely geological or meteorological in nature. From a scientist’s perspective, the view is clean, all changes wrought solely by inanimate nature, without the added factor of life.
In a sense, Mars gives us a view of what geological and meteorological processes would do on Earth, if the Earth was lifeless.
Today’s image, taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on August 29, 2020, exemplifies this. Labeled “Slope Failures in Tempe Terra,” it shows the slow break-up and slumping of debris as it oh-so-slowly falls from higher terrain. The cracks developed as large chunks pulled apart as the material slide downward to the east.
This cracking took a lot of time. On Earth, during that time it would have either been obscured by plant life, or would have been distorted greatly by the traffic of animal life across its surface. Animals would have dug holes, and humans might have reshaped it to build homes and roads. On Mars, none of that happened, so the geology was free to evolve slowly, without interference, and now sits in plain view for scientists to interpret.
Such knowledge will over time strengthen our understanding of Earth geology, because it will give us a better understanding of the influences of life on that geology. Geologists will be better able to separate the influence of life and inanimate natural processes.
The overview map below helps give the wider context of those Martian inanimate natural processes, on a grand planetary scale.
» Read more
NASA and ESA ink Lunar Gateway deal
NASA yesterday announced that it has signed a deal with the European Space Agency (ESA) outlining their partnership in building the Lunar Gateway space station in orbit around the Moon.
Under this agreement, ESA will contribute habitation and refueling modules, along with enhanced lunar communications, to the Gateway. The refueling module also will include crew observation windows. In addition to providing the hardware, ESA will be responsible for operations of the Gateway elements it provides. ESA also provides two additional European Service Modules (ESMs) for NASA’s Orion spacecraft. These ESMs will propel and power Orion in space on future Artemis missions and provide air and water for its crew.
For some reason NASA’s press release makes no mention of what ESA gets from the deal. From this news report:
[ESA] said it will receive “three flight opportunities for European astronauts to travel to and work on the Gateway” as part of the agreement.
I also note that there is no mention of the Artemis Accords in this agreement. As far as I can tell, right now the only ESA member who has signed on is the United Kingdom, and I am not sure of the UK’s status in the ESA considering their exit from the European Union. The two are different political deals, but exiting one might affect the other.
The Trump administration has said repeatedly that it will only partner in its lunar ambitions with countries that sign the accords. However, at this moment Congress has simply not funded those ambitions, so NASA needs partners to get things built. Moreover, Orion is a space capsule (costing about $18 billion and taking 20 years to build) that does not have a service module to provide it air and water. Europe provides that, and had only agreed to build two.
It might be that NASA has traded the accords away to get Europe’s help for both Gateway and Orion. This deal, announced now, might also be an effort by NASA (and Europe) to lobby Congress to fork up the cash.
NASA yesterday announced that it has signed a deal with the European Space Agency (ESA) outlining their partnership in building the Lunar Gateway space station in orbit around the Moon.
Under this agreement, ESA will contribute habitation and refueling modules, along with enhanced lunar communications, to the Gateway. The refueling module also will include crew observation windows. In addition to providing the hardware, ESA will be responsible for operations of the Gateway elements it provides. ESA also provides two additional European Service Modules (ESMs) for NASA’s Orion spacecraft. These ESMs will propel and power Orion in space on future Artemis missions and provide air and water for its crew.
For some reason NASA’s press release makes no mention of what ESA gets from the deal. From this news report:
[ESA] said it will receive “three flight opportunities for European astronauts to travel to and work on the Gateway” as part of the agreement.
I also note that there is no mention of the Artemis Accords in this agreement. As far as I can tell, right now the only ESA member who has signed on is the United Kingdom, and I am not sure of the UK’s status in the ESA considering their exit from the European Union. The two are different political deals, but exiting one might affect the other.
The Trump administration has said repeatedly that it will only partner in its lunar ambitions with countries that sign the accords. However, at this moment Congress has simply not funded those ambitions, so NASA needs partners to get things built. Moreover, Orion is a space capsule (costing about $18 billion and taking 20 years to build) that does not have a service module to provide it air and water. Europe provides that, and had only agreed to build two.
It might be that NASA has traded the accords away to get Europe’s help for both Gateway and Orion. This deal, announced now, might also be an effort by NASA (and Europe) to lobby Congress to fork up the cash.
“That is a blatant lie.”
In a long fifty minute public interview tonight on the Tucker Carlson Show, embedded below the fold, a businessman outlined in great documented detail how Joe Biden, the Democratic Party’s presidential candidate, was lying when he said he had no knowledge and never participated the business dealings of his son Hunter Biden, including a partnership with a Chinese company connected to the Chinese Communist Party.
