Two weeks under water
An evening pause: A clever way to extend research time under water. My only question in thinking about the experiments she was doing: What happens if it gets cooler?
Hat tip Cotour.
An evening pause: A clever way to extend research time under water. My only question in thinking about the experiments she was doing: What happens if it gets cooler?
Hat tip Cotour.

Today was supposed to have been the last day at the cancelled 51st annual Lunar & Planetary Science conference. As such, only a half day of presentations had been scheduled in order to give participants the option of returning home sooner.
While many of the abstracts of the planned-but-now-cancelled presentations were on subjects important to the scientists but not so interesting to the general public, two sessions, one on Martian buried glaciers/ice and a second focused on Mercury, would have made the day very worthwhile to this science journalist, had I been there.
The map above, from the first abstract [pdf] of the Mars session, might possibly epitomize our present knowledge of ice/glaciers on Mars. It provides an update of the continuing survey of ice scarps in the high mid-latitudes of Mars (see the most recent post on Behind the Black from February 12, 2020). Clearly, the more they look, the more they find of these ice scarps, cliff faces with visible exposed pure ice layers that will be relatively easy to access.
But then, finding evidence of some form of buried ice on Mars is becoming almost routine. Of the thirteen abstracts in this Mars session, ten described some sort of evidence of buried ice or glaciers on Mars, in all sorts of places, with the remaining three abstracts studying similar Earth features for comparison. The scientists found evidence of water ice on the top of one of Mars’ largest volcanoes (abstract #2299 [pdf]), in faults and fissures near the equator (#1997 [pdf]), in the eastern margin of one of Mars’ largest deep basins (#3070 [pdf]), in Gale Crater (#2609 [pdf]), in the transition zone between the northern lowlands and southern highlands (#1074 [pdf]), and of course in the northern mid-latitude lowland plains (#2648 [pdf] and #2872 [pdf]).
The results tell us not that there is water ice on Mars, but that it is very plentiful, and that its presence and behavior (as glaciers, as snowfall, and as an underground aquifer) make it a major factor in explaining the geology we see on Mars. I’ve even begun to get a sense that among the planetary scientists researching Mars there is an increasing consideration that maybe ice formed many of the river-like features we see on the surface, not flowing water as has been assumed for decades. This theory has not yet become dominate or even popular, but I have been seeing mention of it increasingly in papers, in one form or another.
If this possibility becomes accepted, it would help solve many Martian geological mysteries, primary of which is the fact that scientists cannot yet explain how water flowed as liquid on the surface some time ago in Mars’ long geological history, given its theorized atmosphere and climate. If ice did the shaping, then liquid water (in large amounts) would not be required.
Now, on to the Mercury session.
» Read more
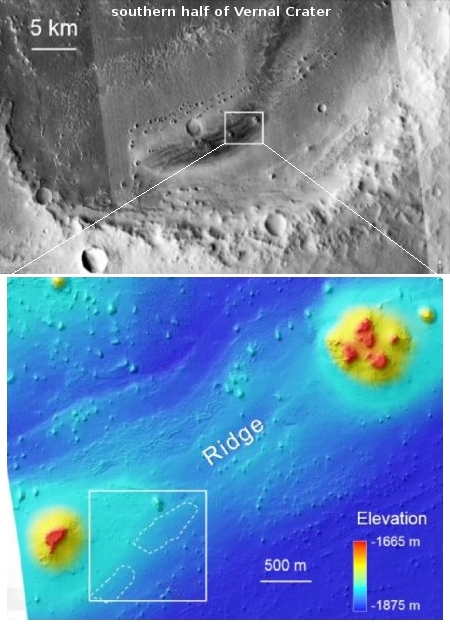

Cool image time! In prepping my report of the interesting abstracts from Friday of the cancelled 51st annual Lunar & Planetary Science conference (to be posted later today), I found myself reading an abstract [pdf] from the astrobiology session about the possibility of now inactive hot springs on Mars! This was such a cool image and possibility I decided to post it separately, first.
The top image to the right, cropped and expanded to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2009. It shows some dark elliptical splotches inside the floor of a crater dubbed Vernal. The second image to the right, taken from the abstract, shows the context, with the top image a wide shot showing the southern half of Vernal Crater where these features are located, and the bottom image zooming into the area of interest. The white box focuses on the elliptical features seen in the first image above. From the abstract:
The elliptical features consist of concentric halos of high but varying albedo, where the highest albedo in each occurs in a small central zone that mimics the shape of the larger anomaly. Each feature is also traversed by circumferential fractures. Several similar tonal features extend for 5-6 km, on stratigraphic trend with the elliptical features. Hypotheses considered for the origin of the elliptical features included springs, mud/lava volcanoes, pingos, and effects of aeolian erosion, ice sublimation, or dust, but the springs alternative was most compatible with all the data.
