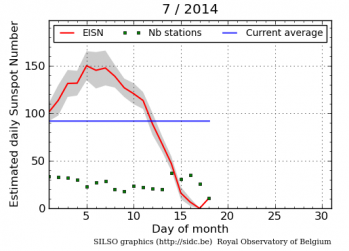
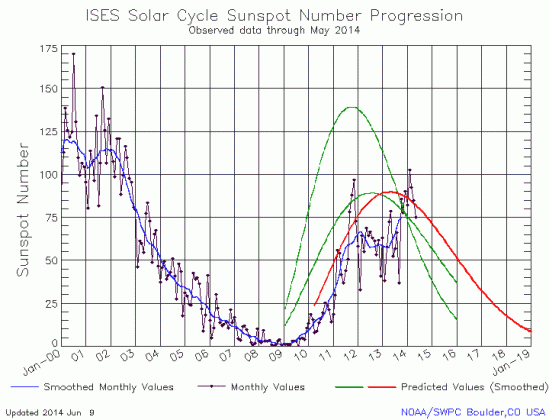
Today NOAA posted its monthly update of the solar cycle, and as I do every month, I am posting it here, with annotations.
Before we take a look at that, however, there is other climate news that is apropos. The Daily Mail in the UK put out an entertaining article on Saturday with the headline “And now it’s global COOLING! Record return of Arctic ice cap as it grows by 60% in a year.”
The article is entertaining because, after illustrating the ice-cap’s recovery this year, it then notes the 2007 prediction by global warming climate scientists that the Arctic Ocean would be “ice-free” by 2013. If this isn’t a good example of the dangers of crying wolf, I don’t know what is.
I should emphasize that the ice-cap recovery this year does not prove that global warming has ceased. A look at this graph from satellite data shows that even though the Arctic icecap has recovered, it is still remains small when compared to the past few decades. The increase this year might only be a blip, or it could be indicating a new trend. We won’t really know for another five years, if then.
The article is also entertaining because it outlines the confusion that is right now going on behind the scenes at the IPCC. The next IPCC report is scheduled to come out next month, but no one agrees with its conclusions because it apparently ignores or minimizes the approximately fifteen year pause in warming that has now been documented since the late-1990s.
In its draft report, the IPCC says it is ‘95 per cent confident’ that global warming has been caused by humans – up from 90 per cent in 2007. This claim is already hotly disputed. US climate expert Professor Judith Curry said last night: ‘In fact, the uncertainty is getting bigger. It’s now clear the models are way too sensitive to carbon dioxide. I cannot see any basis for the IPCC increasing its confidence level.’ [emphasis mine]
It appears that scientists and governments are demanding approximately 1500 changes to the IPCC draft, which suggests its release will be delayed significantly.
Meanwhile, the Sun continues its lackluster and weak solar maximum.
» Read more