More details here. The businessman, Tony Bobulinski, was quite clear and convincing. Bobulinski outlined in detail two meetings he had with Joe Biden in connection with those Chinese business dealings.
[Carlson]: The former vice-president has said that he was not involved in his son’s business dealings and had no knowledge of them at all. But this sounds like direct involvement in them.
[Bobulinski]: That is a blatant lie. When he states that, that is a blatant lie.
Apparently this man has come forward because he knows Biden is lying, and in the process is smearing his name by accusing him of being a party to Russian disinformation. Bobulinski however is a Navy veteran who had top secret clearance. To be accused of literally being a traitor was too much for him to take, which is why he has gone public with his knowledge.
Watch the interview below. It is worth your time, especially now only a week before election day. Joe Biden is not only a liar, he has been willing to make deals with Chinese businesses that work for the Chinese Communist Party, and as Bobulinski notes, is very seriously compromised by all standards of national security. As president it will be very difficult for him to defend the nation’s interests, exposed as he is now as someone with deep financial ties to Chinese government interests.
Even worse, the willingness of almost every major news organization to bury this story condemns them forever as true partisan hacks with zero loyalty to the United States itself. They deserve nothing but of utter contempt and disgust from every American.
In a long fifty minute public interview tonight on the Tucker Carlson Show, embedded below the fold, a businessman outlined in great documented detail how Joe Biden, the Democratic Party’s presidential candidate, was lying when he said he had no knowledge and never participated the business dealings of his son Hunter Biden, including a partnership with a Chinese company connected to the Chinese Communist Party.
More details here. The businessman, Tony Bobulinski, was quite clear and convincing. Bobulinski outlined in detail two meetings he had with Joe Biden in connection with those Chinese business dealings.
[Carlson]: The former vice-president has said that he was not involved in his son’s business dealings and had no knowledge of them at all. But this sounds like direct involvement in them.
[Bobulinski]: That is a blatant lie. When he states that, that is a blatant lie.
Apparently this man has come forward because he knows Biden is lying, and in the process is smearing his name by accusing him of being a party to Russian disinformation. Bobulinski however is a Navy veteran who had top secret clearance. To be accused of literally being a traitor was too much for him to take, which is why he has gone public with his knowledge.
Watch the interview below. It is worth your time, especially now only a week before election day. Joe Biden is not only a liar, he has been willing to make deals with Chinese businesses that work for the Chinese Communist Party, and as Bobulinski notes, is very seriously compromised by all standards of national security. As president it will be very difficult for him to defend the nation’s interests, exposed as he is now as someone with deep financial ties to Chinese government interests.
Even worse, the willingness of almost every major news organization to bury this story condemns them forever as true partisan hacks with zero loyalty to the United States itself. They deserve nothing but of utter contempt and disgust from every American.
The Dock
An evening pause: Some surfing action in Bali off of an artificial floating platform that sometimes “kicks like a snake.”
Hat tip Roland.
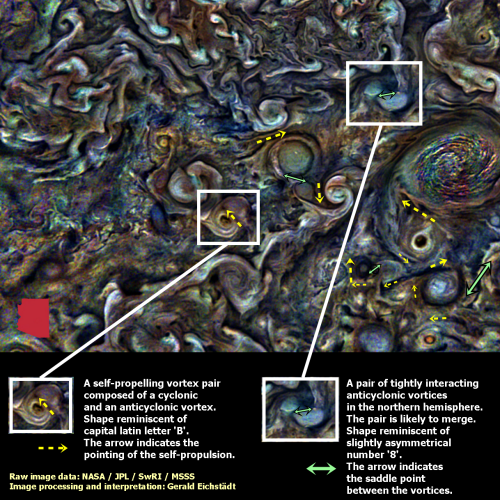
Analyzing the evolving “small” storms in Jupiter’s atmosphere
The cool image to the right is another Juno photo of Jupiter enhanced by citizen scientist Gerald Eichstädt. This time Eichstädt also did some analysis of the motions and interactions of many vortices found in the northern polar regions of Jupiter. The image to the right has been cropped and reduced to post here, with the state of Arizona, about 400 by 300 miles in size, added for scale. There is more annotation in the full image.
As Eichstädt writes:
Large vortices in an atmosphere layer of a rotating planet can be roughly split into two classes, cyclonic and anticyclonic vortices.
Based on this rough classification, two interacting vortices can either be of the same or of opposite sign. Tightly interacting vortices of opposite sign tend to mutually propel each other, hence the whole pair, if they are of similar strength and size.
