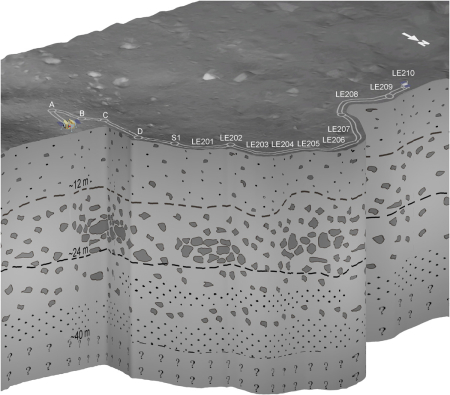
Click for full image.
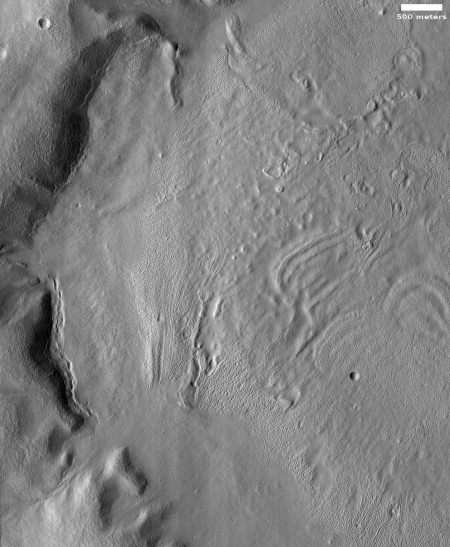
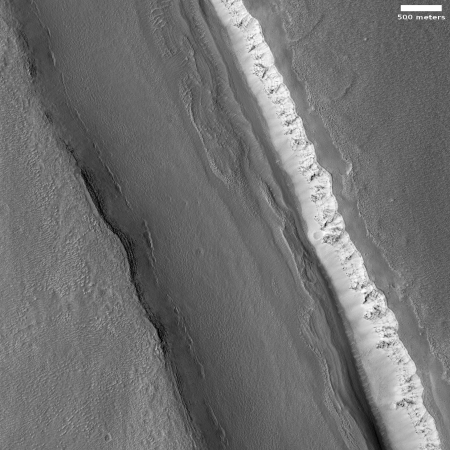
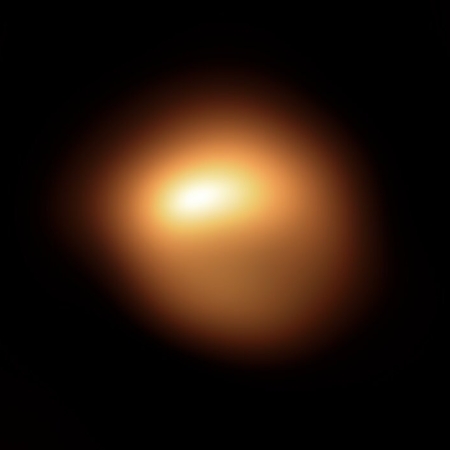
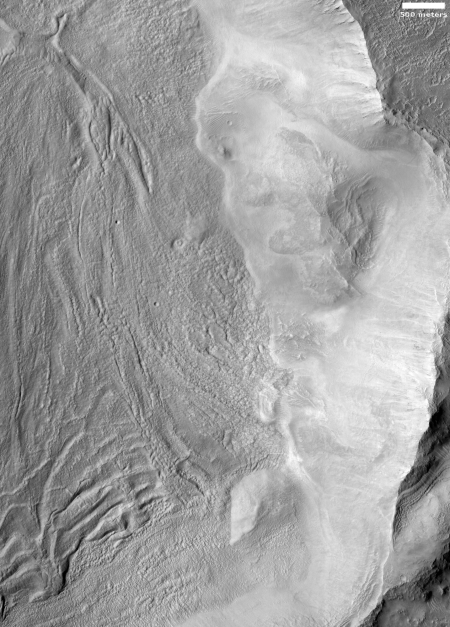
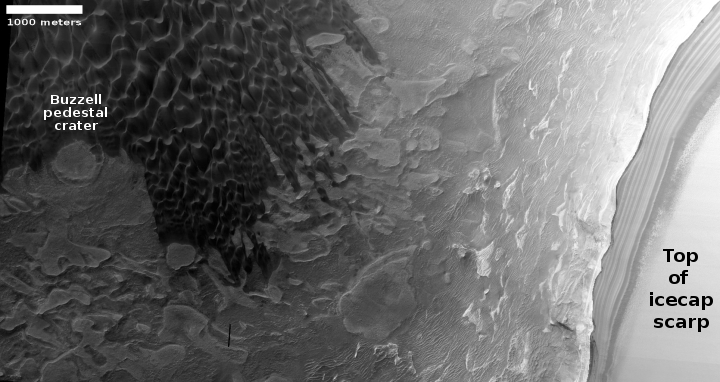
The image to the right, rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on December 19, 2019 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Labeled “Head of Mamers Valles”, it shows the very end of one side canyon to this very extensive canyon system made up of the fractured fissures and mesas of chaos terrain.
