Glacial features in a Mars crater at 29 degrees south latitude?
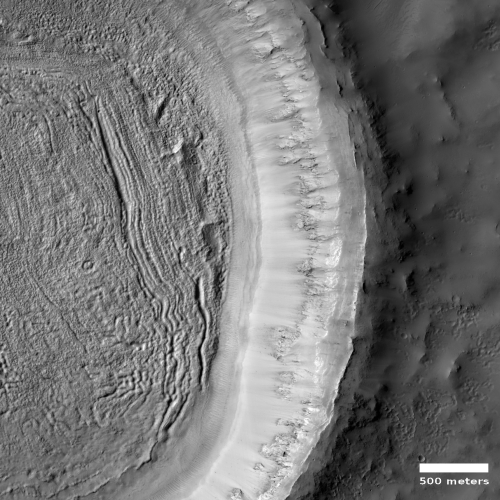
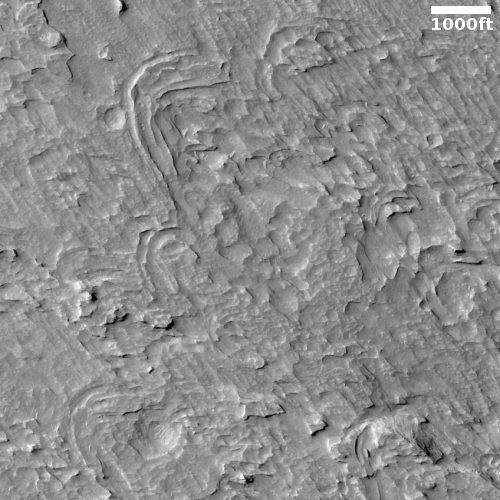
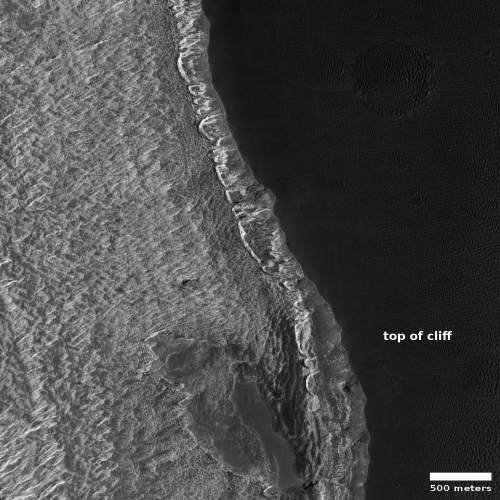
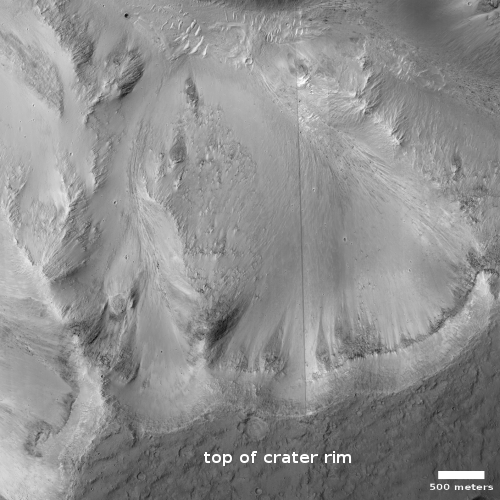
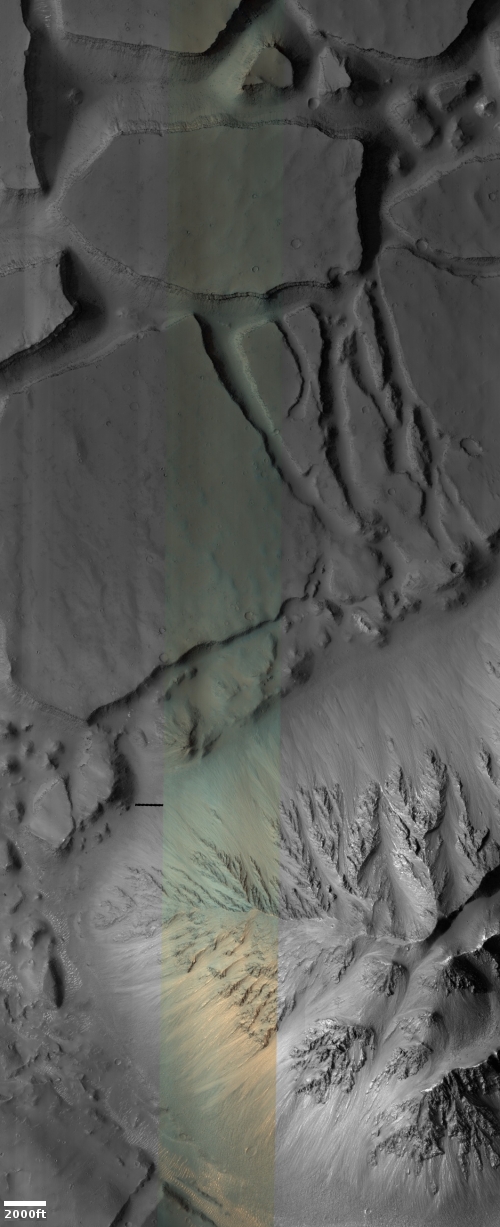
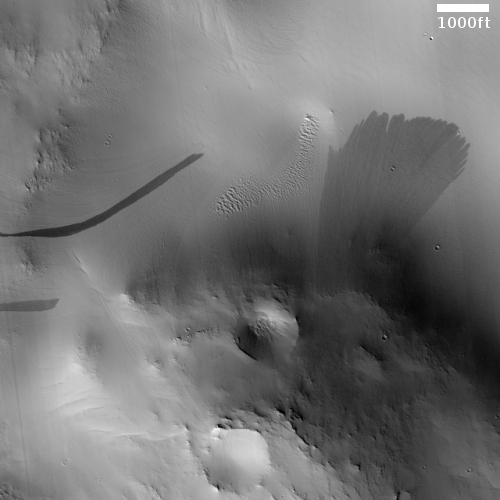
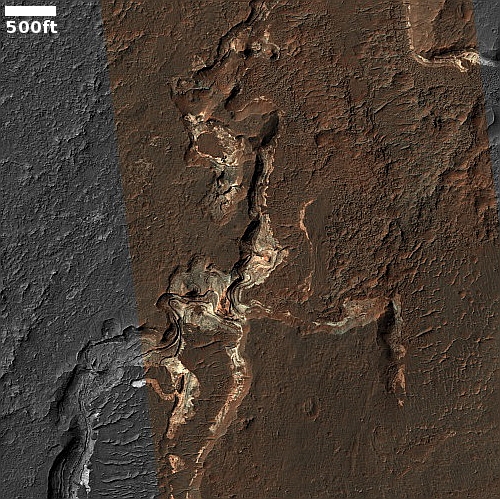
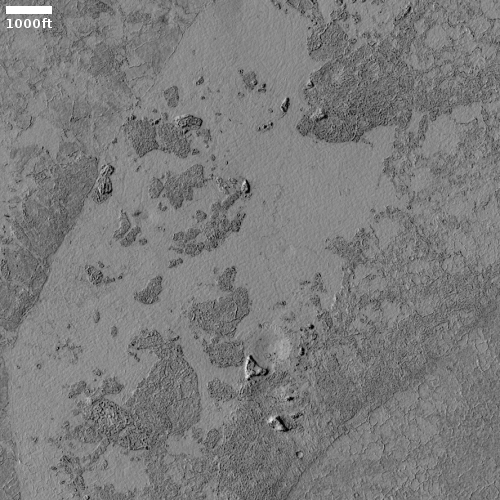