The abstract theorizes that the small ligher central zone is where hot water might have erupted as “focused fluid injection” (like a geyser), spraying the surround area to form the dark ellipses.
I must emphasize that this hypothesis seems to me very tenuous. We do not really have enough data to really conclude these features come from a formerly active hot spring or geyser, though that certainly could be an explanation. In any case, the geology is quite intriguing, and mysterious enough to justify further research and even a future low cost mission, such as small helicopter drone, when many such missions can be launched frequently and cheaply.
Even as the space agency is about to launch a new rover to Mars, it is considering cutting operations for the rover Curiosity as well as considering shutting down its operation as soon as 2021.
Other ongoing missions are threatened by the administration’s fiscal year 2021 budget proposal. “The FY21 budget that the president just recently submitted overall is extremely favorable for the Mars program, but available funding for extended mission longevity is limited,” [said Jim Watzin, director of NASA’s Mars exploration program].
That request would effectively end operations of the Mars Odyssey orbiter, launched in 2001, and reduce the budget for Curiosity from $51.1 million in 2019 to $40 million in 2021, with no funding projected for that rover mission beyond 2021.
The penny-wise-pound-foolish nature of such a decision is breath-taking. Rather than continue, for relatively little cost, running a rover already in place on Mars, the agency will shut it down. And why? So they can initiate other Mars missions costing millions several times more money.
Some of the proposed cuts, such as ending the U.S. funding for Europe’s Mars Express orbiter, make sense. That orbiter has accomplished relatively little, and Europe should be paying for it anyway.
These decisions were announced during a live-stream NASA townhall that was originally to have occurred live at the cancelled Lunar & Planetary Science conference. I suspect its real goal is to garner support for more funding so that the agency will not only get funds for the new missions, it will be able to fund the functioning old ones as well.
Sadly, there would be plenty of money for NASA’s well-run planetary program if our Congress and NASA would stop wasting money on failed projects like Artemis.
It is now time for today’s virtual report from the non-existent 51st annual Lunar & Planetary Science conference, cancelled because of the terrified fear of COVID-19.
Unlike the previous three days, the bulk of the abstracts for presentations planned for today are more what I like to call “in-the-weeds” reports. The science is all good, but it is more obscure, the kind of work the scientists will be interested in but will generally hold little interest to the general public. For example, while very important for designing future missions, most of the public (along with myself) is not very interested in modeling studies that improve the interpretation of instrument data.
This does not mean there were no abstracts of interest. On the contrary. For today the most interesting sessions in the conference program centered on Mars as well as research attempting to better track, identify, and study Near Earth asteroids (NEAs).
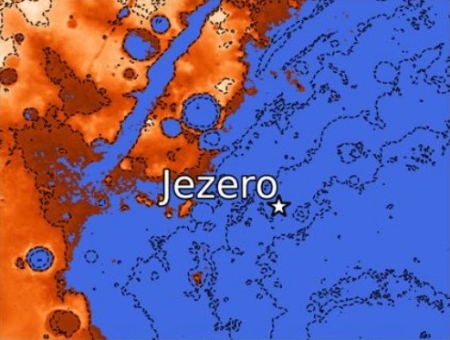
The map above for example shows the location of Jezero Crater, where the rover Perseverance will land in 2021, under what one abstract [pdf] proposed might have been an intermittent ocean. The dark blue indicates where the topography suggests that ocean might have existed, while also indicating its shoreline. If it existed in the past, Perseverance might thus find evidence of features that were “marine in origin.” This ocean would also help explain the gigantic river-like delta that appears to pour into Jezero Crater from its western highland rim.
There were a lot of other abstracts looking closely at Jezero Crater, all in preparation for the upcoming launch of Perseverance in July, some mapping the site’s geology, others studying comparable sites here on Earth.
Other Mars-related abstracts of interest:
» Read more
It isn’t a vaccine that will prevent infection, but tests in France and in the U.S. now show that a drug normally used to treat malaria is very effective in reducing the symptoms of the Wuhan virus.
He said that the first Covid-19 patients he had treated with the drug chloroquine had seen a rapid and effective speeding up of their healing process, and a sharp decrease in the amount of time they remained contagious.
Chloroquine – which is normally used mainly to prevent and treat malaria – was administered via the named drug, Plaquenil.
