Sunspot update March 2019: An upcoming Grand Minimum?
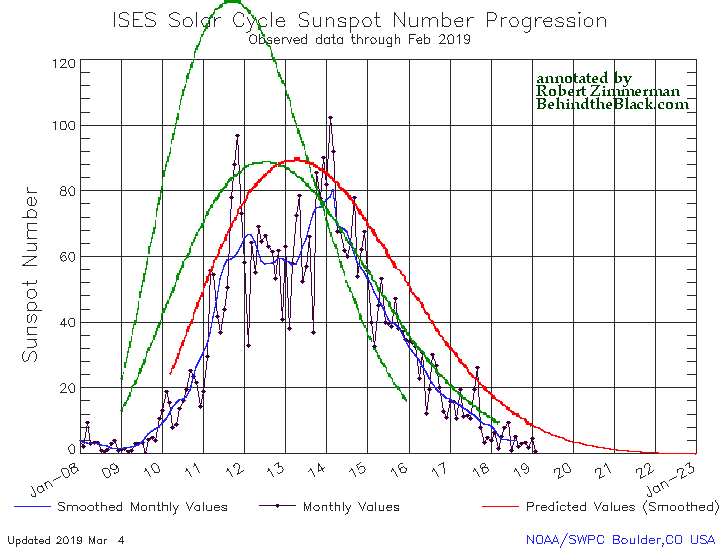
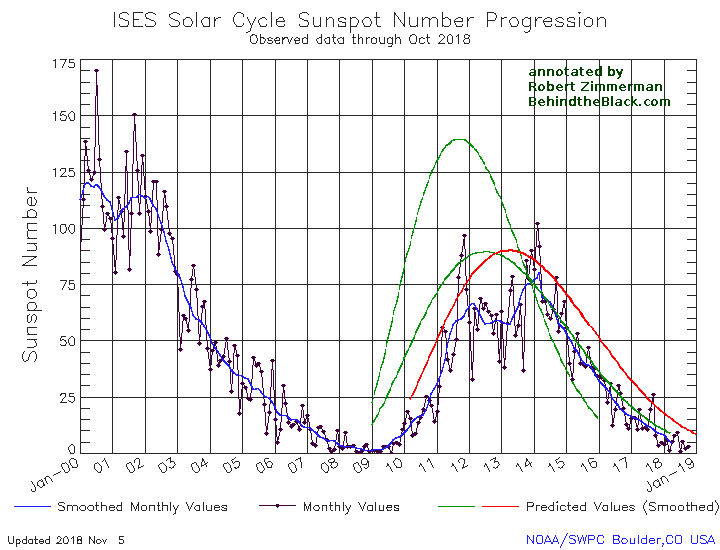
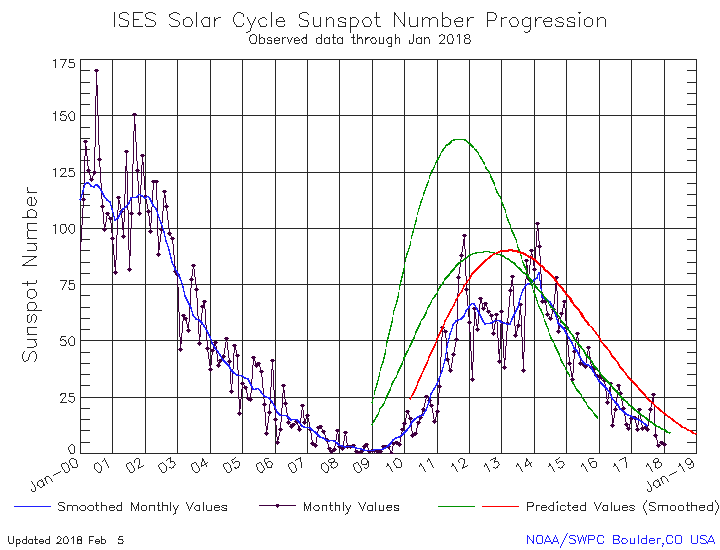
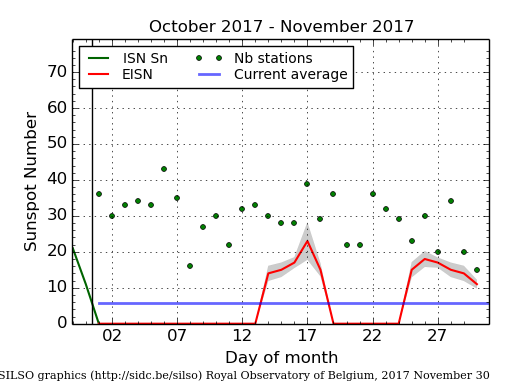
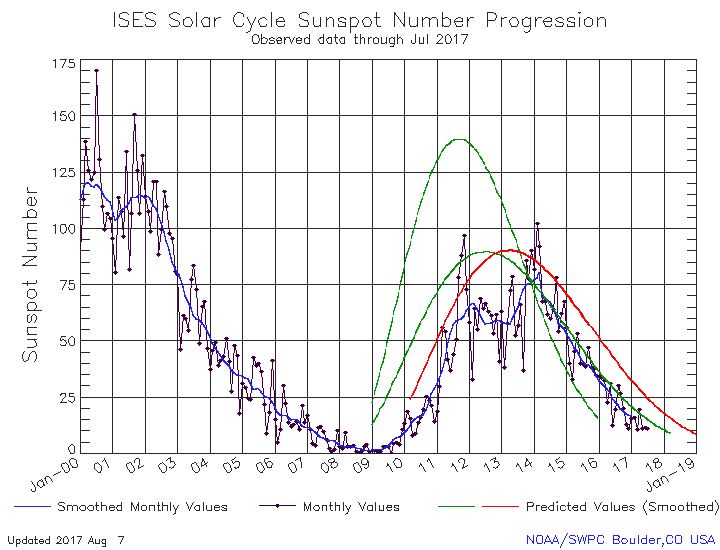
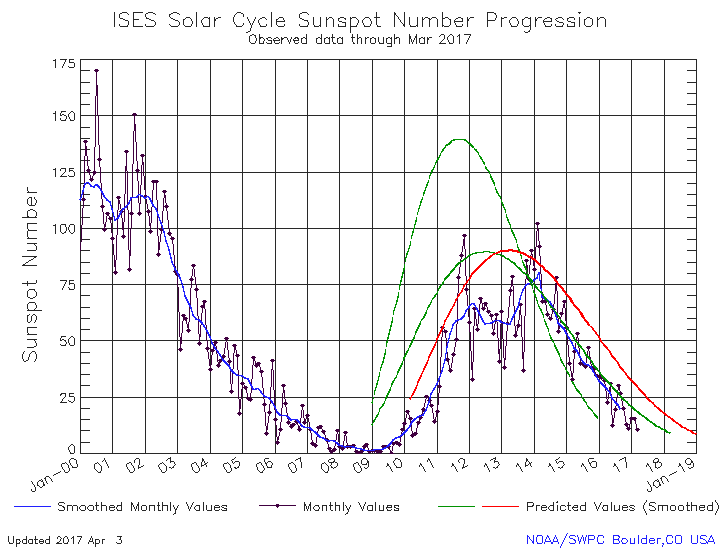
Even though we are now deep into the beginning of what might become the first grand minimum in sunspot activity since the invention of the telescope, that does not mean the Sun has as yet stopped producing sunspots. Yesterday NOAA released its the monthly update of its tracking of the solar cycle, adding sunspot activity for March 2019 to its graph. Below is that graph, annotated by me to give it some context.
It shows the Sun with a slight burst in activity in March, suggesting that though we are now in the solar minimum that minimum still has the ability to produce sunspots.
At the same time, for me to say that we might be heading to a grand minimum, a time period lasting many decades where no sunspots are visible and the sunspot cycle essentially ceases, is not click bait or hyperbole. It is instead based on what I now think the solar science community is thinking, based on this very graph.
