The view of Jezero Crater, from both Ingenuity and Perseverance
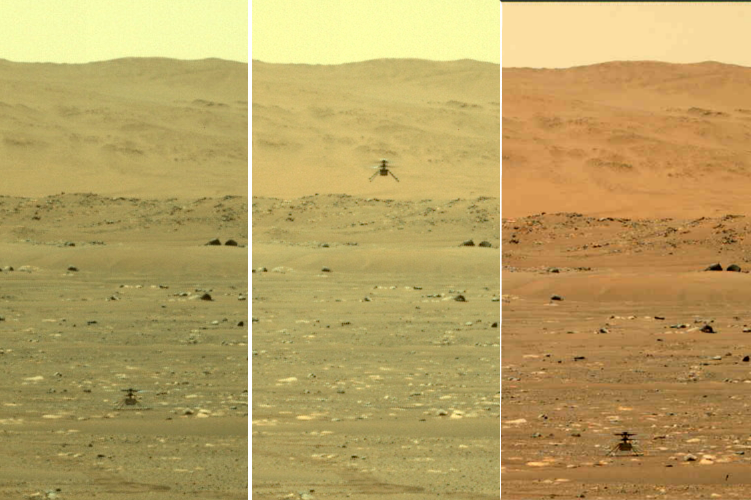
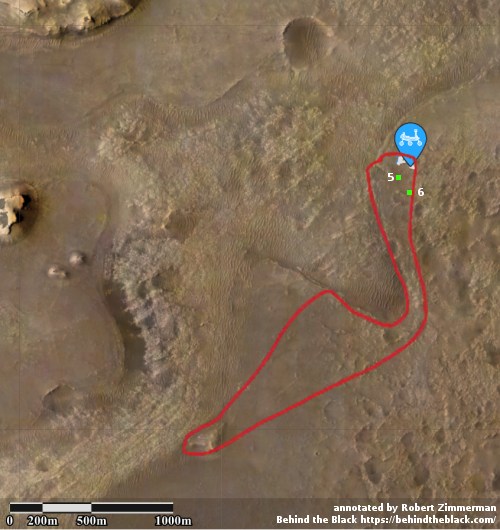
Cool image time! Today the Perseverance science team released the 200 images that Ingeniuty took during its 10th flight on July 24, 2021.
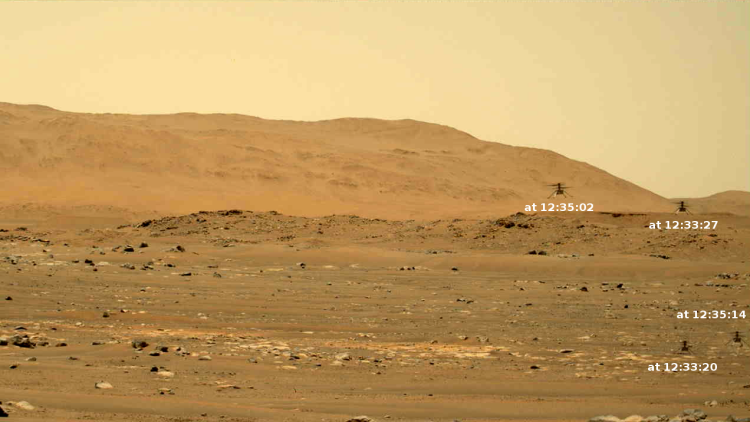
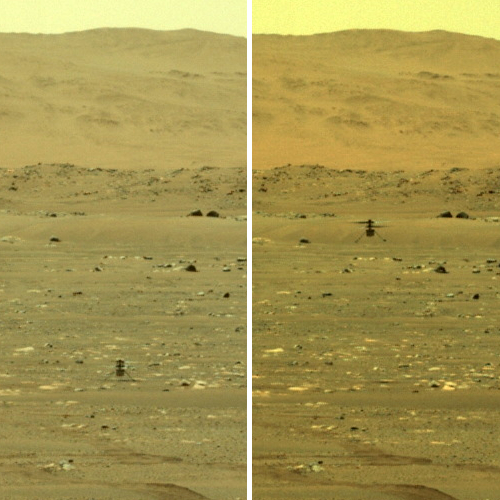
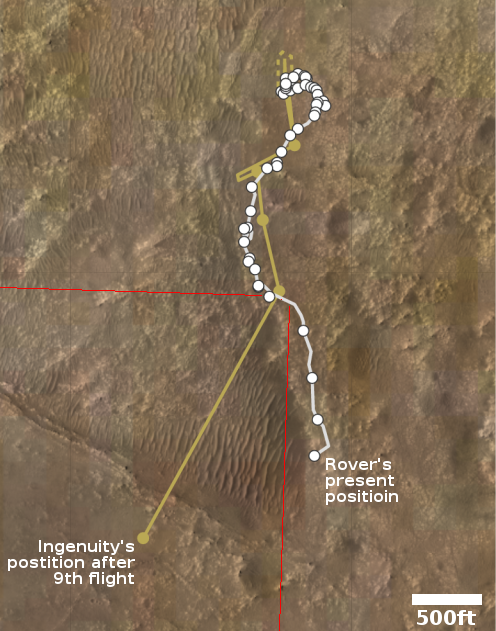
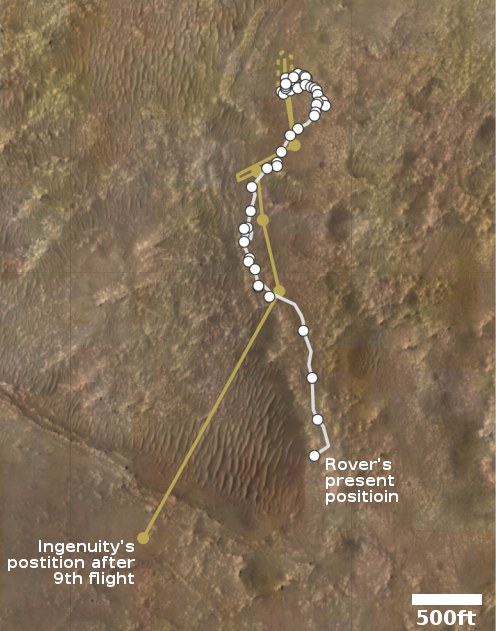
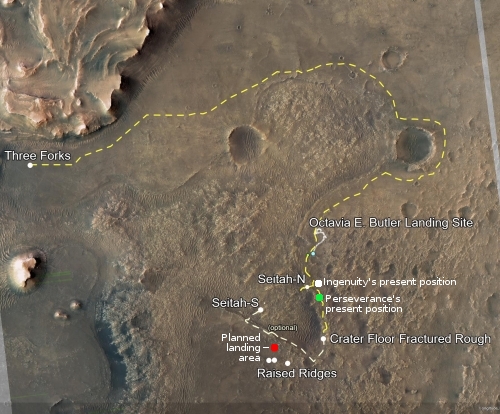
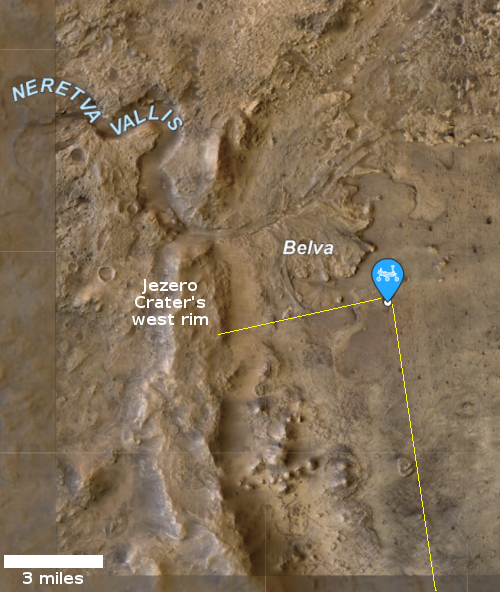
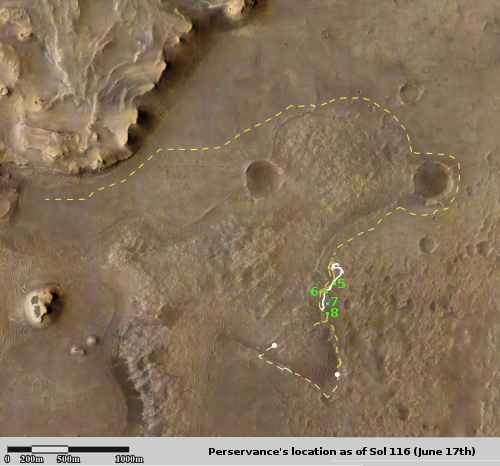
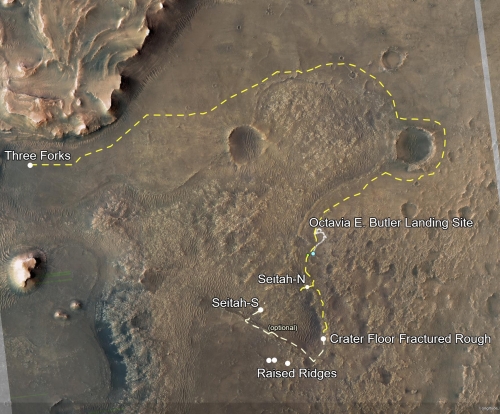
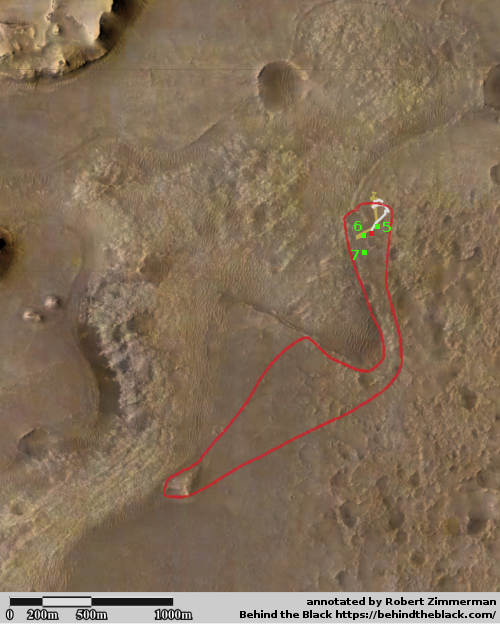