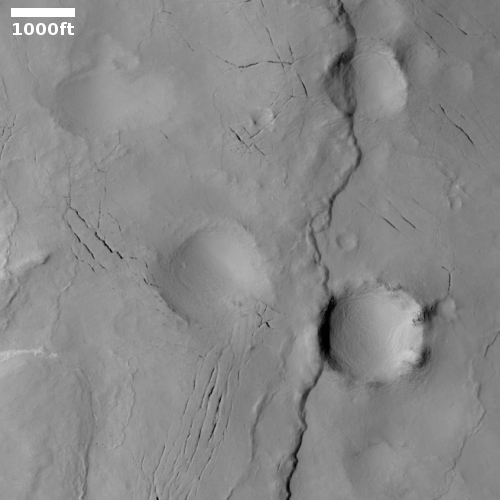
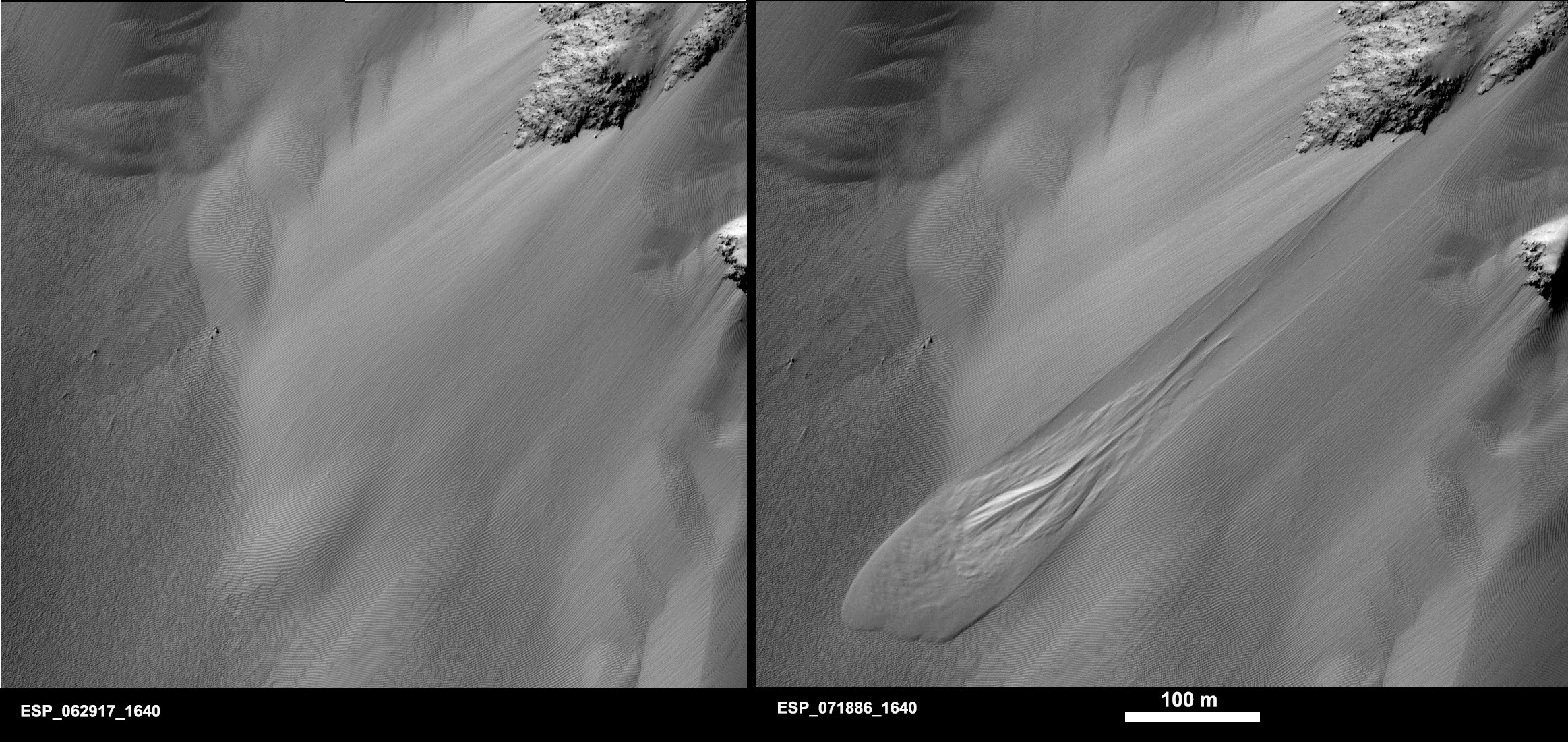
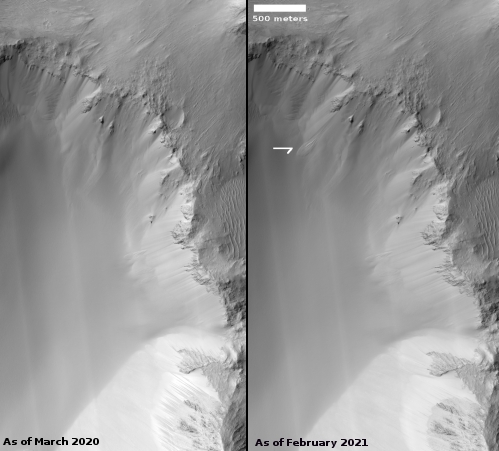
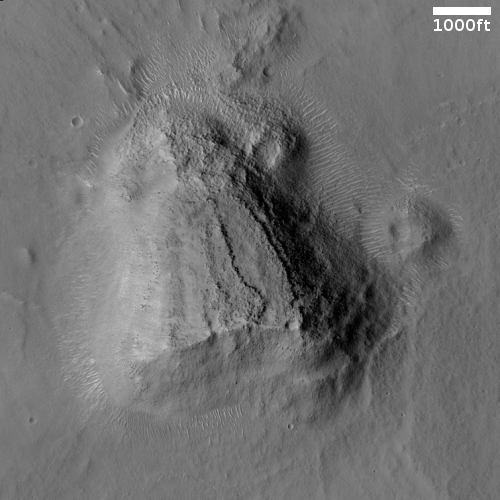
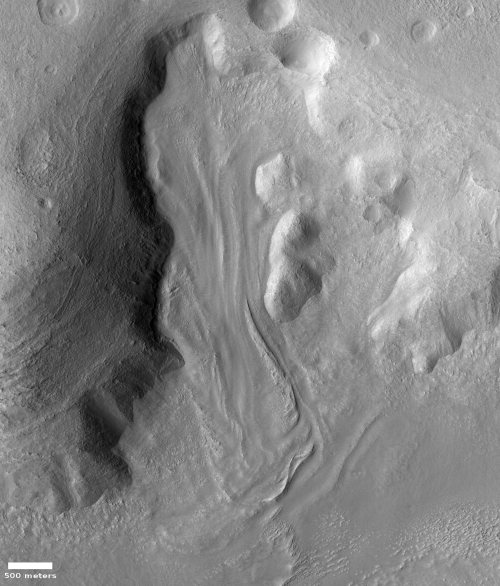
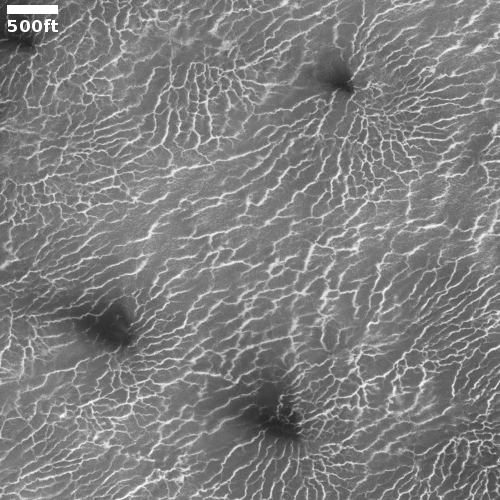
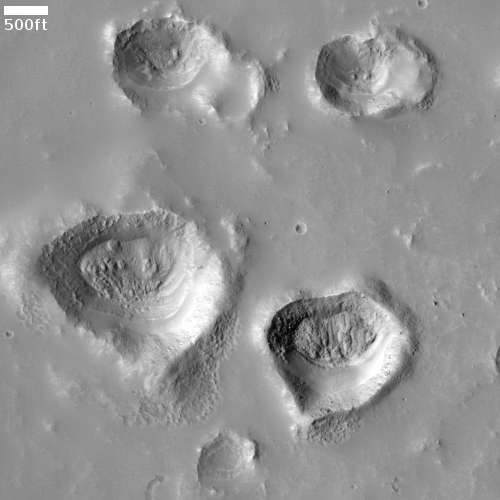
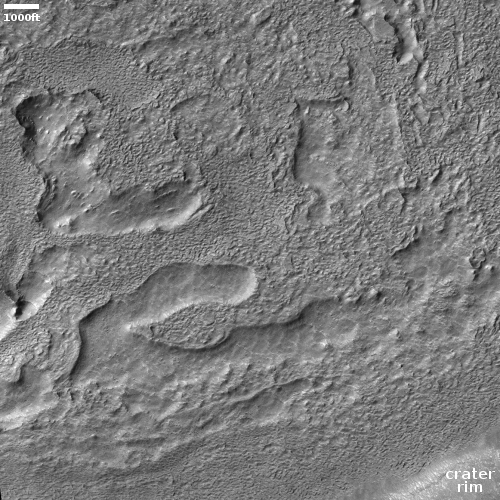
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on January 2, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Simply labeled “slope features,” it was likely taken to monitor the gullies and streaks on the interior walls of this 4-mile-wide crater. Scientists have been using MRO to track the coming and going of frost on this crater’s interior walls since 2016.
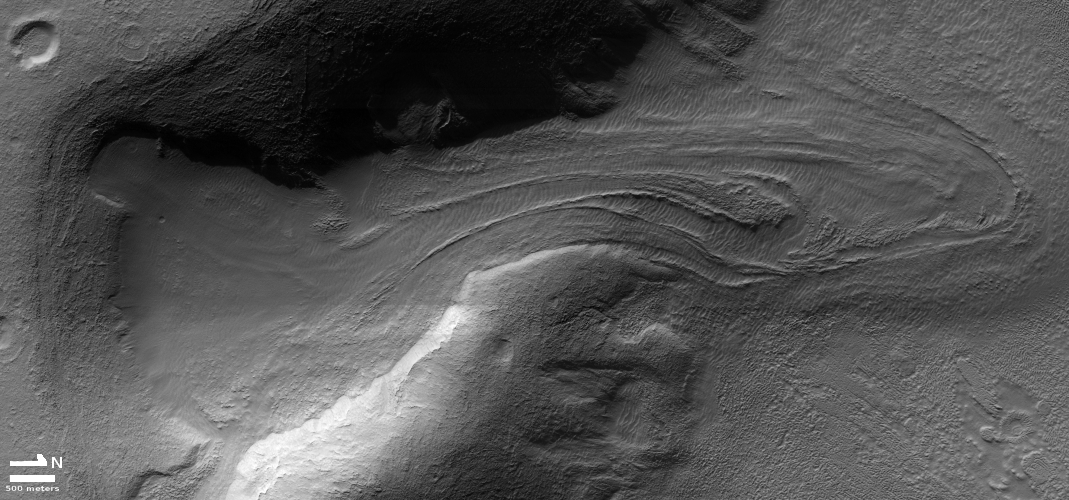
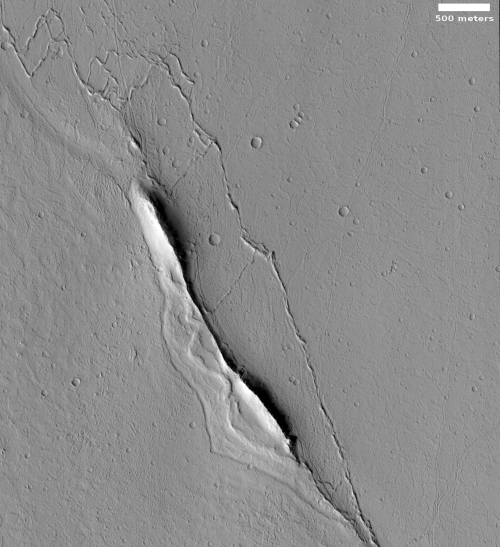
