Ice under Mars’ biggest volcanic ash field, at the equator?
According to new data obtained from the radar instruments on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and Mars Express, scientists now think that the Medusae Fossae Formation, Mars’ biggest volcanic ash field and thought by some to be the source of most of the planet’s dust, might have an underground layer of ash that is also ice-rich. From their abstract:
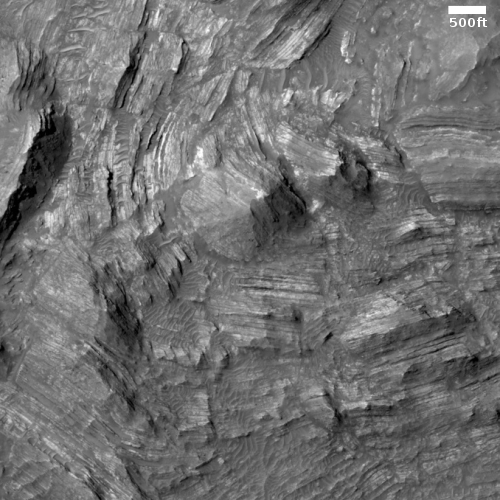
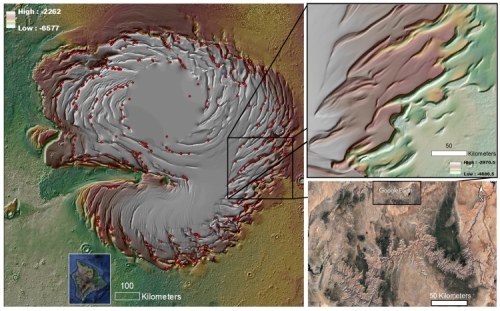
The Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF) on Mars covers a vast area along the boundary between the rugged southern highlands and the smooth northern plains. While the MFF appears to be thick sediments or volcanic ash slowly eroding in the martian winds, how this material was emplaced remains mysterious. Most intriguing is evidence suggesting that some areas of the MFF may contain water ice. In this work we use sounding radar data from the SHARAD instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to probe up to 600 m below the surface and measure the electrical properties of the MFF material. The results suggest that the shallow parts of the MFF deposits are very porous and compress readily under their own weight. To match deeper probing by the Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding instrument on Mars Express requires a second layer of either vast porous deposits or ice‐rich material protected from sublimation by the dry sediments.
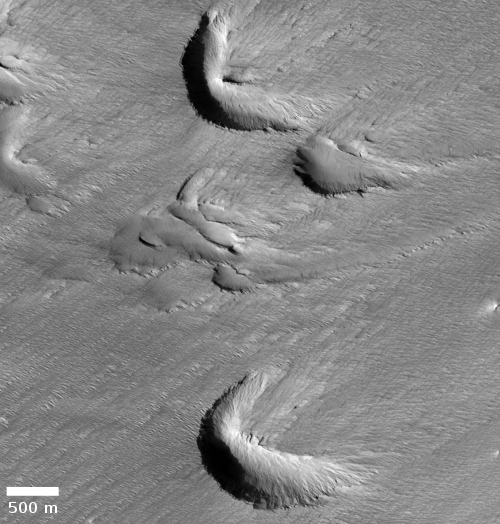
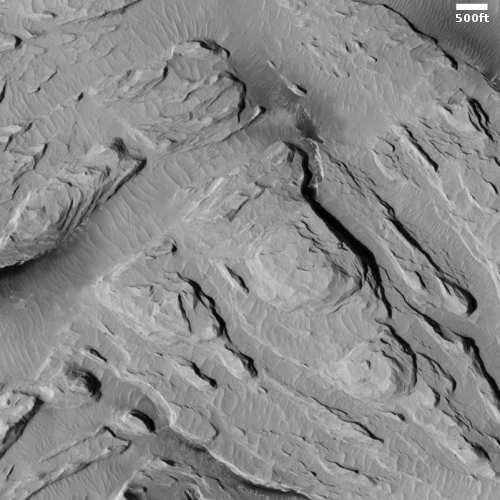
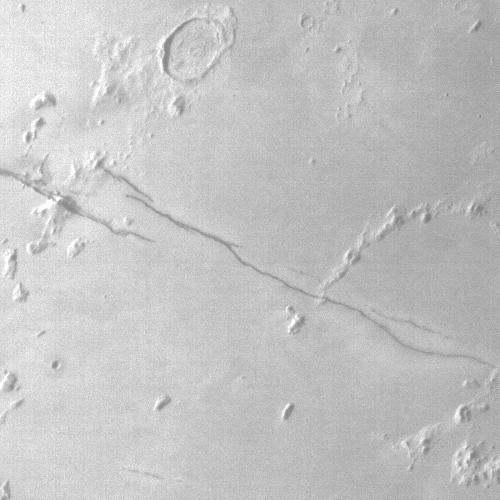
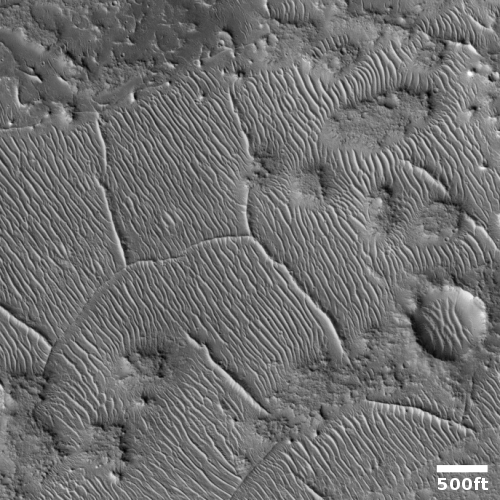
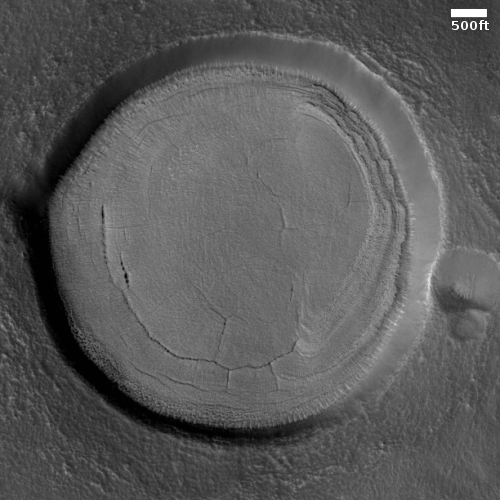
The MRO image above, originally posted here in November 2020, shows one example of the typical wind erosion found in the Medusae ash field. Apparently the ground-penetrating radar from orbit now suggests the possibility that there is an ash layer rich in ice, at depths beginning somewhere between 1,000 to 2,000 feet below the surface.
» Read more
According to new data obtained from the radar instruments on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and Mars Express, scientists now think that the Medusae Fossae Formation, Mars’ biggest volcanic ash field and thought by some to be the source of most of the planet’s dust, might have an underground layer of ash that is also ice-rich. From their abstract:
The Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF) on Mars covers a vast area along the boundary between the rugged southern highlands and the smooth northern plains. While the MFF appears to be thick sediments or volcanic ash slowly eroding in the martian winds, how this material was emplaced remains mysterious. Most intriguing is evidence suggesting that some areas of the MFF may contain water ice. In this work we use sounding radar data from the SHARAD instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to probe up to 600 m below the surface and measure the electrical properties of the MFF material. The results suggest that the shallow parts of the MFF deposits are very porous and compress readily under their own weight. To match deeper probing by the Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding instrument on Mars Express requires a second layer of either vast porous deposits or ice‐rich material protected from sublimation by the dry sediments.
The MRO image above, originally posted here in November 2020, shows one example of the typical wind erosion found in the Medusae ash field. Apparently the ground-penetrating radar from orbit now suggests the possibility that there is an ash layer rich in ice, at depths beginning somewhere between 1,000 to 2,000 feet below the surface.
» Read more