Martian lava flooded crater?
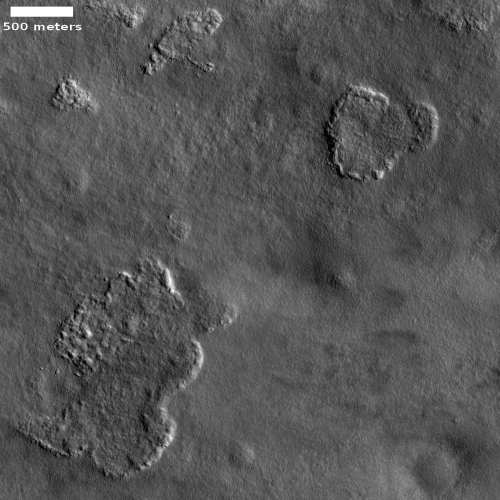
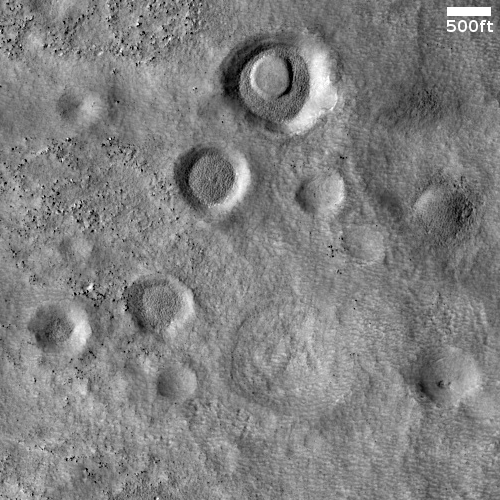
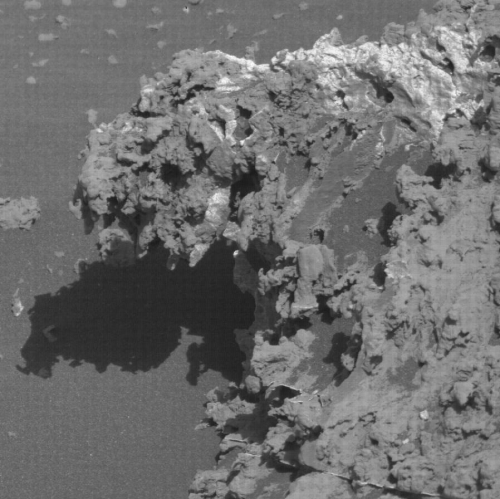
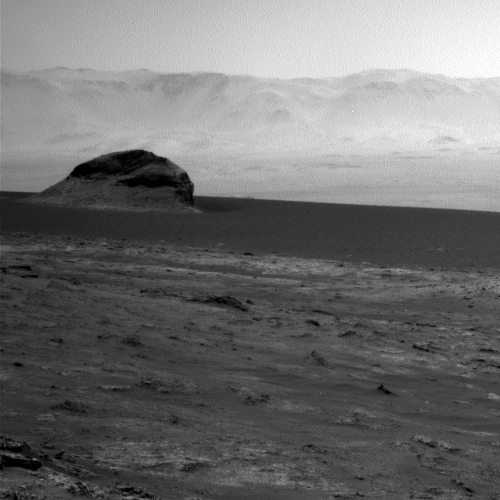
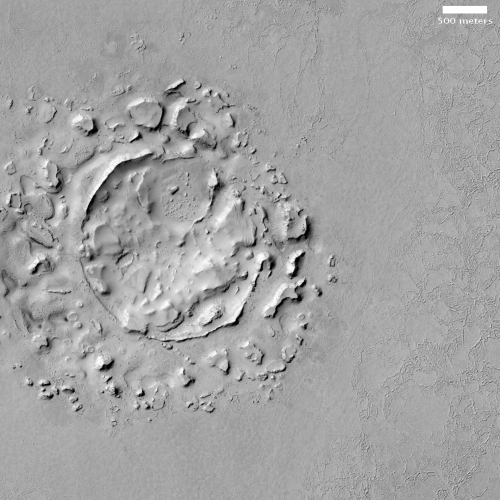
A quick cool image! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) more than a decade ago, on June 1, 2010. I post it now because it is today’s MRO picture of the day, and is definitely cool. The caption:
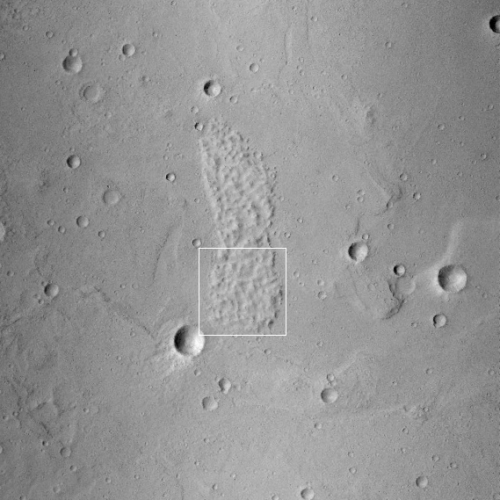
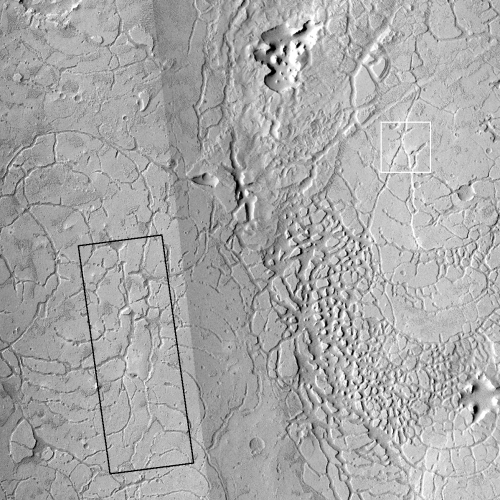
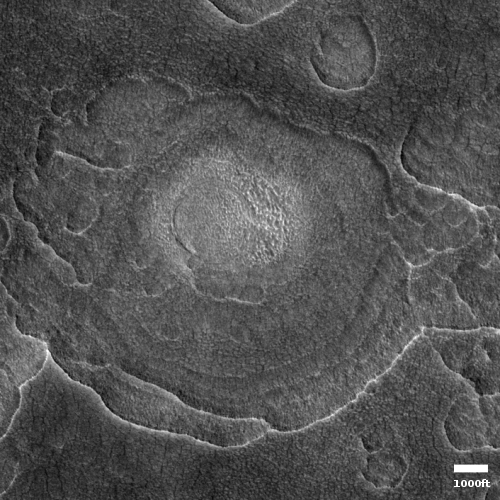
One of a few “scaly-looking” inselbergs within regional platy-ridged flows in Elysium Planitia. This inselberg has a broken and blocky appearance with some of the blocks being tilted. Could this be the remnant of a once extensive mantling deposit? An inselberg is an isolated hill or mountain rising abruptly from a plain.
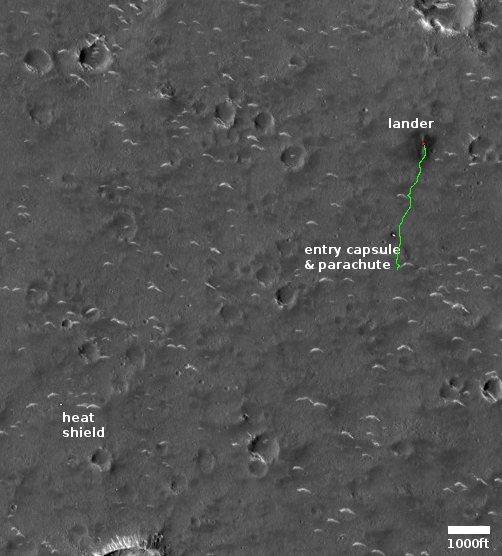