Mamers Valles itself sits in the transition zone between the northern lowland plains and the southern cratered highlands. This specific canyon is close to those lowlands, at a latitude of 40 degrees north, where scientists believe there are many buried inactive glaciers of ice.
The image reinforces this belief. The entire canyon appears practically filled with what looks like ice. In fact, it almost looks like we are looking down at a frozen lake with a layer of snow on top of it. In this case, the layer is not snow, but dust and dirt and debris that covers the ice to protect it and prevent it from sublimating away.
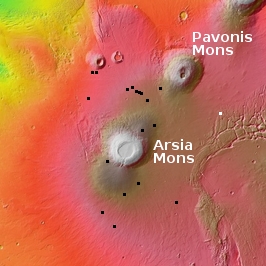
The overview map below shows the location of this canyon, by the red cross, within Mamers Valles.
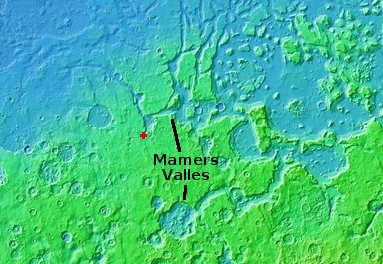
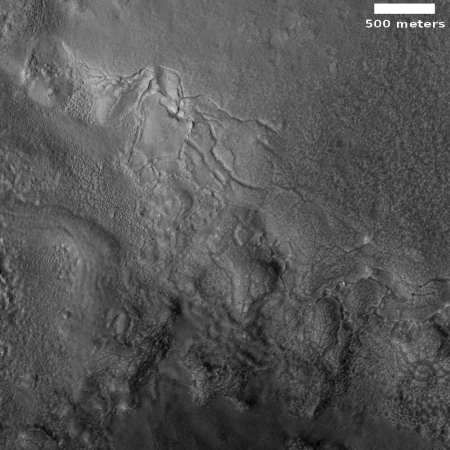
Mamers Valles is actually a very large collection of miscellaneous canyons, flowing into the lowlands. In some areas it looks like very old chaos terrain, with the canyons so eroded that all we see are scattered mesas. In other places the canyons more resemble meandering river canyons sometimes interspersed with crater impacts.
Scientists have analyzed the canyons in Mamers Valles, and from this concluded that they were likely formed from “subsurface hydrologic activity”. which in plain English means that flowing water below ground washed out large underground passages, which eventually grew large enough for their ceilings to collapse and form the canyons we see today.
Yesterday I posted an image of a string of pits that could very well be evidence of this same process in its early stages of canyon formation. In Mamers Valles the process is far more advanced, and the canyons have existed for a long time, long enough for the planet’s inclination to go through several cycles of change, from a low of 25 degrees tilt (what it is now) to has high as 60 degrees. At that high inclination the mid-latitudes were colder than the poles, so that ice would sublimate from the poles to fall as snow in the mid-latitudes, forming active glaciers within canyons such as this.
Now that the planet’s inclination is similar to Earth’s, 25 degrees, the poles are slightly colder than the mid-latitudes, and the glaciers in this canyon are either inactive (if buried) or slowly sublimating away so that the water can return to the poles.
Here however the surface debris appears to be protecting the glaciers, leaving the canyon filled mostly with ice. For future settlers this ice would likely be relatively accessible, and at a latitude where the environment is also relatively mild, for Mars.