The drug is readily available and can be prescribed to anyone who is considered threatened by the virus to help them get better why reducing the chances of them giving it to others.
Comet ATLAS, discovered in 2019 by a telescopic survey looking for near Earth asteroids, is brightening more than expected as it approaches the Sun, and could by May be visible to the naked eye.
Jonathan Shanklin, Director of the British Astronomical Association’s Comet Section, reports that the current comet, C/2019 Y4, brightened quite rapidly in mid February, and adds “as of March 11 there is no sign of a slowdown in the rate of brightening. It is already visible in large binoculars . . . The uncertainty in brightness at the time of perihelion is large, though the worst case indicator is 2nd magnitude. It will remain well placed for UK observers into May and could become a prominent object.”
If 2nd magnitude is the dimmest they presently expect, this comet will be one of the brightest objects in the sky come May. Stay tuned!

My virtual coverage of the cancelled 51st annual Lunar & Planetary Science conference continues today with a review of the abstracts of presentations that were planned for today, but unfortunately will never be presented.
As a side note, the social shutdown being imposed on America due to the panic over COVID-19 has some side benefits, as has been noted in a bunch of stories today. Not only will this possibly destroy the power the left has on college campuses as universities quickly shift to online courses, it will also likely put an end to the endless science conferences that are usually paid for by U.S. tax dollars. (That cost includes not just the expense of the conference, but the fees and transportation costs of the participants, almost all of whom get the money from either their government job or through research grants from the government.)
Anyway, for good or ill, the virus shut down the planetary conference in Texas this week, forcing me to post these daily summaries based not on real presentations where I would have interviewed the scientists and gotten some questions answered, but on their abstracts placed on line beforehand. Today, the three big subjects were the south pole of the Moon (as shown in the map above from one abstract [pdf], produced by one instrument on Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter [LRO]), the Martian environment, and Titan. I will take them it that order.
» Read more
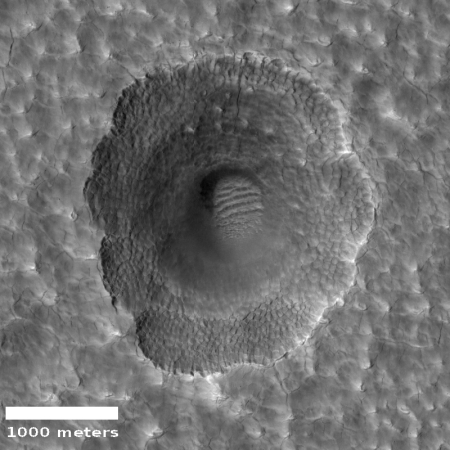

Click for full resolution image.
Cool image time! Today the science team for the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) released a beautiful captioned image of a secondary impact of an object into the icy plains of Utopia Planitia, the northern lowlands northeast of where the rover Perseverance will land in 2021. The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, shows one of several secondary craters in the full image. As planetary scientist Alfred McEwen explains in the caption,
One interpretation [for the crater’s unusual appearance] is that the impact crater exposed nearly pure water ice, which then sublimated away where exposed by the slopes of the crater, expanding the crater’s diameter and producing a scalloped appearance. The small polygons are another indicator of shallow ice.
Note the dunes at the bottom of the crater. This has become a trap of wind-blown sand and dust. Note also how this secondary impact gives us a rough idea of the thickness of this ice, based on the area sublimated away.
There is a lot of relatively accessible ice in those northern lowlands, which is why SpaceX likes them for its possible landing site for Starship. That candidate site is in Arcadia Planitia, on the other side of Mars, but it is still in these same northern lowlands, where scientists have found lots of evidence of buried ice.
Four more stories today indicate once again that the worldwide panic over the corona/COVID-19/Wuhan virus is strongly unwarranted:
The first report, from the science journal Science, provides an update on the situation in South Korea, where testing for the virus has been the most thorough of any nation in the world and where, because of that extensive testing, has shown the death rate has turned out to be far lower than the preliminary statistics have suggested. Out of a population of 50 million, slightly more than 8,000 have been infected, with only 81 dying. This is a death rate of 0.9%, higher than the flu’s 0.1% but not horribly so. And like the flu, most of those deaths have been among the elderly.
The numbers there are now dropping, indicating that the disease might have run its course without causing a catastrophic disaster. There is still a chance it could break out again, but the data suggests otherwise.
Moreover, South Korea controlled the situation without any strong-arm authoritarian tactics, as seen in China and as becoming popular here in the formerly free U.S.
“South Korea is a democratic republic, we feel a lockdown is not a reasonable choice,” says Kim Woo-Joo, an infectious disease specialist at Korea University.
