Mars: On the floor of Valles Marineris
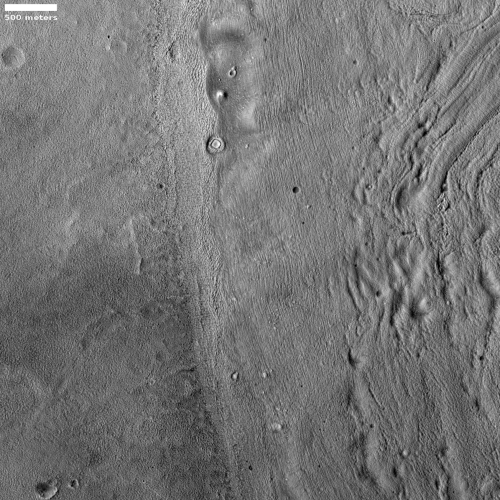
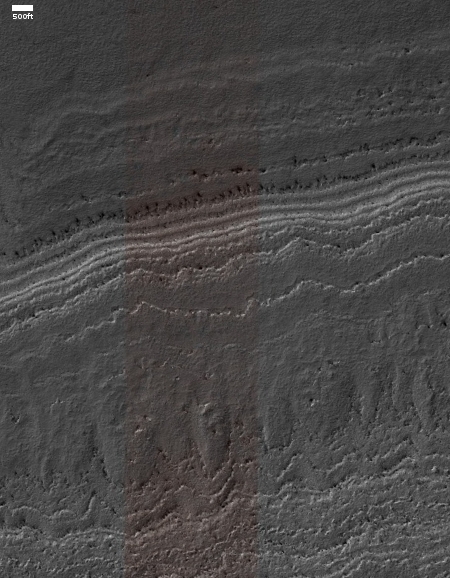
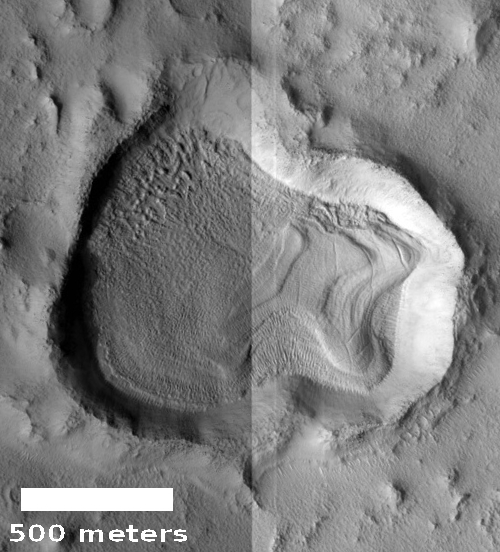
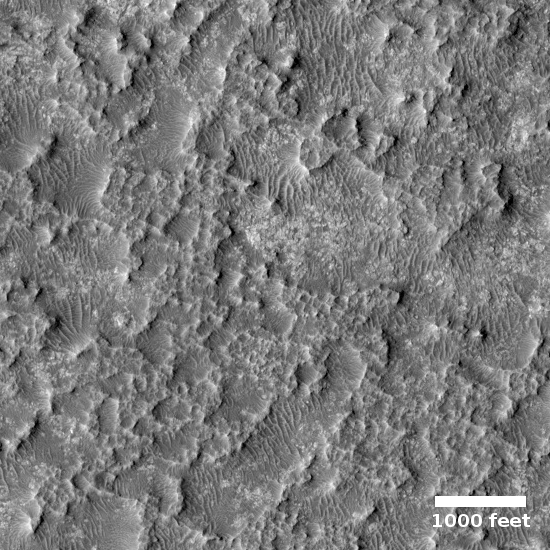
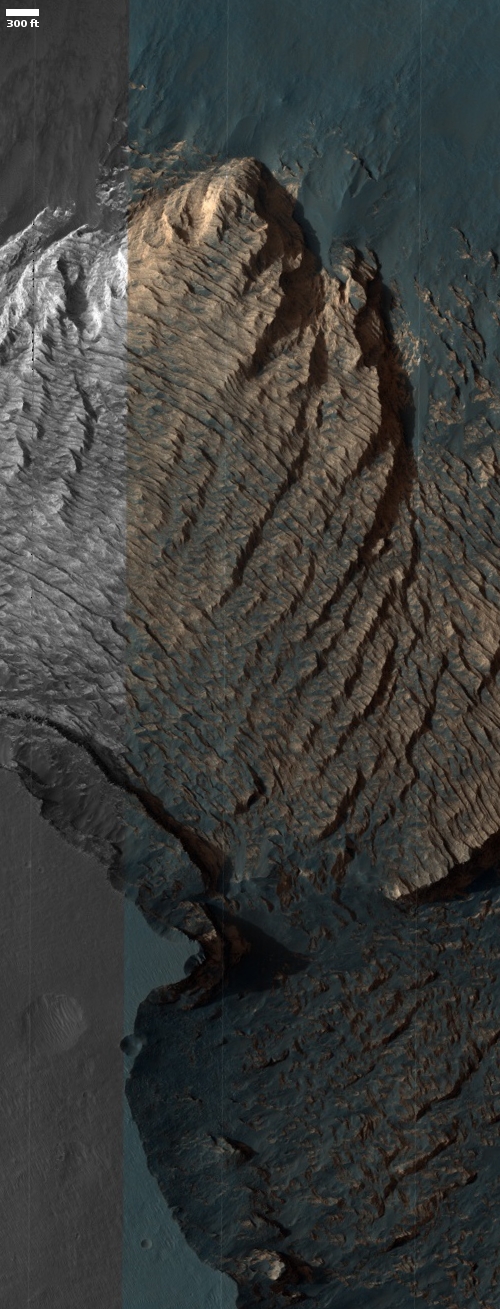
Cool image time! The image to the right, rotated and cropped to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on May 14, 2020, and shows a very strange bright outcrop on the floor of Valles Marineris, the largest canyon on both Mars and in the entire solar system.
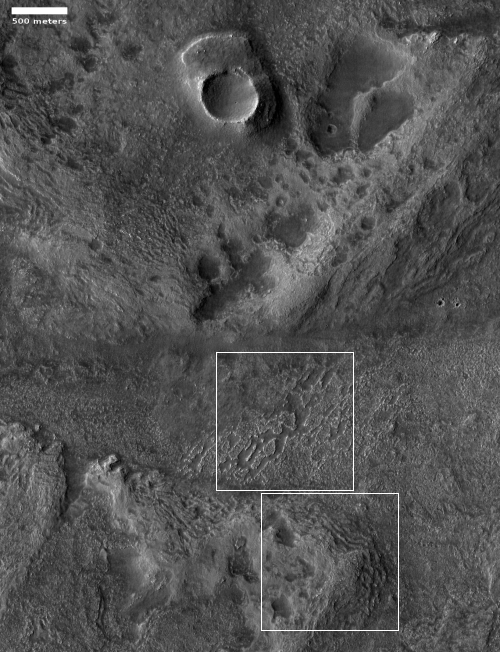
MRO has photographed this spot a few times since 2007. The first image was posted with a detailed caption by Colin Dundas of the U.S. Geological Survey’s Astrogeology Science Center in Arizona, who described the feature like so:
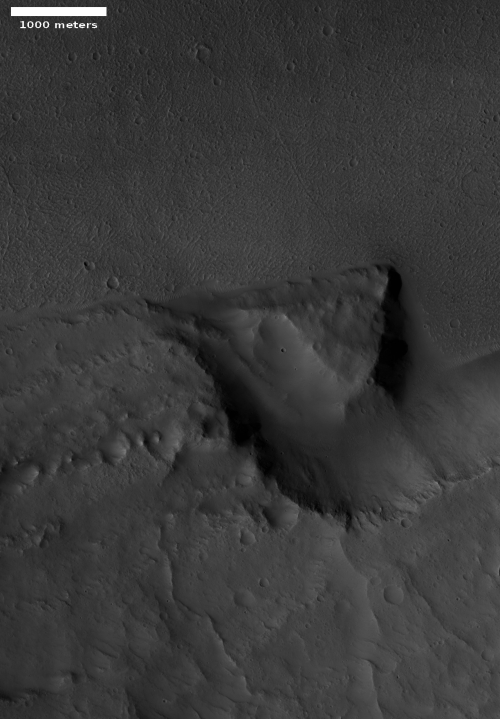
