Starship #15 launches AND lands successfully


Capitalism in space: On the 60th anniversary of Alan Shepard’s suborbital flight, making him the first American to fly in space, SpaceX has successfully launched and landed its fifteenth Starship prototype.
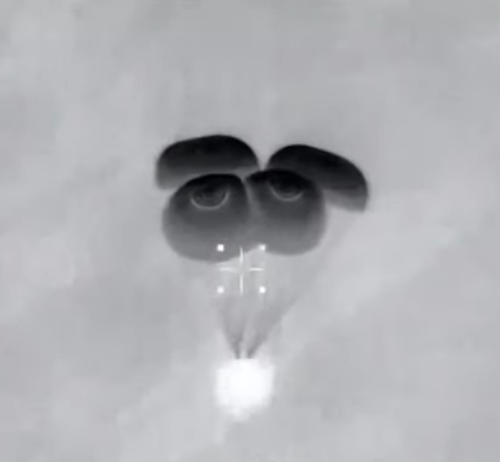
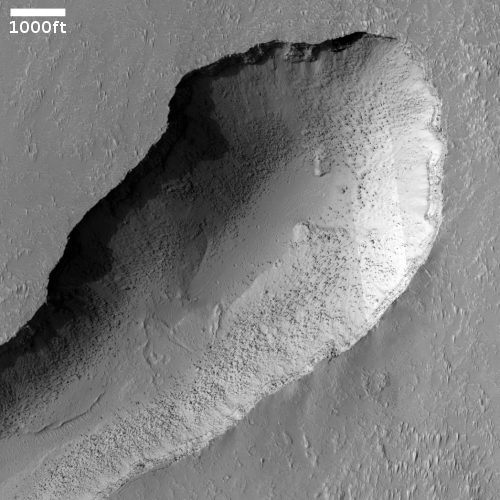
The flight appeared remarkably smooth, except for the cameras on board which dropped out for much of the flight. The first image shows the rocket coming down just before touch down. At this moment it was dropping very smoothly, and landed very gently on the landing pad.
The second image was taken about thirty seconds after landing. There was a fire at the rocket’s base being extinguished by the water fire control system. Other than that, the rocket appears whole and undamaged.
As I write this, it is about ten minutes after landing, the fires at the rocket’s base have been put out, and all seems under control. I expect that SpaceX engineers will finally have a fully intact prototype that they can inspect for future design revisions. For example, the skin of this prototype has many thermal tiles attached. They can now see if their attachment system works.
I have embedded the 16 minute live stream of the flight below the fold. Enjoy!
» Read more