It sadly appears that South Koreans might value freedom more than too many of today’s Americans.
The second article describes research from Wuhan in Hubei province in China, reconfirming the South Korean data. There it appears the death rate was 1.4%, only slightly higher than in South Korea. And once again, the death rate is mostly confined to the older population with already existing health issues, like the flu:
» Read more
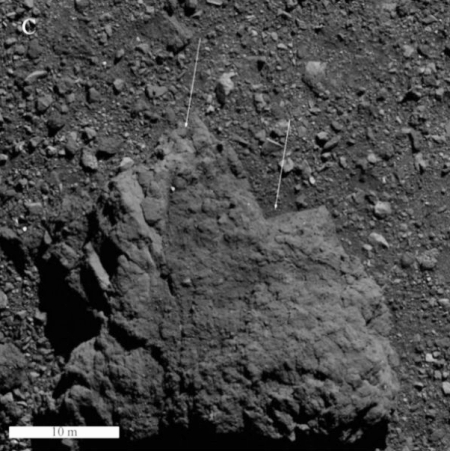

Today was supposed to have been the second day of the week-long 51st annual Lunar & Planetary Conference, sadly cancelled due to fear of the Wuhan virus. As I had planned to attend, I am now spending each day this week reviewing the abstracts of the planned presentations, and giving my readers a review of what scientists had hoped to present. Because I am not in the room with these scientists, however, I cannot quickly get answers to any questions I might have, so for these daily reports my reporting must be more superficial than I would like.
On this day the most significant reports came from scientists working on the probes to the asteroids Bennu and Ryugu as well as the probes to the Moon. The image to right for example is from one abstract [pdf] that studied the texture differences found fourteen boulders on Bennu. The arrows point to the contacts between the different textures, suggesting the existence of layers. Such layers could not have been created on Bennu. Instead, these rocks must have formed on a parent body large enough and existing long enough for such geological processes to take place. At some point that parent body was hit, flinging debris into space that eventually reassembled into the rubble pile of boulders that is Bennu.
Other abstracts from scientists from both the Hayabusa-2 mission to Ryugu and the OSIRIS-REx mission to Bennu covered a whole range of topics:
» Read more
Today I had planned on attending the first day of the 51st annual Lunar & Planetary Science Conference in the suburbs of Houston, Texas. Sadly, for the generally foolish and panicky reasons that is gripping America these days, the people in charge, all scientists, decided to cancel out of fear of a virus that so far appears generally only slightly more dangerous than the flu, though affecting far far far fewer people.
Anyway, below are some of the interesting tidbits that I have gleaned from the abstracts posted for each of Monday’s planned presentations. Unfortunately, because I am not in the room with these scientists, I cannot get my questions answered quickly, or at all. My readers must therefore be satisfied with a somewhat superficial description.
» Read more
Two stories today, one from Nature and the second from space.com, pushed the idea that China’s Mars orbiter/lander/rover mission is still on schedule to meet the July launch window.
A close read of both stories however revealed very little information to support that idea.
The Nature article provided some details about how the project is working around travel restrictions put in place because of the COVID-19 virus epidemic. For example, it told a story about how employees drove six scientific instruments by car to the assembly point rather than fly or take a train, thereby avoiding crowds.
What struck me however was that this supposedly occurred “several days ago,” and involved six science payloads that had not yet been installed on the spacecraft. To be installing such instrumentation at this date, only four months from launch, does not inspire confidence. It leaves them almost no time for thermal and vibration testing of the spacecraft.
The article also provided little information about the status of the entire project.
The space.com article was similar. Lots of information about how China’s space program is dealing with the epidemic, but little concrete information about the mission itself, noting “the lack of official comment on the mission.” Even more puzzling was the statement in this article that the rover “underwent its space environment testing in late January.”
I wonder how that is possible if those six instruments above had not yet been installed. Maybe the instruments were for the lander or orbiter, but if so that means the entire package is not yet assembled and has not been thoroughly tested as a unit. Very worrisome.
Posting today has been light because I was up most of the night dealing with a family health issue, meaning that I ended up sleeping for several hours during the day. All is well, nothing serious (it is NOT coronavirus), but it has left my brain and schedule very confused. Will likely take a good night’s sleep to get back to normal.
Cool image time! Or I should say a bunch of cool images! The photo on the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and annotated by me, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on February 3, 2020. An uncaptioned image, it was entitled “Arabia Terra with Stair-Stepped Hills and Dark Dunes.” Arabia Terra is one of the largest regions of the transition zone on Mars between the northern lowland plains and the southern cratered highlands. It is also where Opportunity landed, and where Europe’s Rosalind Franklin rover will land, in 2022.