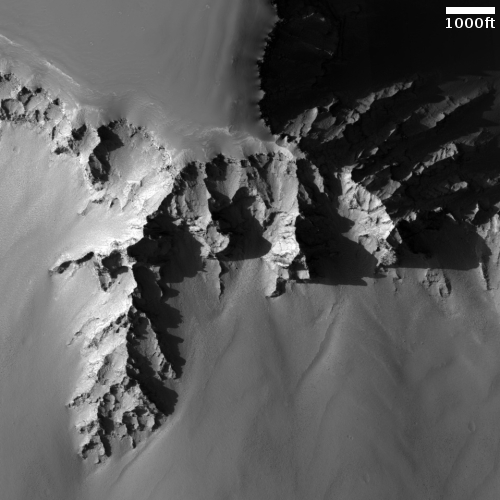
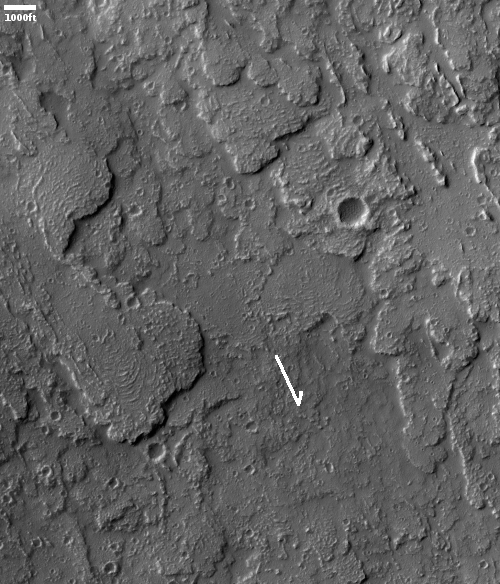
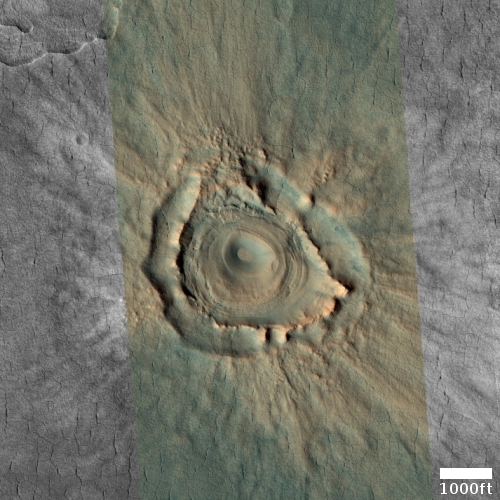
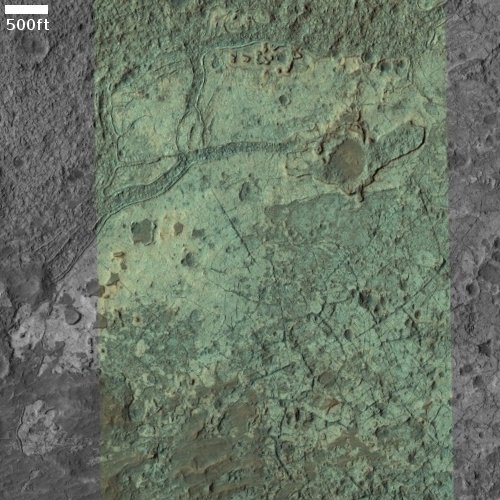
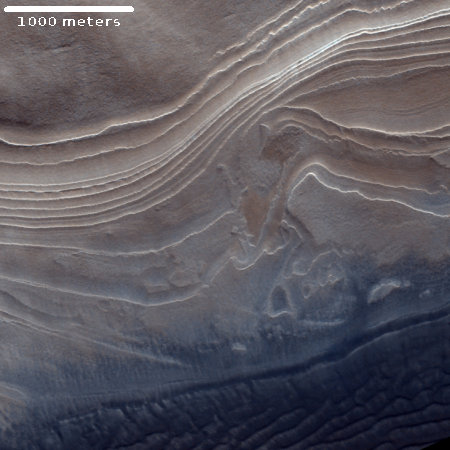
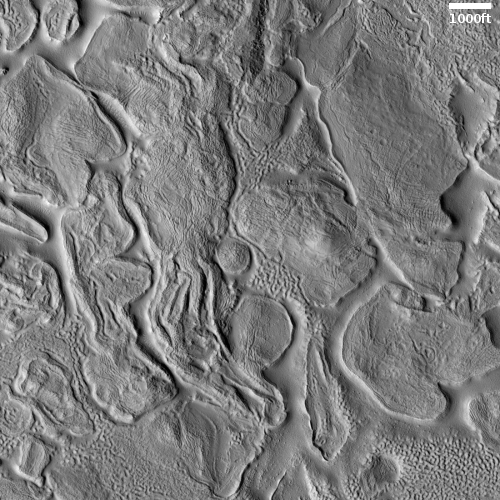
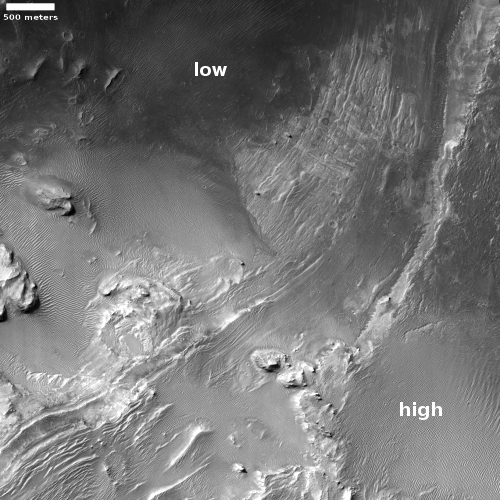
Equally intriguing however are what appear to be squashed layers within the crater’s interior. These appear to be some form of