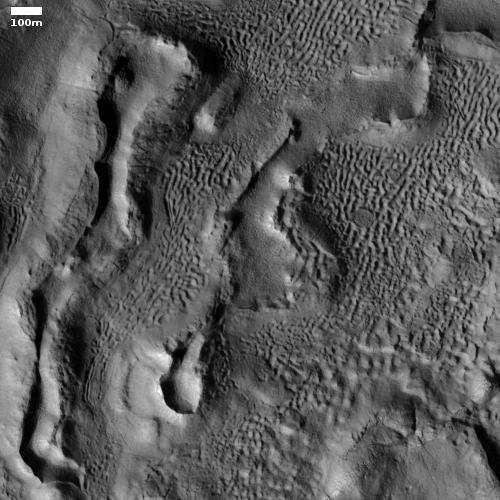
Most of the material is light and shows many small scarps or benches. In places these appear to indicate boundaries between layers, but they are often discontinuous. The light material is buried by a thin mantle of dark material in places; the dark material is from other rock layers—possibly those above the outcrop—and has fallen or been blown over the light rock.
Near the top of the outcrop, there is a distinctive layer that appears as a dark band at low resolution. At the full resolution of HiRISE, this appears to be a layer breaking up into angular boulders, indicating different rock properties than the underlying light rock. There does appear to be some light material above this layer, suggesting that the process that deposited the light material continued for some time.