This image has so many weird and strange features, I decided to show them all, Below are the three areas indicated by the white boxes, at full resolution. One shows the black dunes, almost certainly made up of sand ground from volcanic ash spewed from a long ago volcanic eruption on Mars.
» Read more
NOAA this week released its February update of its monthly graph showing the long term sunspot activity of the Sun. Below is my monthly version, annotated as I have done every month since 2011.
After a tiny uptick in sunspot activity in January, the Sun resumed the unprecedented flatlining of sunspot activity that began last June. Since then, the Sun has produced practically no sunspots, a drought that as far as I can tell has never happened since the 11-year sunspot cycle resumed in the 1700s (after the grand minimum in the 1600s) and astronomers began counting sunspots.
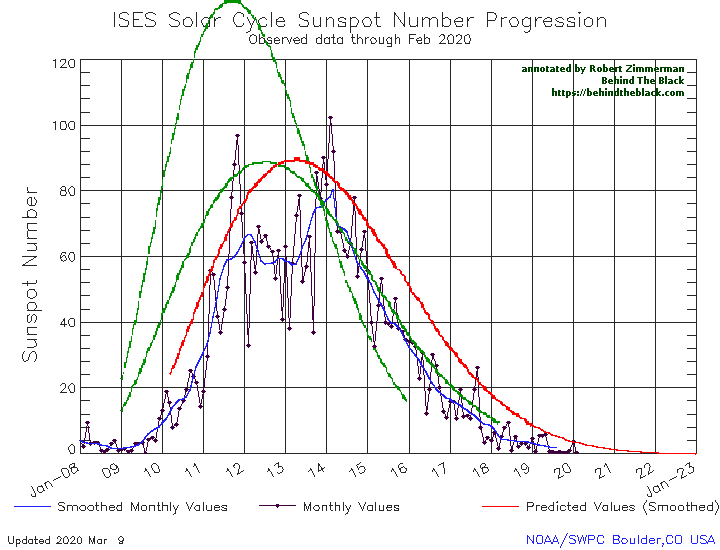
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community for the previous solar maximum. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction, extended in November 2018 four years into the future.
February saw only one sunspot, and it belonged to the old solar cycle. It also occurred at the beginning of the month, and was followed by 33-day streak of blankness, into the middle of March, when a sunspot from the new cycle appeared and quickly faded.
The continuing overall lack of sunspots, from either the old or new cycle, does not mean that we are entering a new grand minimum, with no sunspots for decades (though some scientists believe we are). It does suggest however that the next solar maximum will be weak, and very likely weaker than the very weak maximum that just ended.
Why the Sun does this remains a mystery. Scientists really have no fundamental understanding of the magnetic processes that produce the Sun’s sunspot cycles. And since that cycle appears to have some effect on the Earth’s climate, it also means scientists do not yet have a fundamental understanding of the climate either.
Not that this lack of knowledge matters anymore. We are in an age of panic and certainty, based on emotion and feelings. All that matters is that many people feel they understand the climate and how the Sun works, just as everyone is sure that COVID-19 will destroy the world if we don’t shut down all human activity.
They are certain, and any additional data that illustrates that certainty is unwarranted is irrelevant and must be ignored.
Certainty however is a very dangerous thing. The universe is always more complicated than we know, and to assume we now understand all without doubt leaves us very vulnerable to some bad surprises, as well as the chance we will take actions that are foolish, inappropriate, and even downright evil.
Astronomers have discovered an exoplanet 640 light years away hot enough for iron to be vapor in the atmosphere and to condense out as rain.
The high-resolution spectrum reveals lots of iron vapor within the sliver of atmosphere undergoing the transition from day to night. However, this iron vapor signature is missing from the sliver of atmosphere transitioning from night to day. The astronomers think this happens because strong winds push iron vapor to the nightside, where it cools and condenses into clouds.
“This planet has a twilight zone at a temperature close to the iron condensation temperature,” Ehrenreich explains, “so the change in atmospheric composition (with iron vs. without iron) is occurring right where we are able to observe.”
Because the planet is a gas giant, there’s no surface onto which the droplets can fall, says coauthor Nuno Santos (University of Porto, Portugal). But the planet’s gravity likely pulls the clouds downward, enveloping the nightside in iron fog. The global winds then push the clouds and fog onto the dayside, where the vaporization-condensation cycle repeats again.
Very exotic, and alien, and I guarantee it is probably far more alien than we so far can guess.