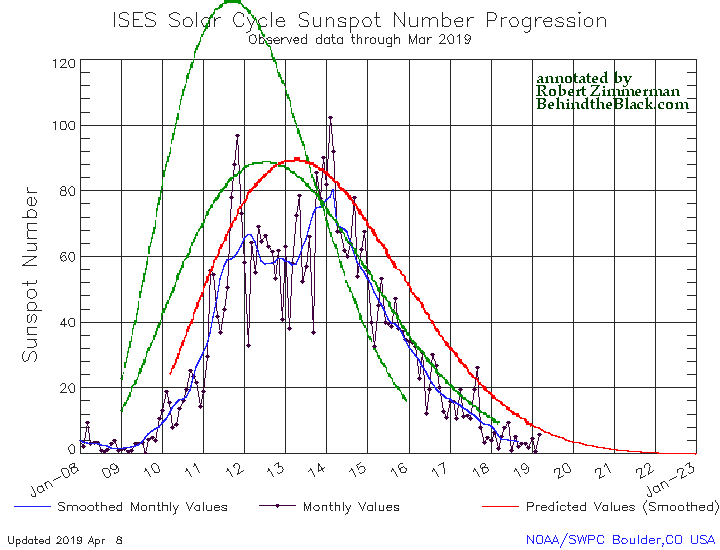
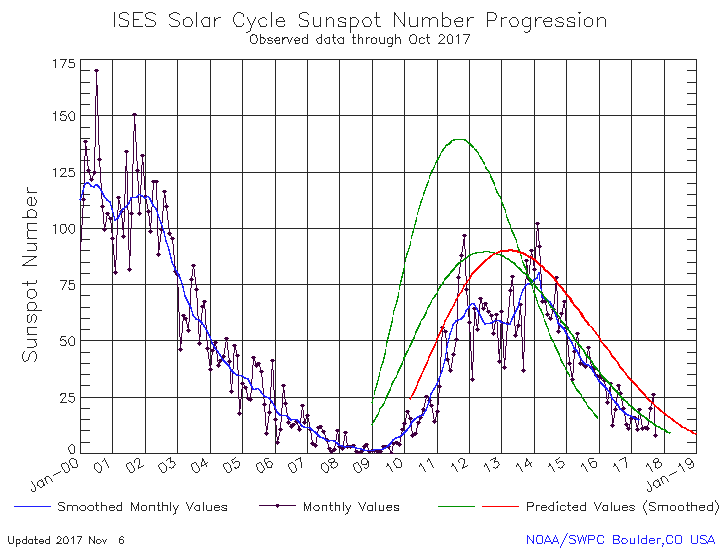
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community for the previous solar maximum. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction, extended in November 2018 four years into the future.
For past half dozen or so cycles the solar science community had issued its prediction for the upcoming solar maximum at about this stage in the overall cycle, during the final ramp down to minimum when it was clear that the Sun had entered that minimum.
This cycle’s prediction however has not yet happened, and in fact appears to be late. In fact, the extension of the May 2009 red curve that was made in November 2018 might very well be the only prediction we see. That extension is shown by the differences between the green 2007 prediction and the red 2009 prediction in the graph. Before November 2018 both curves ended at the same place, the end of 2018.
The extension of that red curve is important. As I noted in my December 2018 sunspot update,
» Read more