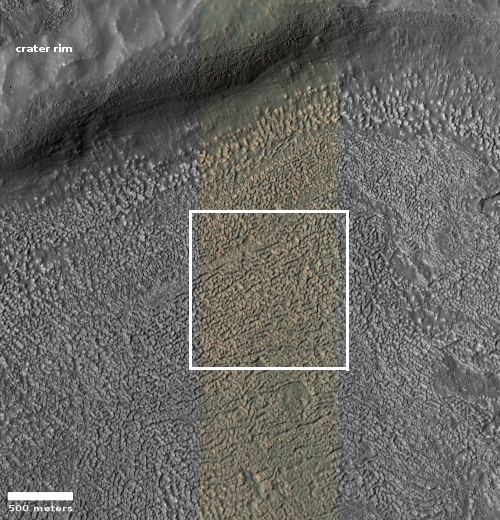
Dundas also added that the lighter material is theorized to have “formed by a variety of processes. Proposed deposition mechanisms for light-toned sediments on Mars include those from rivers or lakes, volcanic ash or wind-blown sand or dust.”
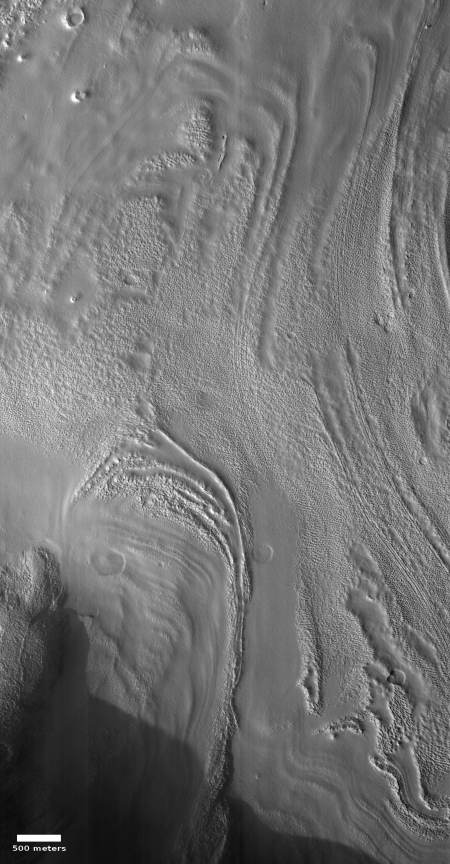
Since this lighter colored outcrop has remained as bright as it has now for more than six Martian years, I doubt it is brighter because of the surface deposit of ash, sand, or dust (though it might be made of these materials which have now become hardened). My guess is that the brightness is inherent to the outcrop. Moreover, note the plateau to the southwest. Its rim is cut sharply, suggesting erosion revealed this outcrop, and that the outcrop is made of more resistant material.