glacial feature created by repeated climate cycles, similar to the glacial features routinely seen throughout the 30 to 60 degree mid-latitude strips north and south.
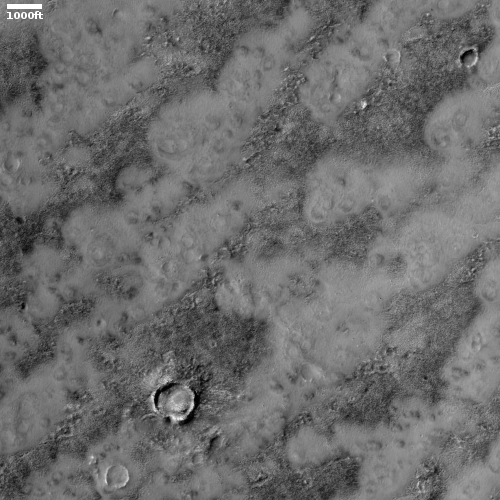
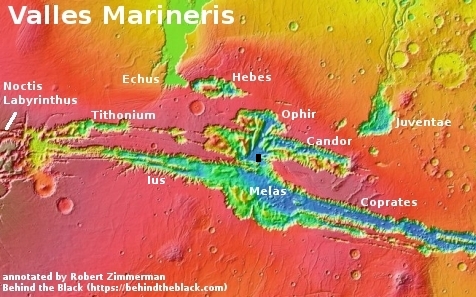
What makes the glacial features in this particular crater particularly intriguing is its location, as shown in the overview map below.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on January 2, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Simply labeled “slope features,” it was likely taken to monitor the gullies and streaks on the interior walls of this 4-mile-wide crater. Scientists have been using MRO to track the coming and going of frost on this crater’s interior walls since 2016.
Equally intriguing however are what appear to be squashed layers within the crater’s interior. These appear to be some form of glacial feature created by repeated climate cycles, similar to the glacial features routinely seen throughout the 30 to 60 degree mid-latitude strips north and south.
What makes the glacial features in this particular crater particularly intriguing is its location, as shown in the overview map below.
» Read more