You can find out more in this second more detailed article.
The European Space Agency (ESA) today announced that they are delaying the launch of their ExoMars2020 rover mission until the next launch window in 2022
The press release says this will give them the time “necessary to make all components of the spacecraft fit for the Mars adventure.” Considering that the spacecraft’s parachutes have yet to have a successful high altitude test, that the entire spacecraft is not yet assembled, and that when they did the first thermal test of the rover the glue for the solar panel hinges failed, this seems that they need to do a lot of testing.
Overall the decision is smart. Better to give them the time to get this right then launch on time and have a failure.
At the same time, there appears to be something fundamentally wrong within the management of this project at ESA. This project was first proposed in 2001, and has gone through repeated restructurings and redesigns. Moreover, they began planning the rover for this 2020 launch in 2011, and after ten years were not ready for launch.
Cool image time! To understand what created the vastly strange and alien Martian surface, it will be necessary for scientists to monitor that surface closely for decades, if not centuries. To the right is one small example. Taken by the high resolution camera of Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, it shows a dune field inside a crater in the southern cratered highlands of Mars. Craters have been found to be great traps for dust and sand on Mars. Once the material is blown inside, the winds are not strong enough to lift the material out above the surrounding rims. Thus you often get giant dunes inside craters, as we see here.
What makes this location of interest to planetary scientists is the changing surface of these dunes. They have been monitoring the location since 2009. In 2013, the MRO science team released a captioned photograph, the second image to the right, also rotated, cropped, and reduced by me to match the same area in the top image. In that caption planetary scientist Corwin Atwood-Stone of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory in Arizona wrote,
This area was previously imaged in August 2009, about two Mars years ago, and in that image dust devil tracks were also visible. However the tracks visible now are completely different from the earlier ones. This tells us that there has been at least one dust storm since then to erase the old tracks, and lots of dust devil activity to create the new ones.
Since then the MRO science team has taken repeated images of this location to monitor how the dust devil tracks change, as well as monitor possible changes to the dunes themselves, including avalanches. The newest image above shows the result of the global dust storm last year. It wiped out the dust devil tracks entirely.
The newer image was entitled, “Monitor Dune Avalanche Slopes,” but I couldn’t find any examples. Based on published research, I am sure there is something there, even if I couldn’t find them. Maybe my readers have a better eye than I.
Using several different techniques, astronomers now estimate that the typical neutron star will have a diameter of 11 kilometers, or about 7 miles.
What is significant about this new estimate is that if that neutron star happens to be orbiting a black hole and get pulled into it, it will be swallowed whole instead of being ripped apart.
Their results, which appeared in Nature Astronomy today, are more stringent by a factor of two than previous limits and show that a typical neutron star has a radius close to 11 kilometers. They also find that neutron stars merging with black holes are in most cases likely to be swallowed whole, unless the black hole is small and/or rapidly rotating. This means that while such mergers might be observable as gravitational-wave sources, they would be invisible in the electromagnetic spectrum.
In other words, such cataclysmic events would be largely invisible to observers.
The new colonial movement: Though the report today in China’s state-run press is remarkably vague and lacking in details, it appears that they have successfully completed a remote communications test between their planned Mars rover and their ground control center.
The report also said that this will be the “only” such test before the summer launch of their orbiter/lander/rover to Mars.
China has been exceedingly closed-mouthed about this Mars project. Except for one landing test (which I found far from impressive), they have provided very little information about their progress.
While this does not mean they are having problems, it also does not engender confidence, especially because the launch window is only about four months away.
The photo to the right is a small section cropped from an image taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on January 2, 2020. It shows the rough, cratered southern highlands dubbed Tyrrhena Terra that lie between the low Isidis Basin to the north and Mars’ deepest basin, Hellas, to the south.
The image was taken not because any specific scientific request, but because MRO was doing spectroscopy over this area and it made sense to also take a photograph. Comparing the photograph with the spectroscopic data allows scientists to better understand that spectroscopy.
The white cross in the map below shows the location of this image. The map itself covers latitudes from 40 degrees north to 55 degrees south.
» Read more
Using data from an ancient fossil shell, scientists have determined that 70 million years ago the Earth’s day was about 30 minutes shorter, and that a year comprised 372 days.
This result is not a surprise, as scientists have known for a long time that the day has been growing longer as the Moon’s gravity, producing tides, wears away at the Earth’s rotation. This data however is the most precise yet, and will allow scientists to better constrain not only the Earth’s changing rotation over time but the Moon’s orbit. As it slows the Earth’s rotation its own orbit around the Earth gets longer, pushing it farther away.

