Buried silo on Mars?
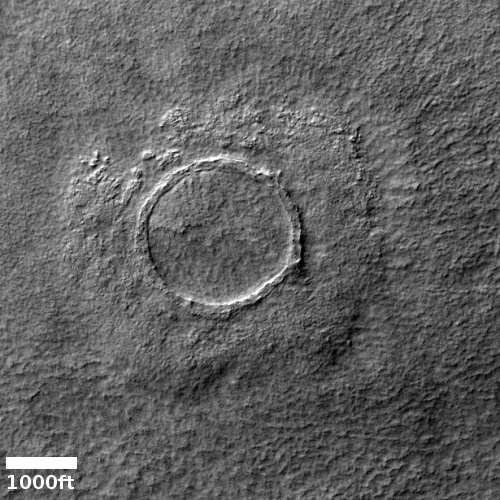
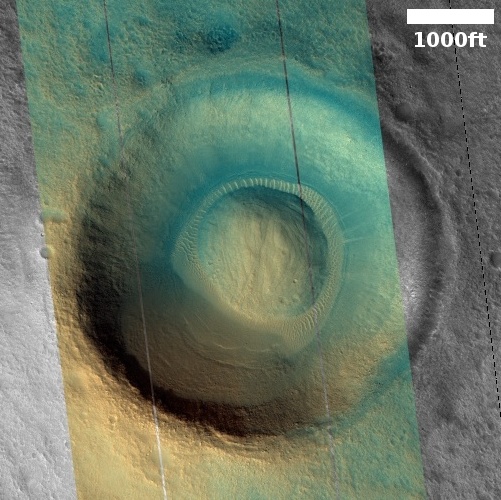
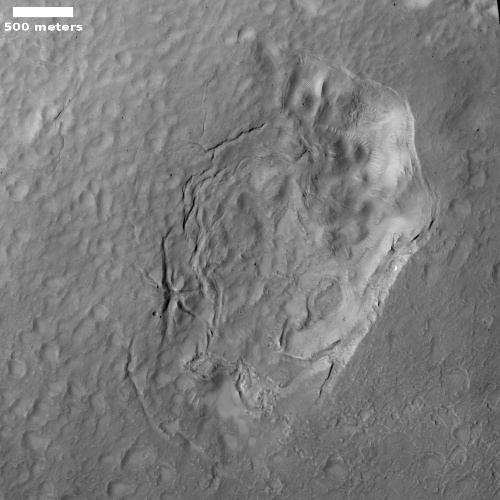
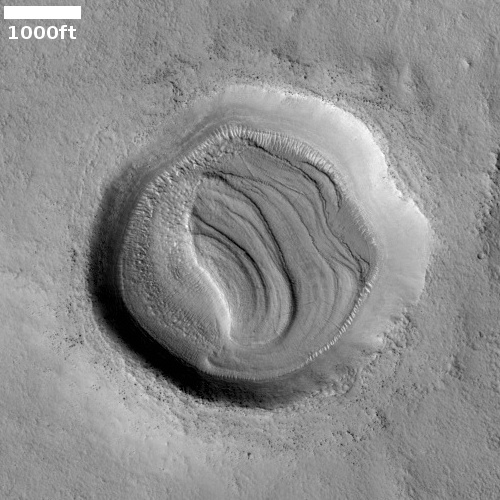
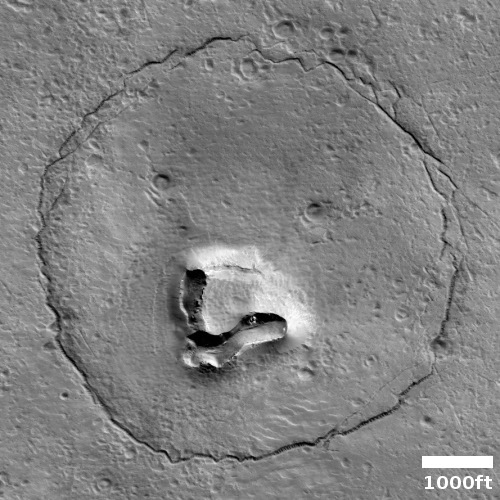
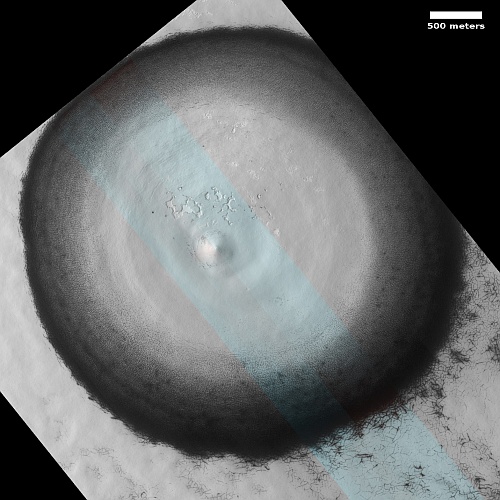
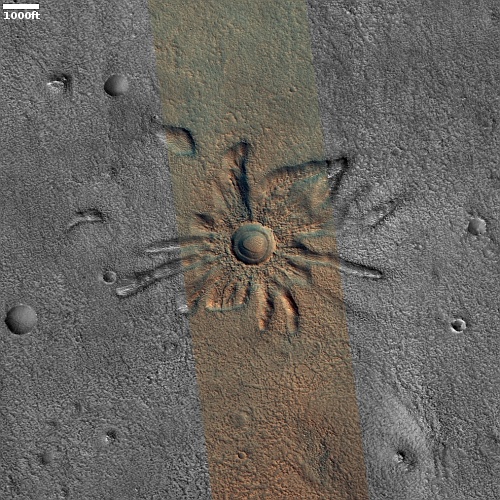
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated and cropped to post here, was taken on December 31, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
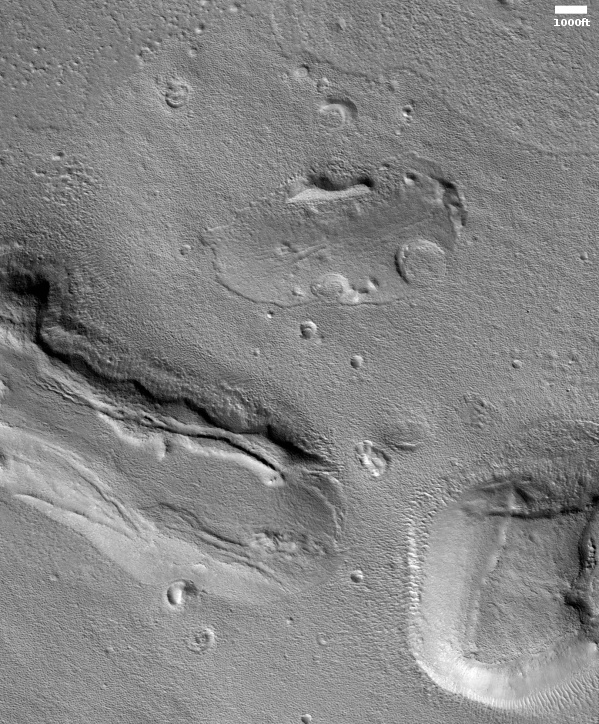
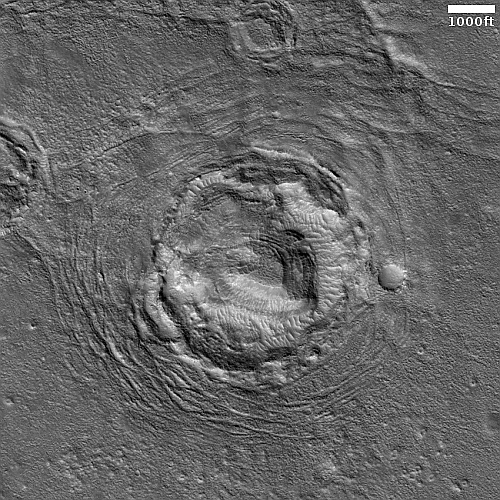
The headline is pure silliness, and should not be taken seriously. However, the geological feature is intriguing nonetheless. Its almost perfect circular shape suggests a partly buried or eroded crater, except that its consistent thickness, almost like a wall, does not match what the rims of any crater should look like. Crater rims are made up of ejected material pushed out during impact, and thus always include some chaotic features.
My guess is that this circular feature is volcanic in nature. Maybe this was once a caldera, and the circle indicates a final vent from which lava extruded and then solidified.
At least, that’s my story.
The feature is located in the southwest quadrant of Hellas Basin, the basement of Mars, at 49 degrees south latitude. While this also suggests that ice might help explain this, we must also remember that much of the geology in that basin remains unexplained. Thus, there is no reason not to add one more feature to the list.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated and cropped to post here, was taken on December 31, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
The headline is pure silliness, and should not be taken seriously. However, the geological feature is intriguing nonetheless. Its almost perfect circular shape suggests a partly buried or eroded crater, except that its consistent thickness, almost like a wall, does not match what the rims of any crater should look like. Crater rims are made up of ejected material pushed out during impact, and thus always include some chaotic features.
My guess is that this circular feature is volcanic in nature. Maybe this was once a caldera, and the circle indicates a final vent from which lava extruded and then solidified.
At least, that’s my story.
The feature is located in the southwest quadrant of Hellas Basin, the basement of Mars, at 49 degrees south latitude. While this also suggests that ice might help explain this, we must also remember that much of the geology in that basin remains unexplained. Thus, there is no reason not to add one more feature to the list.