No plans to shoot down Long March 5B booster; revised prediction
The Biden administration will make no attempt to shoot down the 21-ton core stage of China’s Long March 5B rocket, according to the Defense secretary Lloyd Austin:
At this point we don’t have a plan to shoot the rocket down. We’re hopeful it will land in a place where it won’t harm anyone. Hopefully in the ocean or someplace like that. I think this speaks to the fact that for those of us who operate in the space domain that there should be a requirement to operate in a safe and thoughtful mode and make sure that we take those kinds of things into consideration as we plan and conduct operations.
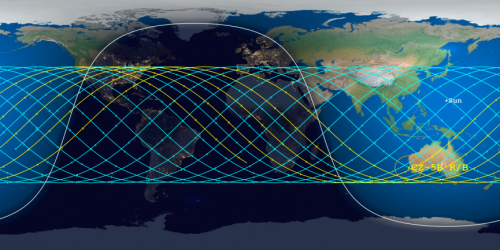
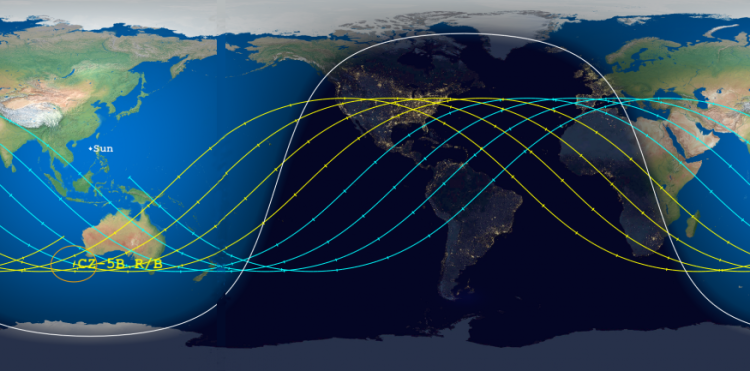
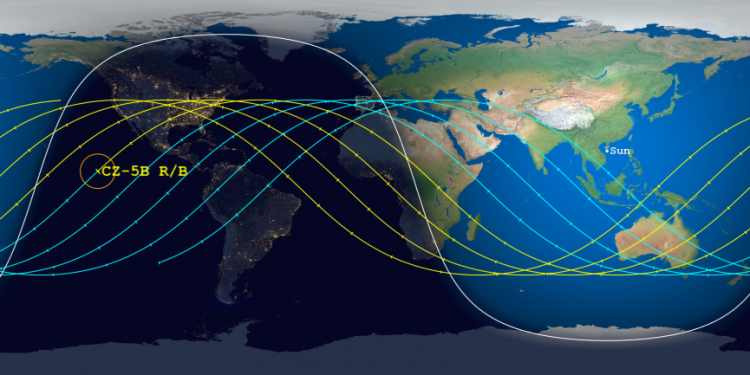
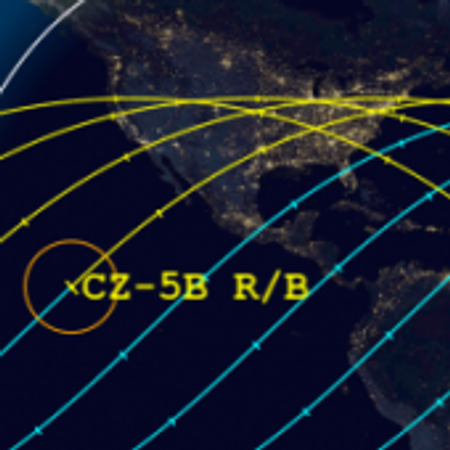
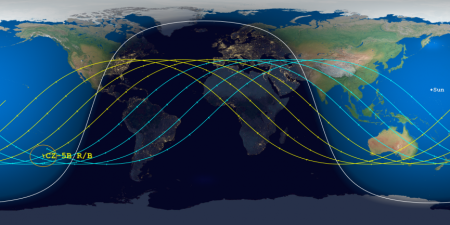
Meanwhile, the predicted reentry window has shrunk again, to 16 hours, and shifted so that its centerpoint is now over Egypt, as shown on this map by the Aerospace Corporation:
» Read more
The Biden administration will make no attempt to shoot down the 21-ton core stage of China’s Long March 5B rocket, according to the Defense secretary Lloyd Austin:
At this point we don’t have a plan to shoot the rocket down. We’re hopeful it will land in a place where it won’t harm anyone. Hopefully in the ocean or someplace like that. I think this speaks to the fact that for those of us who operate in the space domain that there should be a requirement to operate in a safe and thoughtful mode and make sure that we take those kinds of things into consideration as we plan and conduct operations.
Meanwhile, the predicted reentry window has shrunk again, to 16 hours, and shifted so that its centerpoint is now over Egypt, as shown on this map by the Aerospace Corporation:
» Read more