The wavy and beautiful edge of the northern ice cap of Mars
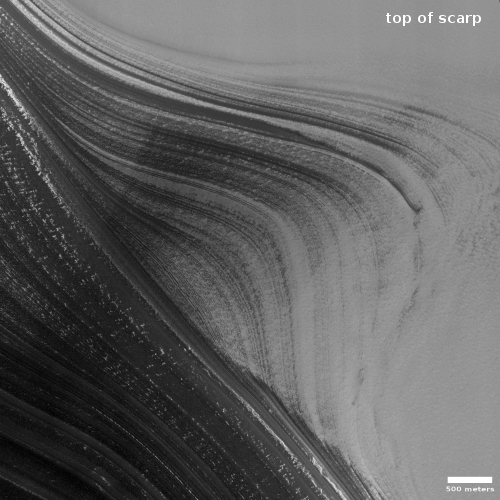
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on August 7, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows the many layered scarp that forms the edge of the northern polar ice cap on Mars, probably more than 2,000 feet high.
Those layers are significant, as they indicate the many climate cycles that scientists think Mars has undergone over the eons as the red planet’s rotational tilt, or obliquity, rocked back and forth from 11 degrees inclination to as much as 60 degrees. At the extremes, the ice cap was either growing or shrinking, while today (at 25 degrees inclination) it appears to be in a steady state.
Why the layers alternate light and dark is not known. The shift from lighter colors at the top half and the dark bottom half marks the separation between the top water ice cap and what scientists label the basal unit. It also marks some major change in Mars’ climate and geology that occurred about 4.5 million years ago.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on August 7, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows the many layered scarp that forms the edge of the northern polar ice cap on Mars, probably more than 2,000 feet high.
Those layers are significant, as they indicate the many climate cycles that scientists think Mars has undergone over the eons as the red planet’s rotational tilt, or obliquity, rocked back and forth from 11 degrees inclination to as much as 60 degrees. At the extremes, the ice cap was either growing or shrinking, while today (at 25 degrees inclination) it appears to be in a steady state.
Why the layers alternate light and dark is not known. The shift from lighter colors at the top half and the dark bottom half marks the separation between the top water ice cap and what scientists label the basal unit. It also marks some major change in Mars’ climate and geology that occurred about 4.5 million years ago.
» Read more