Data from Perseverance confirms Jezero Crater once held a lake
According to a newly published paper, the data obtained by the rover Perseverance has confirmed and refined what orbital data has suggested, that Jezero Crater once held a lake. From the abstract:
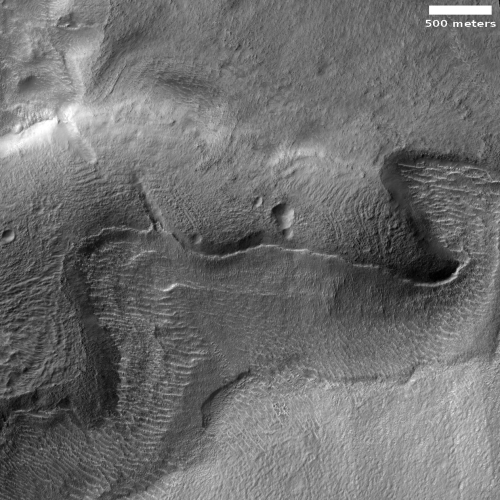
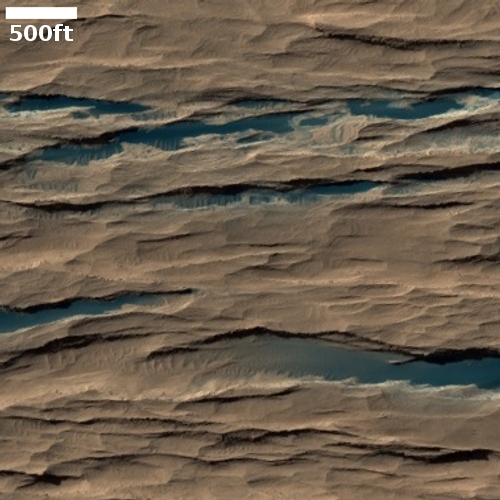
We analyze images taken by the rover in the three months after landing. The fan has outcrop faces that were invisible from orbit, which record the hydrological evolution of Jezero crater. We interpret the presence of inclined strata in these outcrops as evidence of deltas that advanced into a lake. In contrast, the uppermost fan strata are composed of boulder conglomerates, which imply deposition by episodic high-energy floods. This sedimentary succession indicates a transition, from a sustained hydrologic activity in a persistent lake environment, to highly energetic short-duration fluvial flows.
In other words, the crater first held a lake, which as it slowly dried out was periodically renewed by flash floods. The distinct delta of material that made Jezero Crater the prime landing site was apparently formed during the period when the lake existed. The conditions that caused the subsequent flash floods is as yet not been determined, though it likely is related to the red planet’s long term evolution.
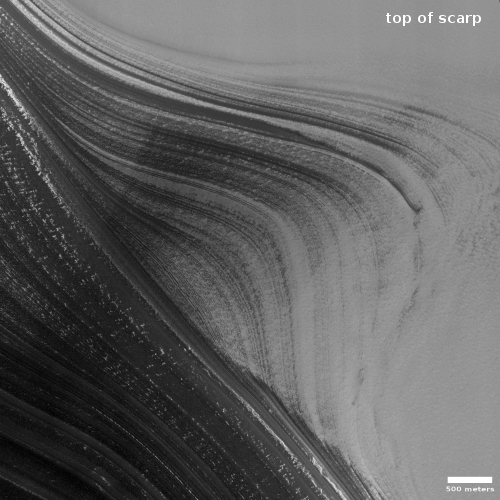
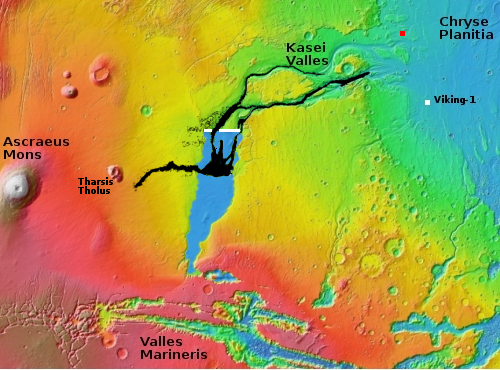
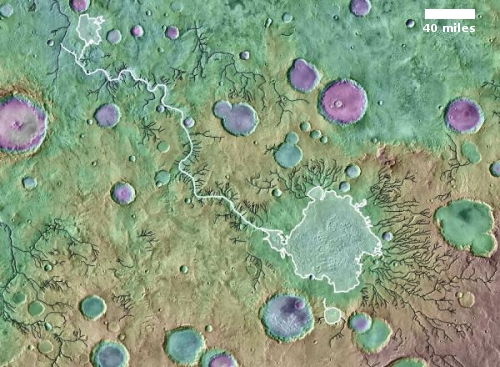
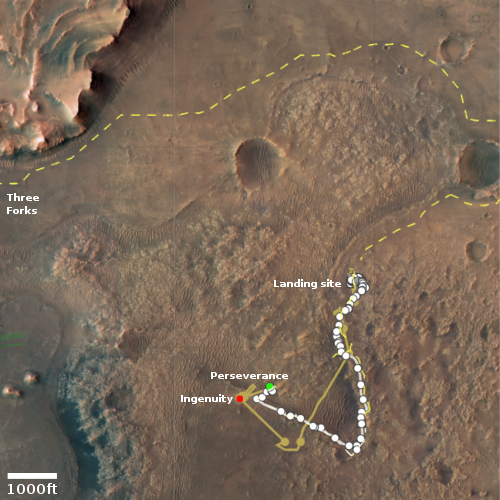
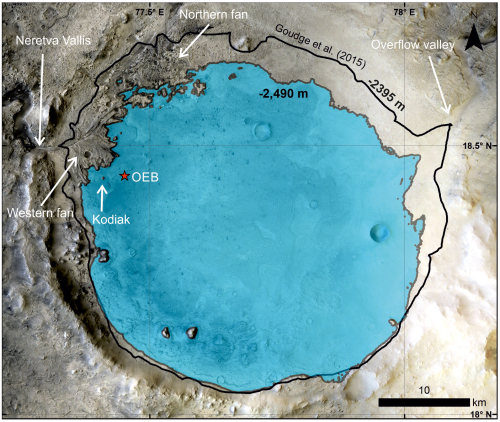
The image above, figure 5 from the paper, shows the inferred lake in that early history. The red cross marks Perseverance’s landing site.
This data reinforces the fundamental scientific mystery of Mars. It shows evidence that liquid water once flowed on the surface of Mars, even though other long term data of the planet’s history says the Martian atmosphere has been too thin and too cold to allow that to happen. There is evidence that the atmosphere might have once been thicker, but no computer model or theory has been able to produce a time when it was warm enough.