Tightly interacting vortex pairs of the same sign tend to merge. More distant like-signed vortex pairs may essentially repel each other. Interacting vortices tend to create filaments, some of which may split into fragments and further collapse into streets of small eddies.
He also notes that in future orbits Juno will provide closer views of this stormy region, as with the orbit the closest point shifts northward.
The cool image to the right is another Juno photo of Jupiter enhanced by citizen scientist Gerald Eichstädt. This time Eichstädt also did some analysis of the motions and interactions of many vortices found in the northern polar regions of Jupiter. The image to the right has been cropped and reduced to post here, with the state of Arizona, about 400 by 300 miles in size, added for scale. There is more annotation in the full image.
As Eichstädt writes:
Large vortices in an atmosphere layer of a rotating planet can be roughly split into two classes, cyclonic and anticyclonic vortices.
Based on this rough classification, two interacting vortices can either be of the same or of opposite sign. Tightly interacting vortices of opposite sign tend to mutually propel each other, hence the whole pair, if they are of similar strength and size.
Tightly interacting vortex pairs of the same sign tend to merge. More distant like-signed vortex pairs may essentially repel each other. Interacting vortices tend to create filaments, some of which may split into fragments and further collapse into streets of small eddies.
He also notes that in future orbits Juno will provide closer views of this stormy region, as with the orbit the closest point shifts northward.
Initial price for Starlink: $99 per month?
According to a CNBC article today, SpaceX is now offering a beta version of its Starlink internet service to customers as the price of $99 per month, plus a $499 charge for equipment.
SpaceX is expanding the beta test of its Starlink satellite internet service, reaching out via email on Monday to people who expressed interest in signing up for the service.
Called the “Better Than Nothing Beta” test, according to multiple screenshots of the email seen by CNBC, initial Starlink service is priced at $99 a month – plus a $499 upfront cost to order the Starlink Kit. That kit includes a user terminal to connect to the satellites, a mounting tripod and a wifi router. There is also now a Starlink app listed by SpaceX on the Google Play and Apple iOS app stores.
“As you can tell from the title, we are trying to lower your initial expectations,” the emails said, signed Starlink Team. “Expect to see data speeds vary from 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s and latency from 20ms to 40ms over the next several months as we enhance the Starlink system. There will also be brief periods of no connectivity at all.”
SpaceX did not confirm this story with CNBC. If it is real, the price is disappointingly high, and might very well limit Starlink’s potential. Then again, this is only the beta version. Later versions when under full operation and available to many more customers might bring that price down.
According to a CNBC article today, SpaceX is now offering a beta version of its Starlink internet service to customers as the price of $99 per month, plus a $499 charge for equipment.
SpaceX is expanding the beta test of its Starlink satellite internet service, reaching out via email on Monday to people who expressed interest in signing up for the service.
Called the “Better Than Nothing Beta” test, according to multiple screenshots of the email seen by CNBC, initial Starlink service is priced at $99 a month – plus a $499 upfront cost to order the Starlink Kit. That kit includes a user terminal to connect to the satellites, a mounting tripod and a wifi router. There is also now a Starlink app listed by SpaceX on the Google Play and Apple iOS app stores.
“As you can tell from the title, we are trying to lower your initial expectations,” the emails said, signed Starlink Team. “Expect to see data speeds vary from 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s and latency from 20ms to 40ms over the next several months as we enhance the Starlink system. There will also be brief periods of no connectivity at all.”
SpaceX did not confirm this story with CNBC. If it is real, the price is disappointingly high, and might very well limit Starlink’s potential. Then again, this is only the beta version. Later versions when under full operation and available to many more customers might bring that price down.
The sad story of Virgin Galactic
Link here. This so-called suborbital space tourism company, which for years has promised to fly tourists on suborbital flights to space but failed to do so, appears now to be trying to shift gears and instead make itself into a company building supersonic airplanes.
Richard Branson’s dream of a suborbital Virgin Galactic vehicle zipping passengers between distant cities at hypersonic speeds above Mach 5 (6,174 km/h, 3,836 mph) is dead. At least for now.
In August, the space tourism company he founded pivoted to a slower supersonic Mach 3 (3,704 km/h, 2,302 mph) business jet. Virgin Galactic unveiled a mission concept for an aircraft that would carry 9-19 passengers at a cruising altitude of 60,000 ft (18,288 m).
Since Branson began selling off his stock in May and became a minority owner in the company, the new management has apparently shifted its focus away from suborbital space tourism to building a supersonic airplane for commercial travel on Earth.
The problem is that there are already a lot of companies working to do this, and Virgin Galactic is in last place, even as it scrambles to find new investment capital simply to begin development.