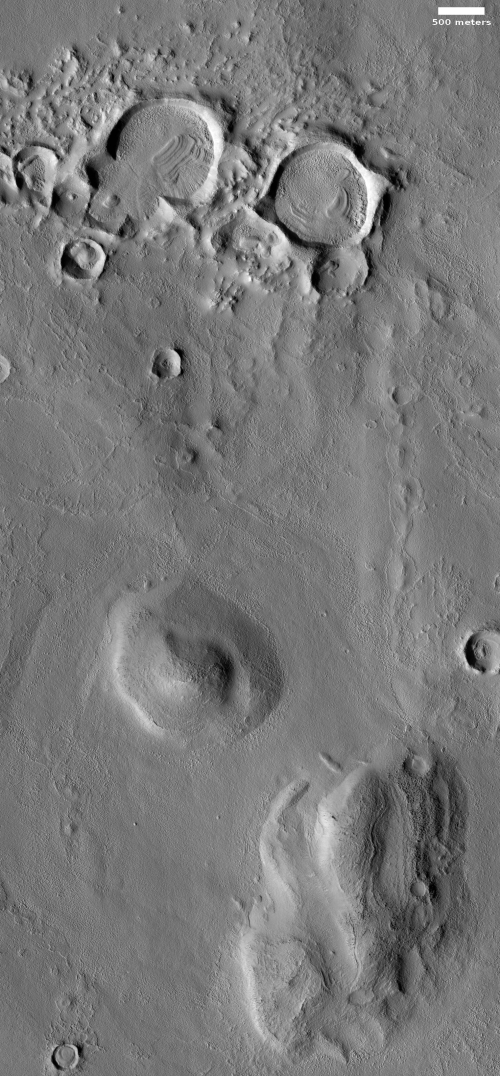
The overview map provides some context that also might help explain the geology at this location.
» Read more
Cool image time! The image to the right, rotated and cropped to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on May 14, 2020, and shows a very strange bright outcrop on the floor of Valles Marineris, the largest canyon on both Mars and in the entire solar system.
MRO has photographed this spot a few times since 2007. The first image was posted with a detailed caption by Colin Dundas of the U.S. Geological Survey’s Astrogeology Science Center in Arizona, who described the feature like so:
Most of the material is light and shows many small scarps or benches. In places these appear to indicate boundaries between layers, but they are often discontinuous. The light material is buried by a thin mantle of dark material in places; the dark material is from other rock layers—possibly those above the outcrop—and has fallen or been blown over the light rock.
Near the top of the outcrop, there is a distinctive layer that appears as a dark band at low resolution. At the full resolution of HiRISE, this appears to be a layer breaking up into angular boulders, indicating different rock properties than the underlying light rock. There does appear to be some light material above this layer, suggesting that the process that deposited the light material continued for some time.
Dundas also added that the lighter material is theorized to have “formed by a variety of processes. Proposed deposition mechanisms for light-toned sediments on Mars include those from rivers or lakes, volcanic ash or wind-blown sand or dust.”
Since this lighter colored outcrop has remained as bright as it has now for more than six Martian years, I doubt it is brighter because of the surface deposit of ash, sand, or dust (though it might be made of these materials which have now become hardened). My guess is that the brightness is inherent to the outcrop. Moreover, note the plateau to the southwest. Its rim is cut sharply, suggesting erosion revealed this outcrop, and that the outcrop is made of more resistant material.
The overview map provides some context that also might help explain the geology at this location.
» Read more