A river of lava on Mars as long as the Columbia
I’ve said it before and I’ll say it again. Mars is strange, Mars is wonderful, but above all, Mars is alien. Today’s cool image illustrates this saying quite nicely.
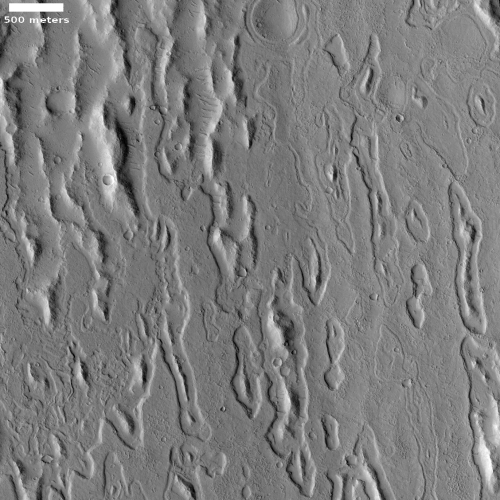
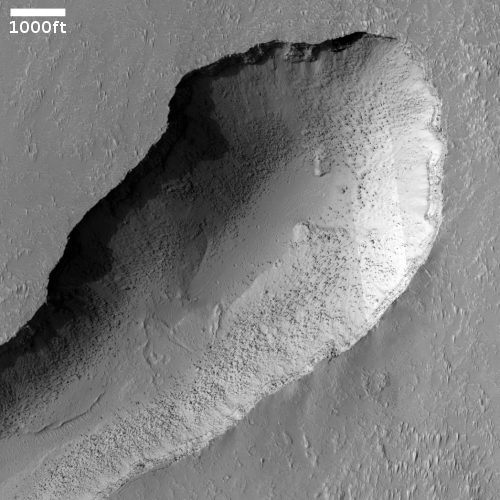
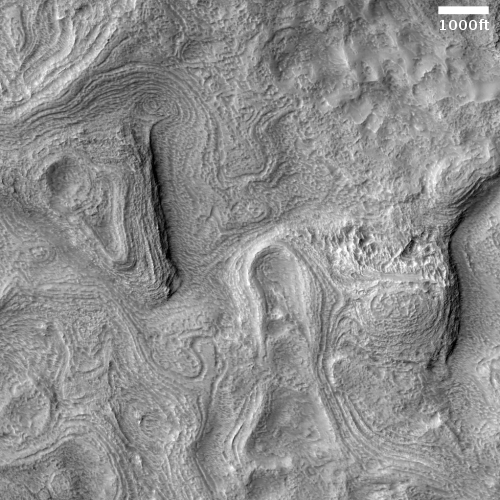
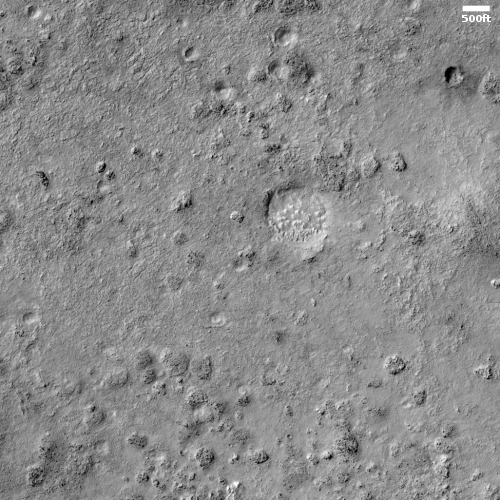
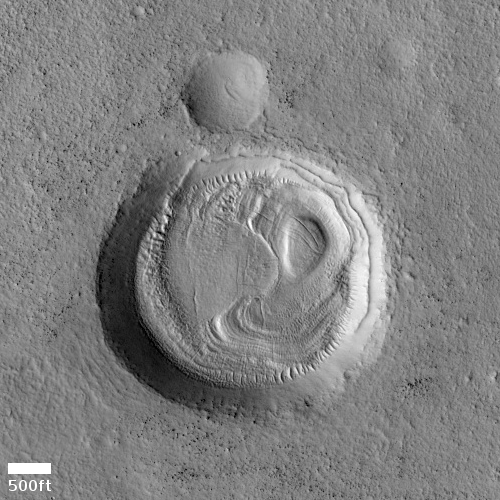
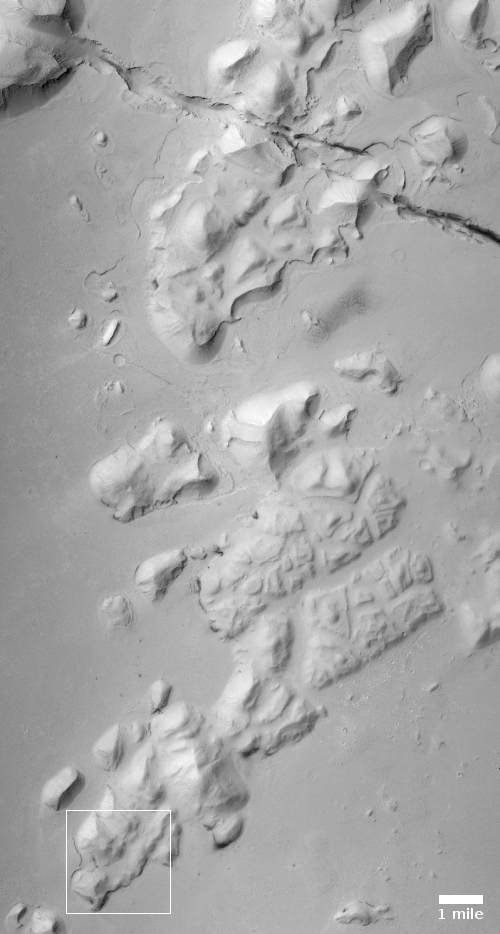
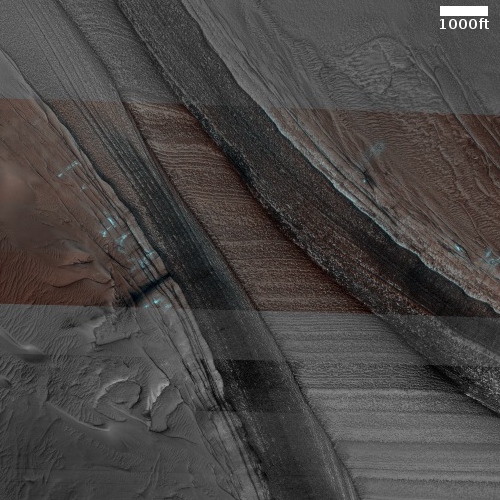
The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on February 1, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and was simply labeled “Sacra Sulci Lava”. Sacra Sulci is a section of the Kasei Valles canyon that runs from the north rim of Valles Marineris north about 600 miles where it turns east for about 400 miles to drain out into the northern lowlands plains of Mars. Sacra Sulci is the region where that valley narrows and then turns east.
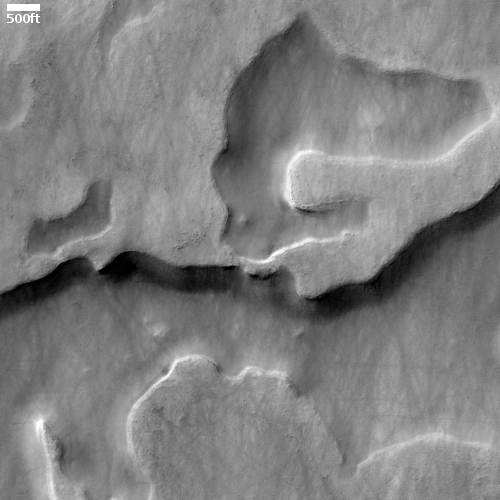
Apparently the flat smoother areas on the east and south on this image that rise about 60 feet above the surrounding terrain and that also seem to flow around mesas and into canyons are believed to be the edge of a massive lava flow that occurred about 150 to 200 million years ago and drained through Kasei Valles, just like water.
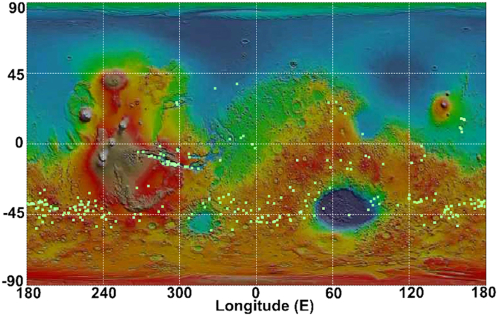
What makes this puzzling, however, is that everything I had read previously about Kasei Valles said that it was thought to have been formed from catastrophic floods of water on early Mars, when the planet was warmer and wetter. In fact, I had posted previously about this theory, and included the map below, taken from figure 8 of this paper [pdf], showing part of the process that some scientists believe occurred.
» Read more
I’ve said it before and I’ll say it again. Mars is strange, Mars is wonderful, but above all, Mars is alien. Today’s cool image illustrates this saying quite nicely.
The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on February 1, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and was simply labeled “Sacra Sulci Lava”. Sacra Sulci is a section of the Kasei Valles canyon that runs from the north rim of Valles Marineris north about 600 miles where it turns east for about 400 miles to drain out into the northern lowlands plains of Mars. Sacra Sulci is the region where that valley narrows and then turns east.
Apparently the flat smoother areas on the east and south on this image that rise about 60 feet above the surrounding terrain and that also seem to flow around mesas and into canyons are believed to be the edge of a massive lava flow that occurred about 150 to 200 million years ago and drained through Kasei Valles, just like water.
What makes this puzzling, however, is that everything I had read previously about Kasei Valles said that it was thought to have been formed from catastrophic floods of water on early Mars, when the planet was warmer and wetter. In fact, I had posted previously about this theory, and included the map below, taken from figure 8 of this paper [pdf], showing part of the process that some scientists believe occurred.
» Read more