NASA extends Ingenuity’s mission through September ’22
NASA yesterday officially extended Ingenuity’s flight operations on Mars at least through September 2022, outlining in detail the helicopter’s hoped-for flight targets.
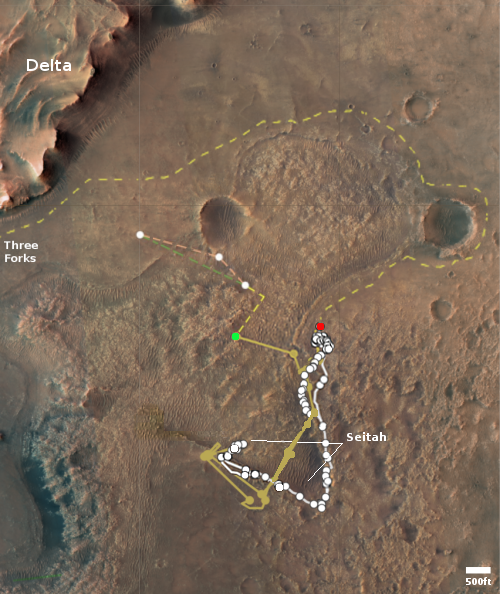
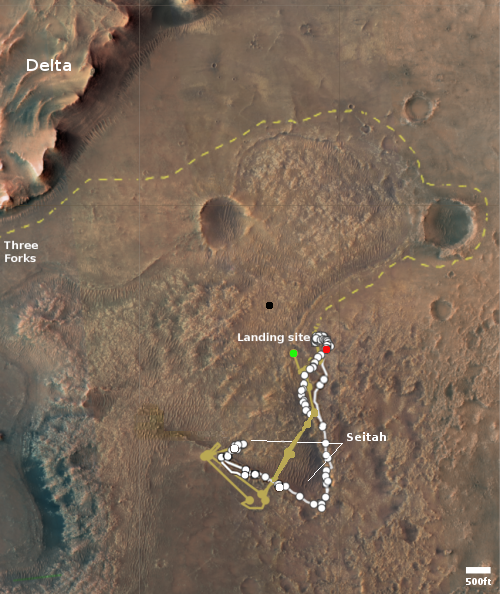
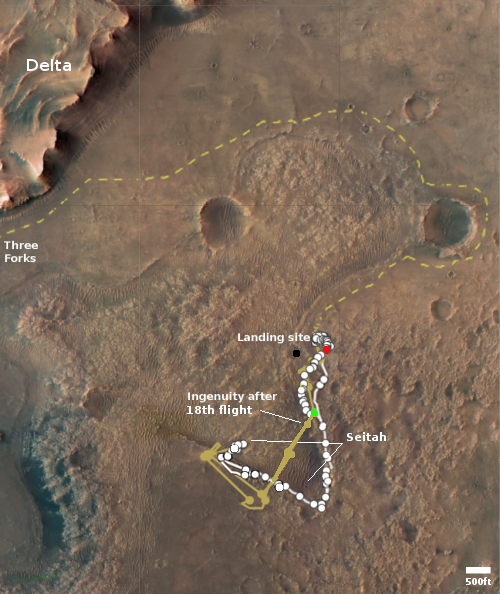
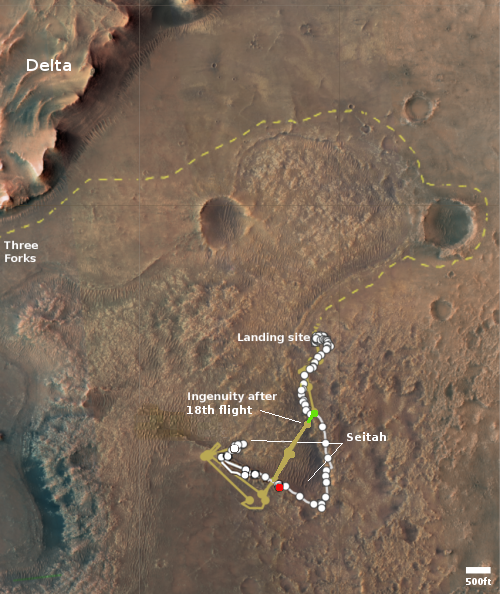
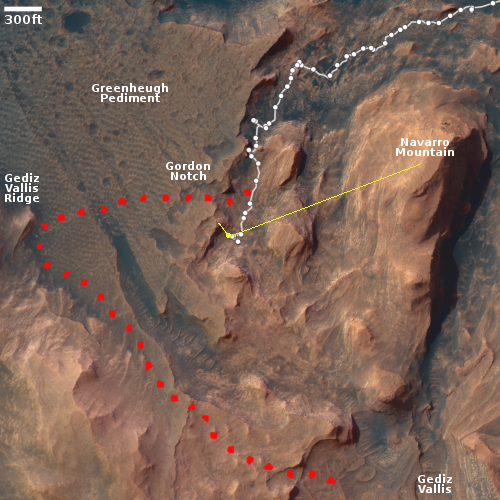
The map to the right shows the helicopter’s present location with the green dot, with its two possible future routes proceeding from this location indicated by dashed lines. The red dot indicates Perseverance’s present location, with its planned route from this spot indicated by the dashed lines.
Scheduled for no earlier than March 19, Ingenuity’s next flight will be a complex journey, about 1,150 feet (350 meters) in length, that includes a sharp bend in its course to avoid a large hill. After that, the team will determine whether two or three more flights will be required to complete the crossing of northwest Séítah.
Once Ingenuity crosses the rough terrain and reaches the delta, it will then be used to do more route scouting for the rover.
Upon reaching the delta, Ingenuity’s first orders will be to help determine which of two dry river channels Perseverance should take when it’s time to climb to the top of the delta. Along with routing assistance, data provided by the helicopter will help the Perseverance team assess potential science targets. Ingenuity may even be called upon to image geologic features too far afield (or outside of the rover’s traversable zone), or perhaps scout landing zones and caching sites for the Mars Sample Return program.
This ambitious plan exists because both the helicopter and its engineering team have far exceeded expectations. At the moment, there is no obvious reason why Ingenuity cannot continue to operate for years, an expectation that no one predicted.
NASA yesterday officially extended Ingenuity’s flight operations on Mars at least through September 2022, outlining in detail the helicopter’s hoped-for flight targets.
The map to the right shows the helicopter’s present location with the green dot, with its two possible future routes proceeding from this location indicated by dashed lines. The red dot indicates Perseverance’s present location, with its planned route from this spot indicated by the dashed lines.
Scheduled for no earlier than March 19, Ingenuity’s next flight will be a complex journey, about 1,150 feet (350 meters) in length, that includes a sharp bend in its course to avoid a large hill. After that, the team will determine whether two or three more flights will be required to complete the crossing of northwest Séítah.
Once Ingenuity crosses the rough terrain and reaches the delta, it will then be used to do more route scouting for the rover.
Upon reaching the delta, Ingenuity’s first orders will be to help determine which of two dry river channels Perseverance should take when it’s time to climb to the top of the delta. Along with routing assistance, data provided by the helicopter will help the Perseverance team assess potential science targets. Ingenuity may even be called upon to image geologic features too far afield (or outside of the rover’s traversable zone), or perhaps scout landing zones and caching sites for the Mars Sample Return program.
This ambitious plan exists because both the helicopter and its engineering team have far exceeded expectations. At the moment, there is no obvious reason why Ingenuity cannot continue to operate for years, an expectation that no one predicted.