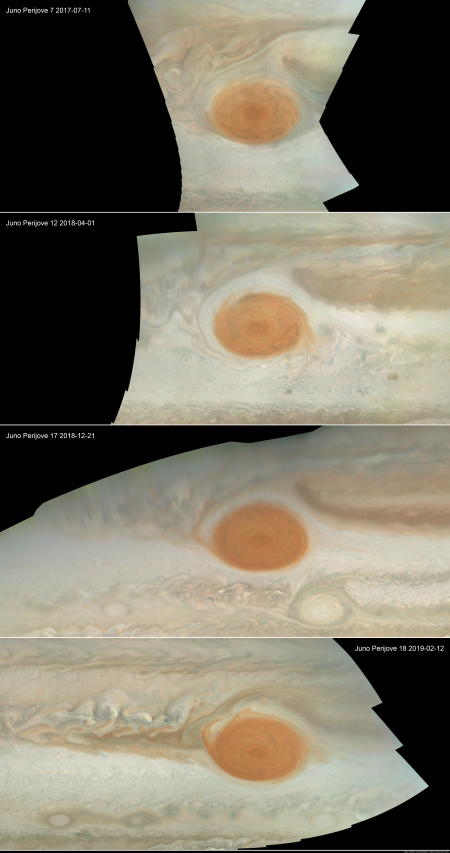
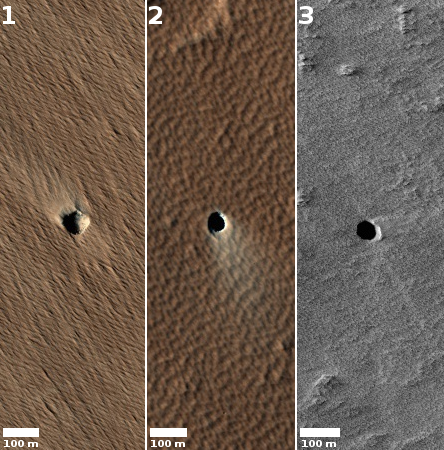
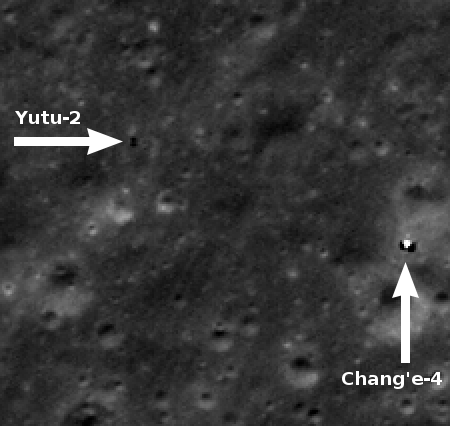
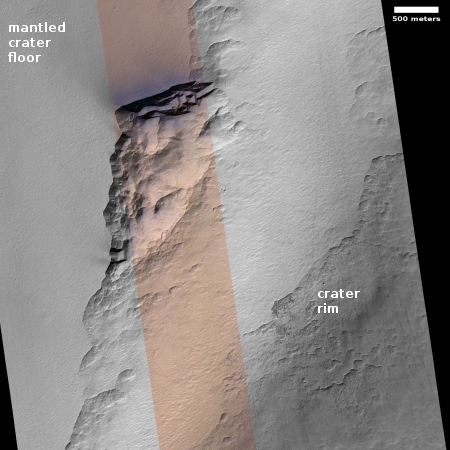
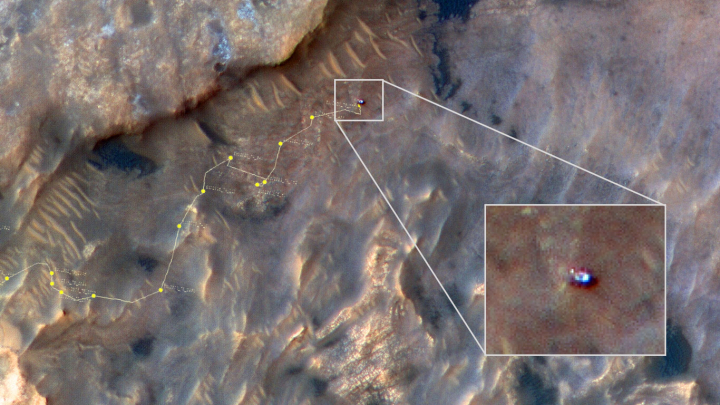
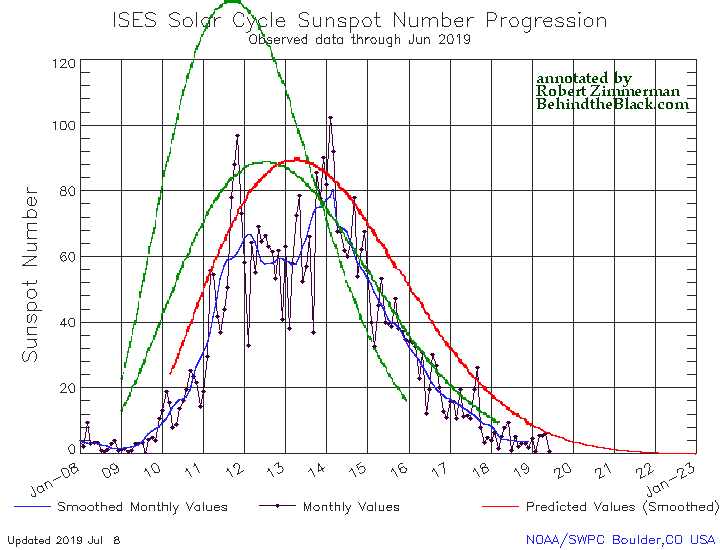
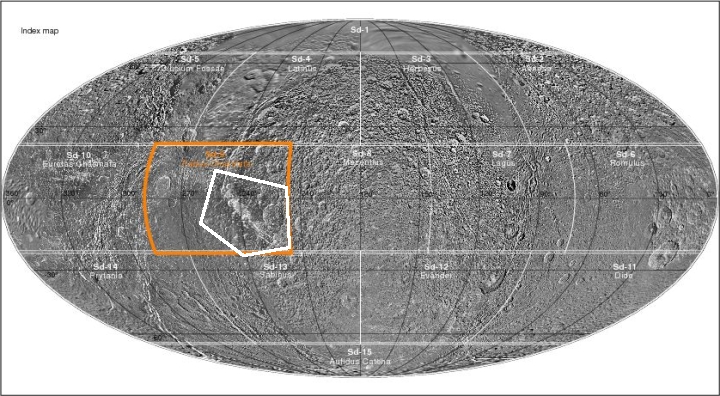
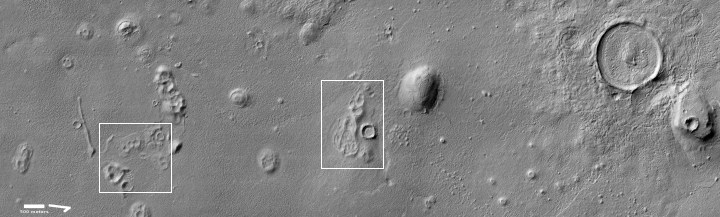
Hayabusa-2: Carbon-rich asteroids too delicate to reach Earth surface
New data from Hayabusa-2 has confirmed the long-held suspicions of astronomers that the reason they find so few fragments of C-class asteroids, such as Ryugu, on Earth is because they are too delicate to reach the Earth’s surface.
Ryugu and other asteroids of the common ‘C-class’ [chondritic] consist of more porous material than was previously thought. Small fragments of their material are therefore too fragile to survive entry into the atmosphere in the event of a collision with Earth.
…Until now, only a few chondritic meteorites found on Earth have been identified as fragments of C-type asteroids, which are very common in the Solar System (‘C’ is the chemical symbol for the element carbon). …”We can now confirm that fragments of these asteroids are very likely to break up further when they enter Earth’s atmosphere, and then usually burn up completely. This means that only the largest fragments reach the Earth’s surface,” explains Grott. “That is why meteorites from this type of asteroid are so rarely found on Earth.”
The good news is that, because of this, Earth’s atmosphere offers increased protection from C-type asteroids, which account for 75 percent of all asteroids. …However, further research is necessary to determine the maximum asteroid size for which this atmospheric protection is effective.