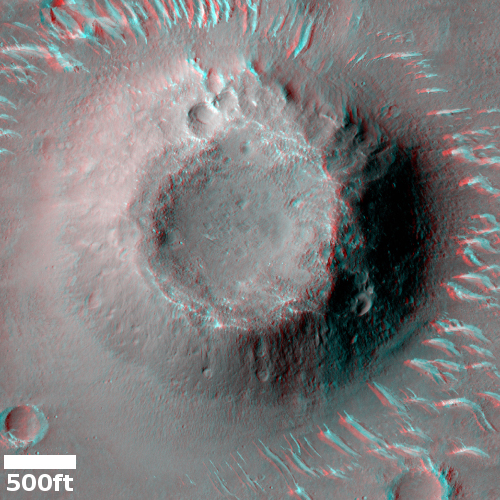
The wider image by MRO’s context camera below, also rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, illustrates even more forcefully how isolated this circular set of blocks is.
» Read more
A quick cool image! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) more than a decade ago, on June 1, 2010. I post it now because it is today’s MRO picture of the day, and is definitely cool. The caption:
One of a few “scaly-looking” inselbergs within regional platy-ridged flows in Elysium Planitia. This inselberg has a broken and blocky appearance with some of the blocks being tilted. Could this be the remnant of a once extensive mantling deposit? An inselberg is an isolated hill or mountain rising abruptly from a plain.
The wider image by MRO’s context camera below, also rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, illustrates even more forcefully how isolated this circular set of blocks is.
» Read more