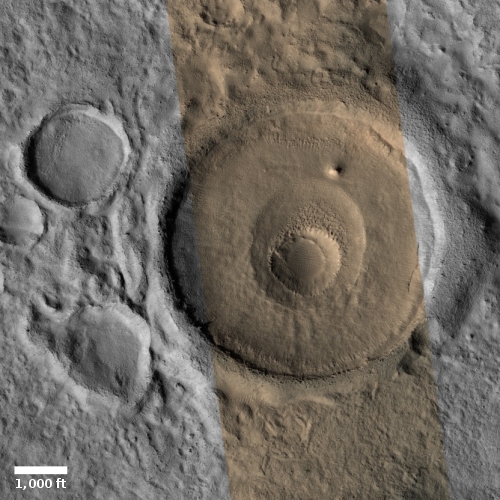
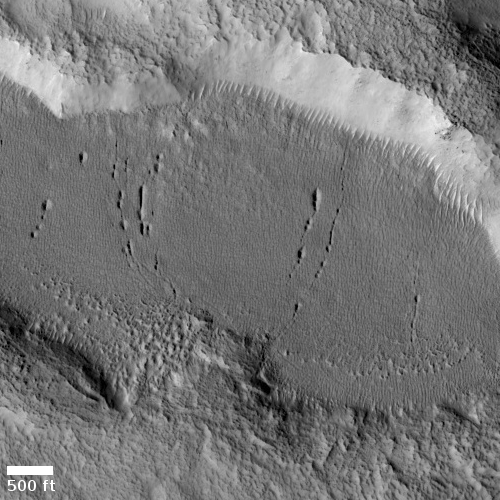
Starship prototype #8 passes tank tests; engine installation next
Capitalism in space: SpaceX’s eighth Starship prototype has passed its tank, thruster, and even fin tests, setting it up for the installation of its three Raptor engines.
Once installed, they will perform several static fire tests, on the launchpad. If those tests are successful, the company will then proceed with a full 50,000 foot test flight. Based on the pace of operations, my guess is that this hop will occur in about two to four weeks.
I’ve embedded one of the videos at the link below the fold, showing a variety of activity at the site.
In other SpaceX news, the Tesla that was put in solar orbit on the first Falcon Heavy test launch has just made its first “fly-by” of Mars, getting to within 5 million miles of the red planet. At that distance the planet really isn’t very close, which is why I put the word fly-by in quotes. That Tesla’s future:
The Roadster will eventually barrel into either Venus or Earth, likely within the next few tens of millions of years, a 2018 orbit-modeling study determined . But the chances of an Earth or Venus impact in the next million years are just 6% and 2.5%, respectively.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX’s eighth Starship prototype has passed its tank, thruster, and even fin tests, setting it up for the installation of its three Raptor engines.
Once installed, they will perform several static fire tests, on the launchpad. If those tests are successful, the company will then proceed with a full 50,000 foot test flight. Based on the pace of operations, my guess is that this hop will occur in about two to four weeks.
I’ve embedded one of the videos at the link below the fold, showing a variety of activity at the site.
In other SpaceX news, the Tesla that was put in solar orbit on the first Falcon Heavy test launch has just made its first “fly-by” of Mars, getting to within 5 million miles of the red planet. At that distance the planet really isn’t very close, which is why I put the word fly-by in quotes. That Tesla’s future:
The Roadster will eventually barrel into either Venus or Earth, likely within the next few tens of millions of years, a 2018 orbit-modeling study determined . But the chances of an Earth or Venus impact in the next million years are just 6% and 2.5%, respectively.