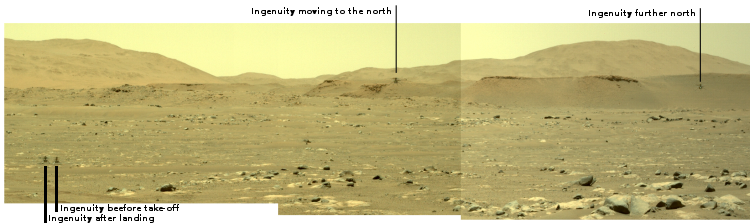
The photo to the right was taken about 25 seconds before the helicopter landed, and looks to the southwest. In the foreground can be seen the ridge of rocks and pebbles that the scientists sent Ingeniuty to photograph. In the distance can be seen the rim of Jezero Crater, about 7.5 miles away, with some rounded hills that sit in the crater floor about 5.5 miles away.
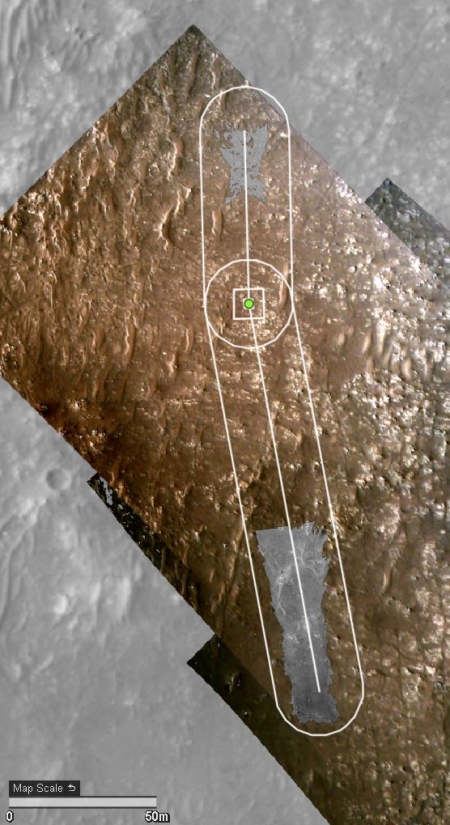
The white box indicates the area covered by two high resolution images taken by Perseverance on July 28th that I have combined into the panorama below.
» Read more
Cool image time! Today the Perseverance science team released the 200 images that Ingeniuty took during its 10th flight on July 24, 2021.
The photo to the right was taken about 25 seconds before the helicopter landed, and looks to the southwest. In the foreground can be seen the ridge of rocks and pebbles that the scientists sent Ingeniuty to photograph. In the distance can be seen the rim of Jezero Crater, about 7.5 miles away, with some rounded hills that sit in the crater floor about 5.5 miles away.
The white box indicates the area covered by two high resolution images taken by Perseverance on July 28th that I have combined into the panorama below.
» Read more