The strange surface of Mars’ north pole icecap
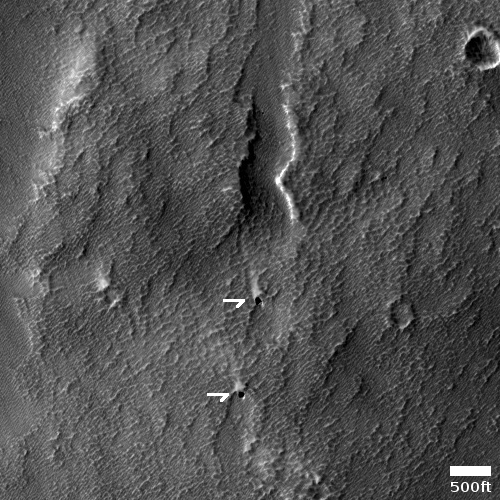
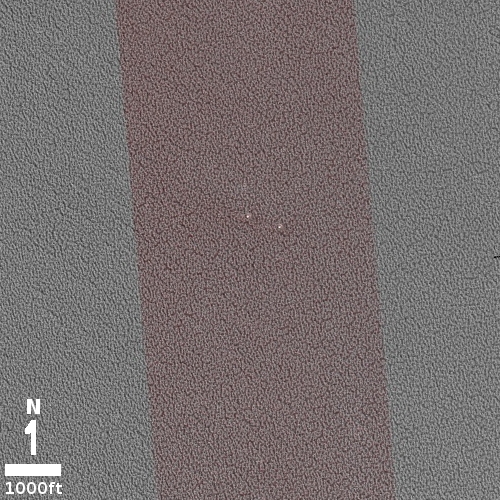
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and annotated to post here, was taken on September 17, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows us a very small section of Mars’ north pole icecap.
What are we looking at? The picture was taken in summer, so by this point the thin mantle of dry ice that falls as snow in the winter and covers the north pole down to about 60 degrees latitude has sublimated away. This surface thus is water ice interspersed with Martian dust.
Yet, unlike the Antarctic icecap on Earth, the ice surface is not smooth and flat. Instead, this Martian ice has a surface that is a complex arrangement of hollows and ridges, all about the same size. Why?
And what are the two larger white spots? What caused them and why are they the only differently-sized objects in the picture?
The full resolution close-up, found at the image website, provides some answers to these questions.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and annotated to post here, was taken on September 17, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows us a very small section of Mars’ north pole icecap.
What are we looking at? The picture was taken in summer, so by this point the thin mantle of dry ice that falls as snow in the winter and covers the north pole down to about 60 degrees latitude has sublimated away. This surface thus is water ice interspersed with Martian dust.
Yet, unlike the Antarctic icecap on Earth, the ice surface is not smooth and flat. Instead, this Martian ice has a surface that is a complex arrangement of hollows and ridges, all about the same size. Why?
And what are the two larger white spots? What caused them and why are they the only differently-sized objects in the picture?
The full resolution close-up, found at the image website, provides some answers to these questions.
» Read more