Stucco on Mars!
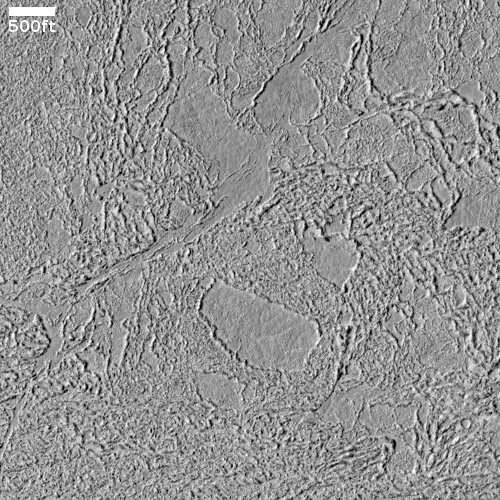
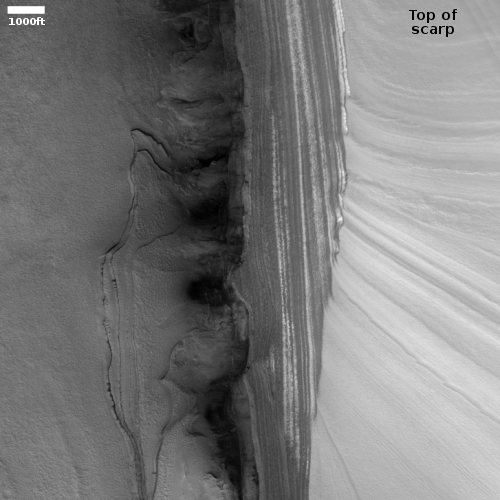
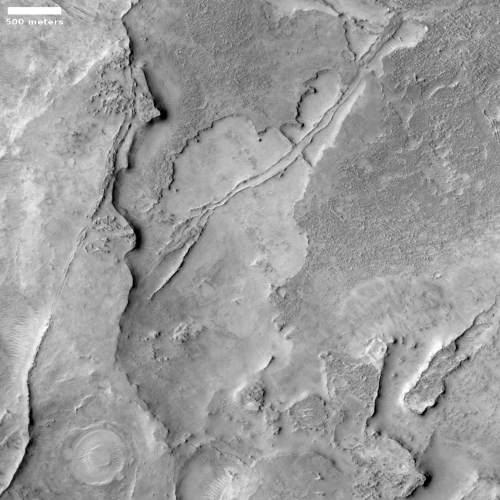
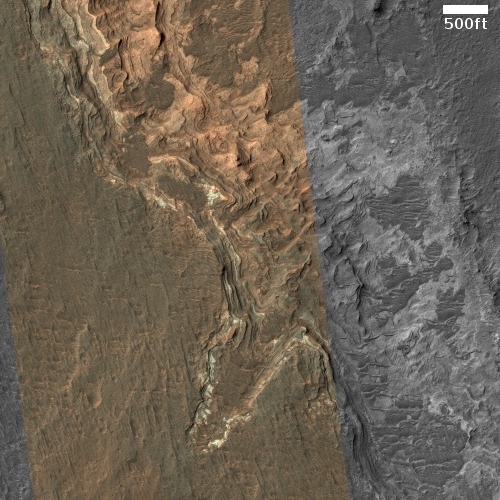
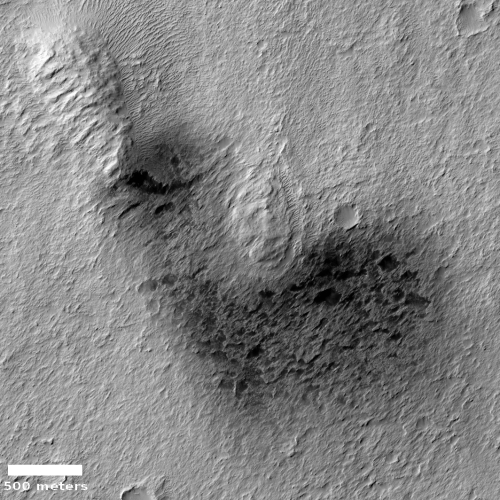
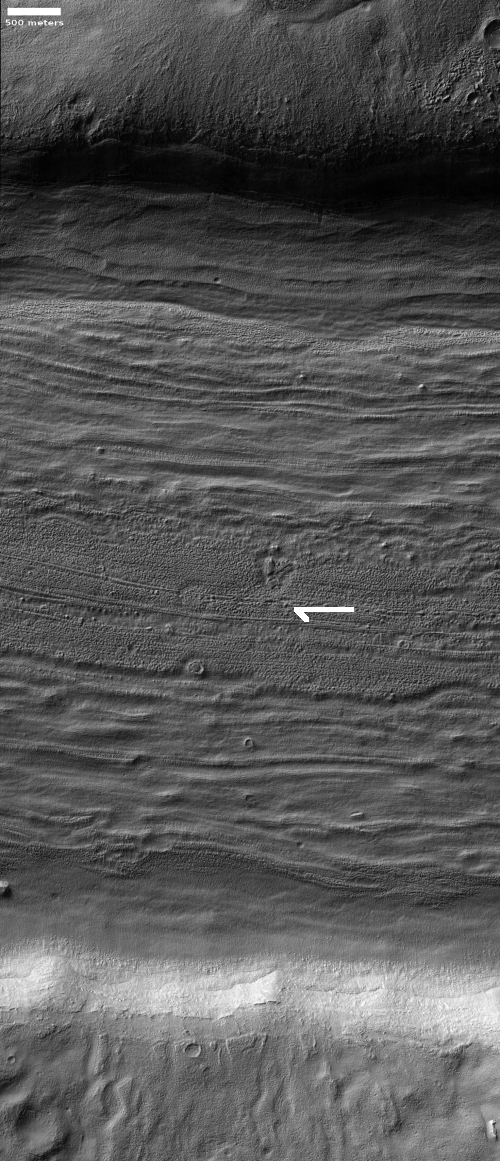
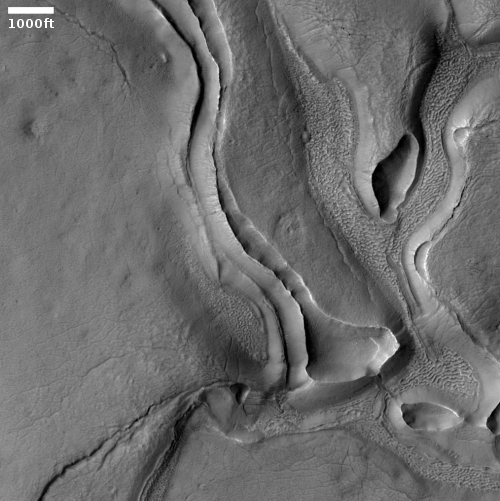
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on June 8, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a strangely flat plain with a complex stucco-type surface of ridges and depressions. The sunlight is coming from the west, which makes the smoother flat areas depressions.
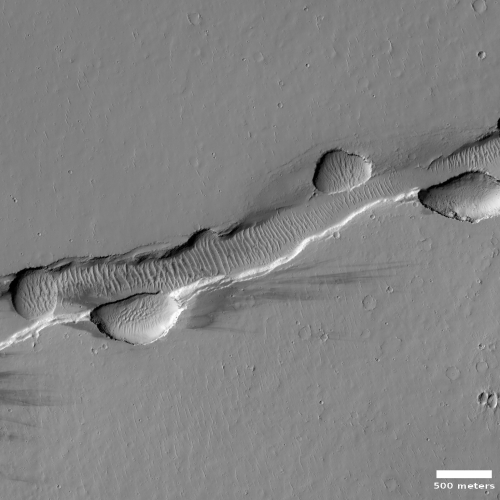
What are we looking at? What causes this strange surface? Make sure you look at the full image, because the section I cropped out doesn’t give a true sense of the terrain’s vastness.
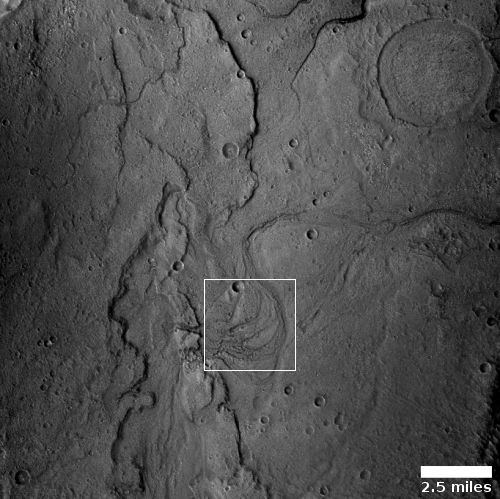
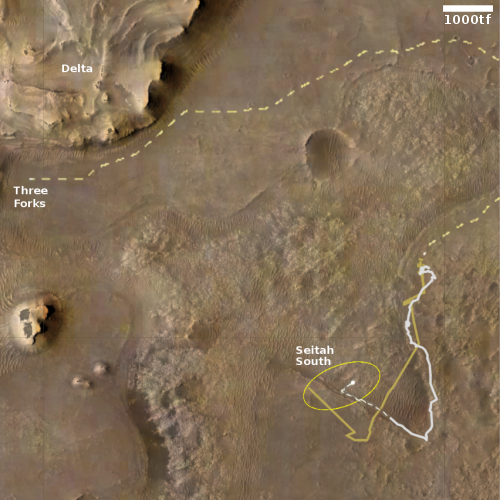
The MRO science team labeled the photo “volcanic terrain,” but that tells only part of the story, since this volcanic terrain is actually part of Mars’ most interesting lava plains, as the overview map below shows.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on June 8, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a strangely flat plain with a complex stucco-type surface of ridges and depressions. The sunlight is coming from the west, which makes the smoother flat areas depressions.
What are we looking at? What causes this strange surface? Make sure you look at the full image, because the section I cropped out doesn’t give a true sense of the terrain’s vastness.
The MRO science team labeled the photo “volcanic terrain,” but that tells only part of the story, since this volcanic terrain is actually part of Mars’ most interesting lava plains, as the overview map below shows.
» Read more