According to a newly published paper, the data obtained by the rover Perseverance has confirmed and refined what orbital data has suggested, that Jezero Crater once held a lake. From the abstract:
We analyze images taken by the rover in the three months after landing. The fan has outcrop faces that were invisible from orbit, which record the hydrological evolution of Jezero crater. We interpret the presence of inclined strata in these outcrops as evidence of deltas that advanced into a lake. In contrast, the uppermost fan strata are composed of boulder conglomerates, which imply deposition by episodic high-energy floods. This sedimentary succession indicates a transition, from a sustained hydrologic activity in a persistent lake environment, to highly energetic short-duration fluvial flows.
In other words, the crater first held a lake, which as it slowly dried out was periodically renewed by flash floods. The distinct delta of material that made Jezero Crater the prime landing site was apparently formed during the period when the lake existed. The conditions that caused the subsequent flash floods is as yet not been determined, though it likely is related to the red planet’s long term evolution.
The image above, figure 5 from the paper, shows the inferred lake in that early history. The red cross marks Perseverance’s landing site.
This data reinforces the fundamental scientific mystery of Mars. It shows evidence that liquid water once flowed on the surface of Mars, even though other long term data of the planet’s history says the Martian atmosphere has been too thin and too cold to allow that to happen. There is evidence that the atmosphere might have once been thicker, but no computer model or theory has been able to produce a time when it was warm enough.