Click for full resolution version.
Time for some more cool images! The panorama above, cropped and reduced to post here, was assembled from images taken by Curiosity on March 6, 2020 by its left navigation camera, just after it topped the slope and settled on the very rocky plateau of what the scientists have dubbed the Greenheugh Piedmont, the highest point on Mars that Curiosity has so far traveled. It looks north, across Gale Crater to its far rim, about thirty miles away. That rim rises about a mile higher than where Curiosity sits today.
To quote Michelle Minitti, the planetary geologist who wrote the update describing this achievement:
Kudos to our rover drivers for making it up the steep, sandy slope below the “Greenheugh pediment” (visible in the [right] side of the above image) and delivering us to a stretch of geology we had our eyes on even before we landed in Gale crater!
The panorama below is also assembled from photos taken by the left navigation camera, but this time it looks south, across the piedmont toward Mt. Sharp. Its view of the the piedmont’s very very rough terrain I think proves that once the scientists have gathered their data from this point, the rover will descend back down and resume its original route, circling the piedmont to skirt its southern edge where orbital data suggests the going will be smoother.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the left, cropped to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on January 21, 2020, and shows several boulders at the bottom of a slope, along with the tracks those boulders made as they rolled downhill sometime in the far past.
Uphill is to the south. We know the dark spots at the end of these tracks are large boulders partly because of the wind streaks emanating away from them to the north. As the wind goes around each rock it produces eddies that produce the tracks. Based on the scale and the image resolution (about 10 inches per pixel), these boulders range in size from about one to five feet in diameter.
This image has two points of interest. First, the tracks left by the boulders seem to have a repeating pattern. My guess is that the pattern most likely formed because the boulders are not spherical in shape, and as they rolled each roll repeated a certain pattern reflecting that shape. This theory is reinforced by a close look at each boulder. Though the resolution is insufficient to resolve the boulders themselves, the pixel distribution for each strongly suggests an asymmetric shape.
Second, this image, when compared with an earlier MRO image of the same spot, taken fourteen years ago in December 2006, shows no obvious change. These tracks, and their boulders, have therefore probably sat here, as we see them, for a long time. Since there appear to be two sets of tracks, with one overlying the other, this suggests that two separate events (an earthquake or nearby impact) each time caused a bunch of boulders to break free and roll downward together, with the second set of boulder tracks crossing over the earlier set.
Establishing when those two events occurred, however, will require some on-site data, something that will likely not occur until humans roam the surface of Mars in large numbers.
NASA today announced that they have named their next Mars rover, due to launch in July, “Perseverance.”
The name was announced Thursday by Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator of the Science Mission Directorate, during a celebration at Lake Braddock Secondary School in Burke, Virginia. Zurbuchen was at the school to congratulate seventh grader Alexander Mather, who submitted the winning entry to the agency’s “Name the Rover” essay contest, which received 28,000 entries fromK-12 students from every U.S. state and territory.
“Alex’s entry captured the spirit of exploration,” said Zurbuchen. “Like every exploration mission before, our rover is going to face challenges, and it’s going to make amazing discoveries. It’s already surmounted many obstacles to get us to the point where we are today – processing for launch. Alex and his classmates are the Artemis Generation, and they’re going to be taking the next steps into space that lead to Mars. That inspiring work will always require perseverance. We can’t wait to see that nameplate on Mars.”
I truly hope that the rover is well-named, and lives a very long life on Mars, long enough that it is still in use the day an human arrives to touch it again.
Yesterday I got a bit of frustrating and disappointing news. The 51st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC-51) to be held in the Houston suburbs beginning on March 15 (to which I was planning to attend) had been canceled due to coronavirus/COVID-19 fears. From the organizers’ email:
We regret to inform you that LPSC 51 will be cancelled due to concerns about COVID-19. This difficult decision has been made after a careful assessment of the risks as determined by the CDC and WHO; consultation with NASA PSD leadership; and consideration of community feedback. We are fully committed to ensuring that our conference attendees remain safe and well.
The organizers had earlier in the week sent out an email stating that they were considering their options because of the epidemic, and would announce a decision on March 6. That they pushed forward the cancellation decision by two days was almost certainly prompted by the revelation yesterday that a case of coronavirus had been confirmed in Houston.
To say this is a disappointment is an understatement. I was very much looking forward to meeting face-to-face many of the planetary scientists I have been corresponding with during the past few years. I was also eagerly anticipating getting an up-front look at the most recent discoveries in the exploration of the solar system, and to pass those discoveries on to my readers.
