Is this the planned landing site of China’s Mars rover?

According to this Space News article, a report in the Chinese press, since revised to remove the information, had provided precise coordinates on Mars for the prime candidate landing site for China’s Tianwen-1 rover.
[I]nformation published in an article (in Chinese) in the official China Space News publication following launch in July provides a specific primary landing site. The article reported landing coordinates of 110.318 degrees east longitude and 24.748 degrees north latitude, within the southern portion of Utopia Planitia. Online versions of the article have since been edited to remove the coordinates; however, these remain published by sources citing the article.
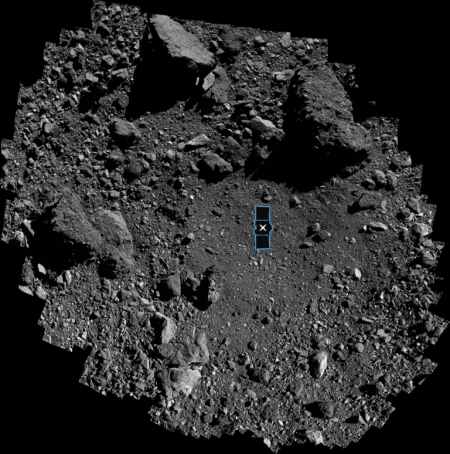
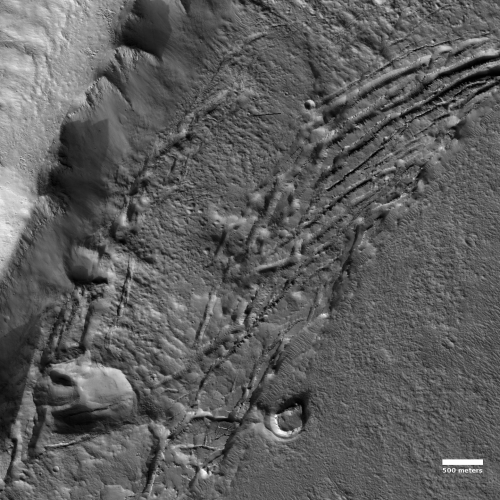
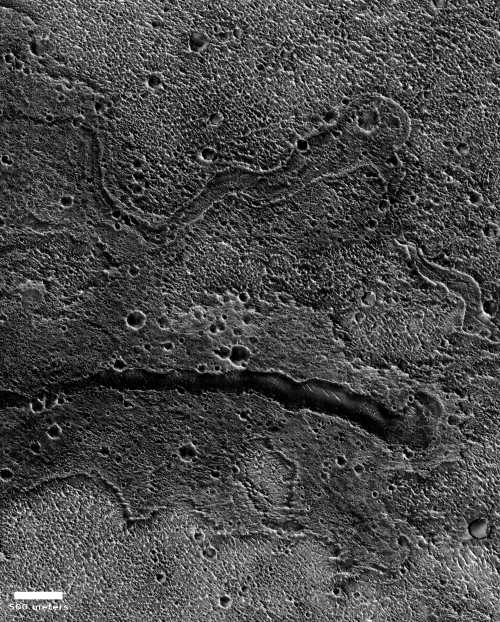
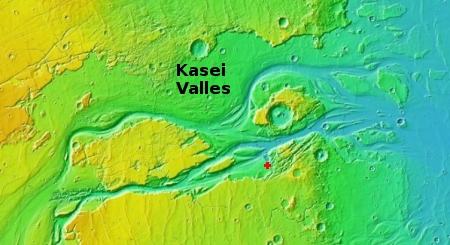
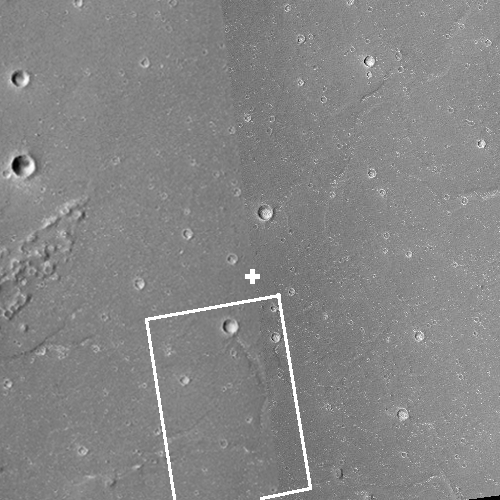
The mosaic on the right, made up of two images taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s (MRO) context camera (found here and here) shows this location with the white cross. The white box is the area covered by the only image taken of this area by MRO’s high resolution camera.
As these photos show, this location, in a part of Mars’ northern lowland plains dubbed Utopia Planitia, is generally smooth and flat, making for a relatively safe landing site. At the same time, it has craters and some ridges and hills that could pose issues.
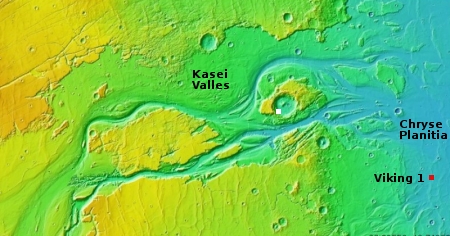
That the coordinates were removed from the Chinese press story suggests that this might be the prime site, but until Tianwen-1 gets into Mars orbit and begins scouting the site with its own high resolution images, they want to reserve judgement. The spacecraft arrives in orbit in February ’21, and they presently plan to land the rover in May. That gives them three months to scout this location as well as a secondary landing site on the other side of Mars, in the Chryse Planitia northern lowlands [pdf], the same region where Viking 1 and Mars Pathfinder landed.
Once they have done this they will be able to refine the location more precisely.

According to this Space News article, a report in the Chinese press, since revised to remove the information, had provided precise coordinates on Mars for the prime candidate landing site for China’s Tianwen-1 rover.
[I]nformation published in an article (in Chinese) in the official China Space News publication following launch in July provides a specific primary landing site. The article reported landing coordinates of 110.318 degrees east longitude and 24.748 degrees north latitude, within the southern portion of Utopia Planitia. Online versions of the article have since been edited to remove the coordinates; however, these remain published by sources citing the article.
The mosaic on the right, made up of two images taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s (MRO) context camera (found here and here) shows this location with the white cross. The white box is the area covered by the only image taken of this area by MRO’s high resolution camera.
As these photos show, this location, in a part of Mars’ northern lowland plains dubbed Utopia Planitia, is generally smooth and flat, making for a relatively safe landing site. At the same time, it has craters and some ridges and hills that could pose issues.
That the coordinates were removed from the Chinese press story suggests that this might be the prime site, but until Tianwen-1 gets into Mars orbit and begins scouting the site with its own high resolution images, they want to reserve judgement. The spacecraft arrives in orbit in February ’21, and they presently plan to land the rover in May. That gives them three months to scout this location as well as a secondary landing site on the other side of Mars, in the Chryse Planitia northern lowlands [pdf], the same region where Viking 1 and Mars Pathfinder landed.
Once they have done this they will be able to refine the location more precisely.