After sixteen years, this company has so far accomplished nothing, while spending probably more than $2 billion in private capital. It now wants more, even as Richard Branson has sold off his stock at a nifty profit. (I am no stock market expert, but if I has any interest in buying stock (I do not), this would not be the stock I’d buy.)
Branson however is not entirely off the hook. His entire empire, built on transportation and tourism, is in big trouble because of the Wuhan panic. It might now all collapse, tragically crashing to Earth as did the first SpaceShipTwo several years ago.
Link here. This so-called suborbital space tourism company, which for years has promised to fly tourists on suborbital flights to space but failed to do so, appears now to be trying to shift gears and instead make itself into a company building supersonic airplanes.
Richard Branson’s dream of a suborbital Virgin Galactic vehicle zipping passengers between distant cities at hypersonic speeds above Mach 5 (6,174 km/h, 3,836 mph) is dead. At least for now.
In August, the space tourism company he founded pivoted to a slower supersonic Mach 3 (3,704 km/h, 2,302 mph) business jet. Virgin Galactic unveiled a mission concept for an aircraft that would carry 9-19 passengers at a cruising altitude of 60,000 ft (18,288 m).
Since Branson began selling off his stock in May and became a minority owner in the company, the new management has apparently shifted its focus away from suborbital space tourism to building a supersonic airplane for commercial travel on Earth.
The problem is that there are already a lot of companies working to do this, and Virgin Galactic is in last place, even as it scrambles to find new investment capital simply to begin development.
After sixteen years, this company has so far accomplished nothing, while spending probably more than $2 billion in private capital. It now wants more, even as Richard Branson has sold off his stock at a nifty profit. (I am no stock market expert, but if I has any interest in buying stock (I do not), this would not be the stock I’d buy.)
Branson however is not entirely off the hook. His entire empire, built on transportation and tourism, is in big trouble because of the Wuhan panic. It might now all collapse, tragically crashing to Earth as did the first SpaceShipTwo several years ago.
Europa Clipper to be delayed because of SLS bottleneck
Because Boeing will be unable to provide an SLS rocket in time for the planned 2024 launch of Europa Clipper, once the probe is completed NASA will be forced to put it in storage.
The problem is that Congress has mandated that the Jupiter probe be launched on SLS, but has only funded the first two Artemis launches to the Moon. Boeing will also need at least three years to build it, meaning that even if the money from Congress appeared today, it would likely not be ready for its ’24 launch date.
In terms of rocket science, right now, Europa Clipper can launch on a commercial vehicle, like SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy or United Launch Alliance’s Delta-IV Heavy rocket, although the mission would then need a longer cruise time to reach its destination.
But in terms of the law, NASA’s hands are tied.
“Because of that, we’re planning to build the Europa Clipper and then put it into storage, because we’re not going to have an SLS rocket available until 2025,” Bridenstine said. “That’s the current plan. I don’t think that’s the right plan, but we’re going to follow the law.”
Though the common sense thing for Congress to do would be to release NASA from this mandate and allow the agency to pick the launch rocket, do not expect that to happen. Congress wants SLS because of all the pork it produces. They will not allow NASA to reduce its reliance on SLS one iota, if they can. Unless pressured publicly (which I think is NASA’s goal with this announcement), Congress will let Europa Clipper sit in a warehouse for years, at a cost of between $36 to $60 million per year, waiting for SLS.
Because Boeing will be unable to provide an SLS rocket in time for the planned 2024 launch of Europa Clipper, once the probe is completed NASA will be forced to put it in storage.
The problem is that Congress has mandated that the Jupiter probe be launched on SLS, but has only funded the first two Artemis launches to the Moon. Boeing will also need at least three years to build it, meaning that even if the money from Congress appeared today, it would likely not be ready for its ’24 launch date.
In terms of rocket science, right now, Europa Clipper can launch on a commercial vehicle, like SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy or United Launch Alliance’s Delta-IV Heavy rocket, although the mission would then need a longer cruise time to reach its destination.
But in terms of the law, NASA’s hands are tied.
“Because of that, we’re planning to build the Europa Clipper and then put it into storage, because we’re not going to have an SLS rocket available until 2025,” Bridenstine said. “That’s the current plan. I don’t think that’s the right plan, but we’re going to follow the law.”
Though the common sense thing for Congress to do would be to release NASA from this mandate and allow the agency to pick the launch rocket, do not expect that to happen. Congress wants SLS because of all the pork it produces. They will not allow NASA to reduce its reliance on SLS one iota, if they can. Unless pressured publicly (which I think is NASA’s goal with this announcement), Congress will let Europa Clipper sit in a warehouse for years, at a cost of between $36 to $60 million per year, waiting for SLS.