My disappointment however must pale in comparison to the disappointment of the scientists involved, especially the younger ones trying to establish themselves in the field. They need conferences like this to not only promote their work, but to network and to learn for themselves what others in their field are doing.
What makes this decision more appalling to me is how completely pointless and fear-driven it is. While it makes sense to try to slow the spread of the disease while scientists scramble to understand it and possibly develop a vaccine, it also makes no sense to stop living and to cease all effort out of mindless fear and ignorant panic.
And what we have today is the latter. This planetary conference was not the only one cancelled this week. On March 2 the American Physical Society panicked and cancelled its only annual convention, only 36 hours before it was about to begin, out of a fear that a gathering of 11,000 scientists from all over the world would help spread the disease.
This decision was absurd, however, as a large bulk of the conference’s attendees had already arrived. The cancellation thus accomplished practically nothing to stop coronavirus, while succeeding ably in stymying the spread of knowledge.
The simple fact is that though COVID-19 is a concern and must not be ignored, it is hardly the worldwide crisis being touted by our mindless press, odious politicians, and largely politically correct intellectual community.
A rational look at the facts give a bit of context that deflates the balloon of this madness. Several facts, both good and bad:
» Read more
The Japanese government has confirmed that it has suspended payment of its annual contribution to the budget of the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) because of the project’s inability to begin construction on Mauna Kea in Hawaii.
Japanese astronomers strongly prefer placing TMT on Mauna Kea because it is relatively close to Japan, unlike the proposed replacement site in the Grand Canary Islands in the Atlantic.
I would say this is the next nail in the coffin for TMT in Hawaii. The National Science Foundation (NSF) has money to fund construction of a big telescope for U.S. astronomers, but has not been able to decide on whether to give the money to TMT, or to the Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT), already under construction in Chile, or to both.
Astronomers have been lobbying for dual funding, using the argument that the two telescopes are in the opposite north and south hemispheres. Moving TMT to the Grand Canaries, at a higher latitude than Hawaii, strengthens this argument. With the apparent exit of Japan it could be that the way is now cleared to give up on Hawaii and for TMT to make the move to a more welcoming site.
Hawaii’s protesters, supported by the state’s Democratically-controlled government, will of course celebrate. What they will be celebrating however will be the death-knell of science in Hawaii.
The spacecraft OSIRIS-REx yesterday made its closest reconnaissance yet of the asteroid Bennu, sweeping past its primary touch-and-go landing site Nightingale by a distance of only 820 feet.
The main goal of yesterday’s low flyover was to collect high-resolution imagery of the site’s surface material. The spacecraft’s sample collection mechanism is designed to pick up small rocks less than 0.8 inches (2 cm) in size, and the PolyCam images from this low pass are very detailed, allowing the team to identify and locate rocks of this size. Several of the spacecraft’s other instruments also took observations of the Nightingale site during the flyover event, including the OSIRIS-REx Thermal Emissions Spectrometer (OTES), the OSIRIS-REx Visual and InfraRed Spectrometer (OVIRS), the OSIRIS-REx Laser Altimeter (OLA), and the MapCam color imager.
After completing the flyover, the spacecraft returned to orbit – but for the first time, OSIRIS-REx reversed the direction of its safe-home orbit and is now circling Bennu clockwise (as viewed from the Sun). This shift in orbital direction positioned the spacecraft for its next close encounter with the asteroid – its first rehearsal for the sample collection event.
The touch-and-go sample grab is targeted to take place in August.
Scientists have discovered bits of a protein molecule inside a meteorite that fell in Algeria in 1990 and was quickly recovered.
The protein is called hemolithin.
For hemolithin to have formed naturally in the configuration found would require glycine to form first, perhaps on the surface of grains of space dust. After that, heat by way of molecular clouds might have induced units of glycine to begin linking into polymer chains, which at some point, could evolve into fully formed proteins. The researchers note that the atom groupings on the tips of the protein form an iron oxide that has been seen in prior research to absorb photons—a means of splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen, thereby producing an energy source that would also be necessary for the development of life.
The real significance of this find is what it reveals we do not know. Most asteroid material from the very beginnings of the solar system (the type of material that would contain such a protein) is very fragile, and does not survive the journey though the Earth’s atmosphere. Thus, our meteorite sample obtained here on Earth, which is our entire sample, is very biased.
When we start getting samples back from asteroids (as both Hayabusa-2 and OSIRIS-REx are about to do), our understanding of the early solar system, as well as that of asteroids, will change radically. This story only gives us a hint of that fact.
Hat tip reader and fellow caver John Harman.