Zhurong continues south, inspecting dunes

The Chinese science team for their Zhurong Mars rover released new images yesterday, including a map showing the rover’s present position.
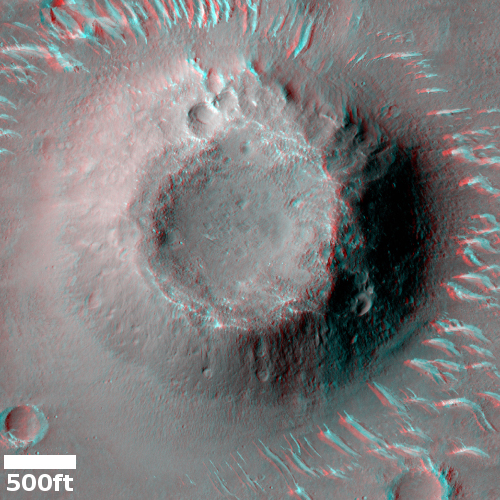
The new images and location has confirmed that the white streaks seen in orbital pictures are small dunes of sand blown by the thin Martian wind.
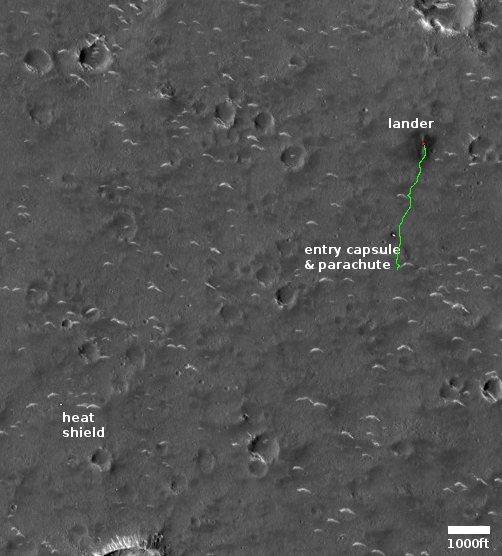
The map to the right, created using their map but annotated and providing a wider context, shows their present location relative to the lander and surrounding terrain. So far the rover has traveled about 1,900 feet, about 1,000 feet per month. Since it seems to be operating as planned, I expect China will extend the mission once it completes its nominal three-month tour in about two weeks.
At that travel pace there is much of interest that is within the rover’s range. I expect they are heading south partly because this brings them closer to their original landing site, which is an area they probably studied at length before landing. Whether they head to the largest crater, visible only partly on the image’s south edge, remains unclear.

The Chinese science team for their Zhurong Mars rover released new images yesterday, including a map showing the rover’s present position.
The new images and location has confirmed that the white streaks seen in orbital pictures are small dunes of sand blown by the thin Martian wind.
The map to the right, created using their map but annotated and providing a wider context, shows their present location relative to the lander and surrounding terrain. So far the rover has traveled about 1,900 feet, about 1,000 feet per month. Since it seems to be operating as planned, I expect China will extend the mission once it completes its nominal three-month tour in about two weeks.
At that travel pace there is much of interest that is within the rover’s range. I expect they are heading south partly because this brings them closer to their original landing site, which is an area they probably studied at length before landing. Whether they head to the largest crater, visible only partly on the image’s south edge, remains unclear.