It is likely that even the largest rubble-pile C-asteroids will not pose much risk. Even if some pieces reach the Earth’s surface they are probably going to be small and unable to do much harm.
New data from Hayabusa-2 has confirmed the long-held suspicions of astronomers that the reason they find so few fragments of C-class asteroids, such as Ryugu, on Earth is because they are too delicate to reach the Earth’s surface.
Ryugu and other asteroids of the common ‘C-class’ [chondritic] consist of more porous material than was previously thought. Small fragments of their material are therefore too fragile to survive entry into the atmosphere in the event of a collision with Earth.
…Until now, only a few chondritic meteorites found on Earth have been identified as fragments of C-type asteroids, which are very common in the Solar System (‘C’ is the chemical symbol for the element carbon). …”We can now confirm that fragments of these asteroids are very likely to break up further when they enter Earth’s atmosphere, and then usually burn up completely. This means that only the largest fragments reach the Earth’s surface,” explains Grott. “That is why meteorites from this type of asteroid are so rarely found on Earth.”
The good news is that, because of this, Earth’s atmosphere offers increased protection from C-type asteroids, which account for 75 percent of all asteroids. …However, further research is necessary to determine the maximum asteroid size for which this atmospheric protection is effective.
It is likely that even the largest rubble-pile C-asteroids will not pose much risk. Even if some pieces reach the Earth’s surface they are probably going to be small and unable to do much harm.