InSight has buried its Mole

Using the scoop on InSight’s robot arm, engineers have now successfully filled the large hole that had formed around the spacecraft’s mole, the drill that has been trying but failing to dig down about fifteen feet so that a heat sensor could measure the internal temperature of Mars.
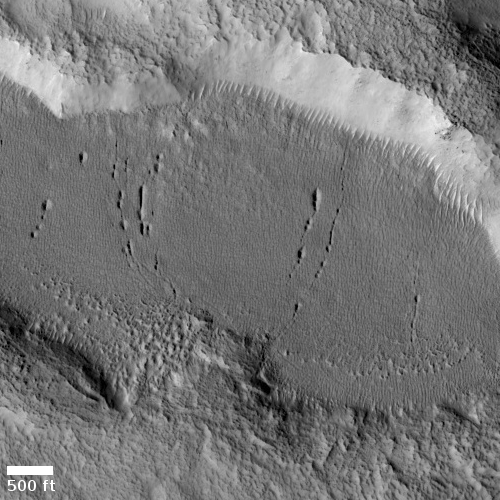
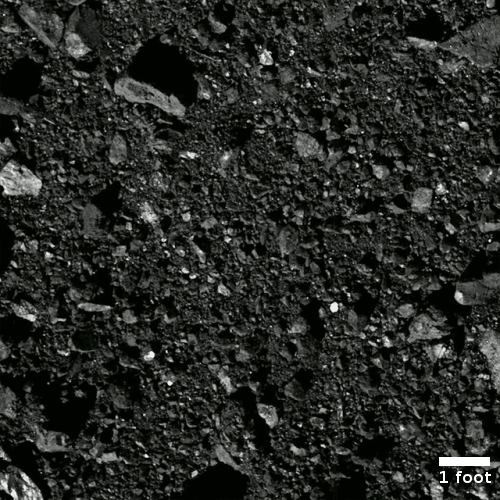
The image to the right shows the filled hole with the mole’s communications tether snaking away. Earlier this month they used InSight’s scoop to scrape surface material into the hole, as planned in June. According to the mole’s principle investigate, Tilman Spohn,
I had estimated that the first scrape of 12 centimetres swath length would raise the bottom of the pit but leave the Mole sticking out of the sand. By the way, this was the condition for some to agree to the quite controversial ‘scratch test’. As one can see in the image from Sol 600 shown below, that estimate was not quite right. The scraping was a complete success! The scrape was much more effective than expected and the sand filled the pit almost completely. The Mole is now covered, but there is only a thin layer of sand on the back cap.
Their next step will be to use the scoop to press down on the dirt of the filled hole, with the hope this added pressure will keep the dirt pressed against the mole as it hammers downward, thus holding it place with each downward stroke.

Using the scoop on InSight’s robot arm, engineers have now successfully filled the large hole that had formed around the spacecraft’s mole, the drill that has been trying but failing to dig down about fifteen feet so that a heat sensor could measure the internal temperature of Mars.
The image to the right shows the filled hole with the mole’s communications tether snaking away. Earlier this month they used InSight’s scoop to scrape surface material into the hole, as planned in June. According to the mole’s principle investigate, Tilman Spohn,
I had estimated that the first scrape of 12 centimetres swath length would raise the bottom of the pit but leave the Mole sticking out of the sand. By the way, this was the condition for some to agree to the quite controversial ‘scratch test’. As one can see in the image from Sol 600 shown below, that estimate was not quite right. The scraping was a complete success! The scrape was much more effective than expected and the sand filled the pit almost completely. The Mole is now covered, but there is only a thin layer of sand on the back cap.
Their next step will be to use the scoop to press down on the dirt of the filled hole, with the hope this added pressure will keep the dirt pressed against the mole as it hammers downward, thus holding it place with each downward stroke.