Long March 5B booster reentry prediction narrows again
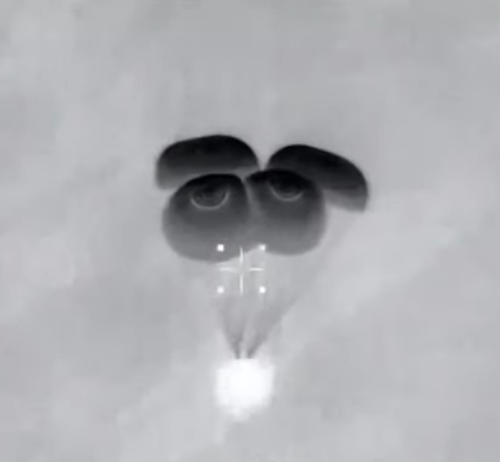
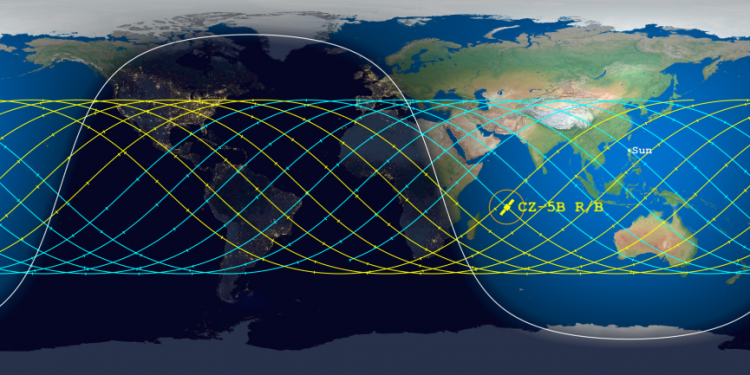
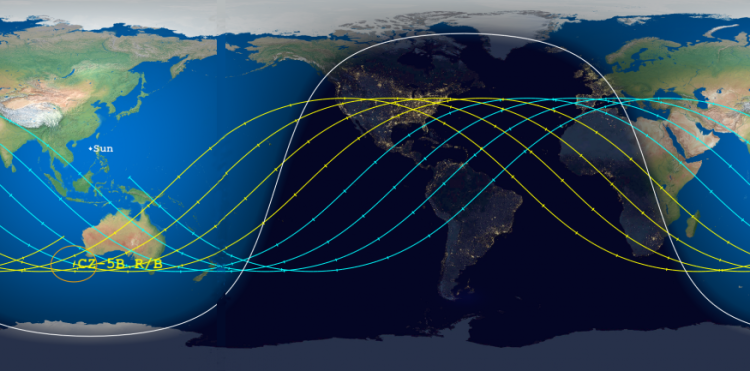
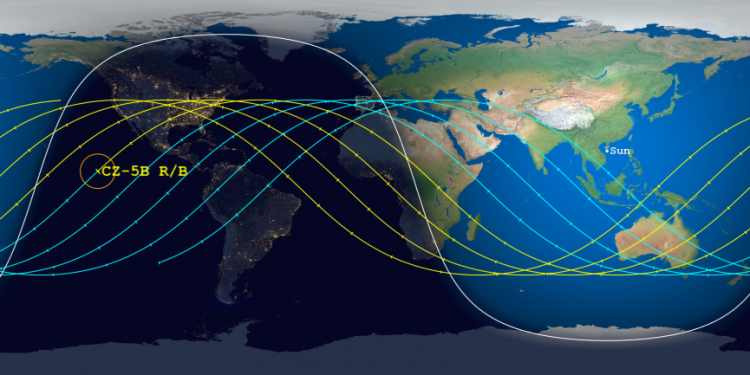
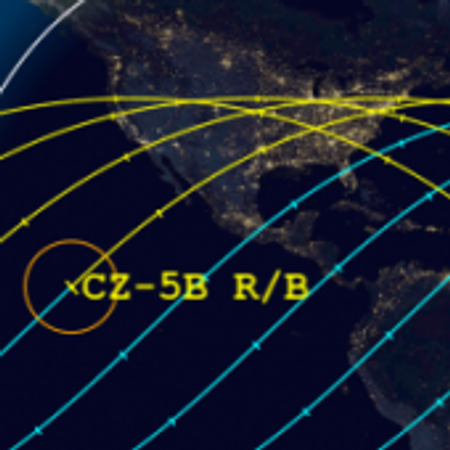
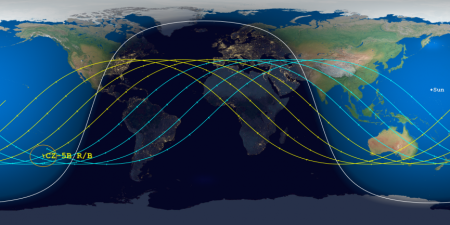
The Aerospace Corporation has once again narrowed the reentry window for the 21-ton core stage of China’s Long March 5B rocket, launched on April 29th, as shown by the map above. The window is now only eleven hours long, centered over a point in the Indian Ocean at just before midnight on May 8th. The yellow tracks indicate its path after that centerpoint, while the blue lines show its path prior to it. Tick marks show five minute intervals.
The last orbit as shown by this prediction puts it over the following land areas. If the core stage crashes 5 to 20 minutes early, it would land anywhere from Spain to Africa. Another fifteen minutes earlier and Florida and Mexico would be in the landing zone. If it lands 45 to 50 minutes later, it will land somewhere on the continental United States.
China however might be lucky with this booster. The centerpoint of the prediction has definitely begun to stabilize around the Indian Ocean.
With future boosters, who knows? China plans at least three more Long March 5B launches, two in ’22 to launch modules for its space station, and one in ’24 to launch a Hubble-class space telescope to fly in formation with that space station. We shall see this same Keystone cop charade on all three flights, with the core stage tumbling out-of-control and falling back to Earth to crash somewhere that cannot be predicted.
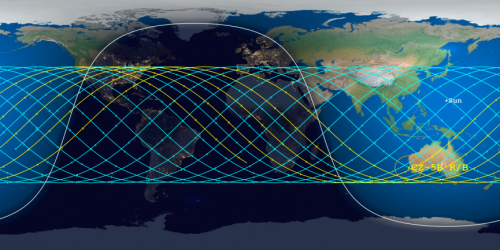
The Aerospace Corporation has once again narrowed the reentry window for the 21-ton core stage of China’s Long March 5B rocket, launched on April 29th, as shown by the map above. The window is now only eleven hours long, centered over a point in the Indian Ocean at just before midnight on May 8th. The yellow tracks indicate its path after that centerpoint, while the blue lines show its path prior to it. Tick marks show five minute intervals.
The last orbit as shown by this prediction puts it over the following land areas. If the core stage crashes 5 to 20 minutes early, it would land anywhere from Spain to Africa. Another fifteen minutes earlier and Florida and Mexico would be in the landing zone. If it lands 45 to 50 minutes later, it will land somewhere on the continental United States.
China however might be lucky with this booster. The centerpoint of the prediction has definitely begun to stabilize around the Indian Ocean.
With future boosters, who knows? China plans at least three more Long March 5B launches, two in ’22 to launch modules for its space station, and one in ’24 to launch a Hubble-class space telescope to fly in formation with that space station. We shall see this same Keystone cop charade on all three flights, with the core stage tumbling out-of-control and falling back to Earth to crash somewhere that cannot be predicted.