Trump proposes an increase in science spending in 2021
Read any analysis by any mainstream news or science publication of Trump’s 2021 proposed science budget, released this week, and you will come away thinking that the future of science research in the U.S. is doomed and that Donald Trump is a neanderthal who wishes to send us back to the dark ages.
Consider for example this article from the journal Science, Trump’s new budget cuts all but a favored few science programs, which begins like so:
For the fourth straight year, President Donald Trump has proposed sizable reductions in federal research spending. To be sure, it’s no longer news that the president wants deep cuts to the budgets of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Science Foundation (NSF), and science programs at the Department of Energy (DOE) and NASA. And in past years, Congress has rejected similar proposals and provided increases. But Trump’s 2021 request brings into sharper focus what his administration values across the research landscape—and what it views as unimportant.
The article then outlines how Trump is slashing spending on science research across the board, even to the point of spinning the NASA budget to make a significant budget increase appear as a cut, by cherry-picking only some of that budget’s science programs.
This article is typical of the mainstream press. These articles never provide any context for the proposed budget numbers. They look at what was spent the year before, see what is being proposed for the next year, and if they see any reduction they scream. And if it is an evil Republican president proposing the cuts they scream far harder, implying that those cuts will guarantee the coming of a new dark age.
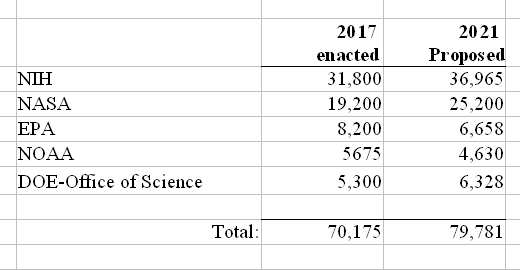
To the right however are the budget numbers (shown in thousands) for five of the biggest science agencies in the federal government, comparing Trump’s 2021 proposed budget numbers with the last science budget approved at the end of the Obama administration in 2016.
Notice anything? » Read more
