A Martian “glacier” made of volcanic ash
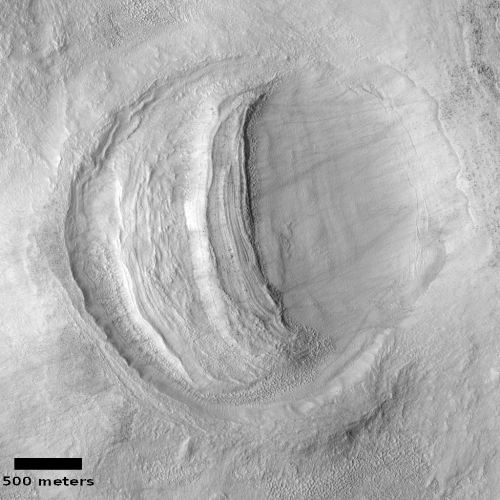
Of the numerous cool images I’ve posted on Mars, many have documented the growing evidence that in the mid-latitudes of the Red Planet are many buried glaciers of ice.
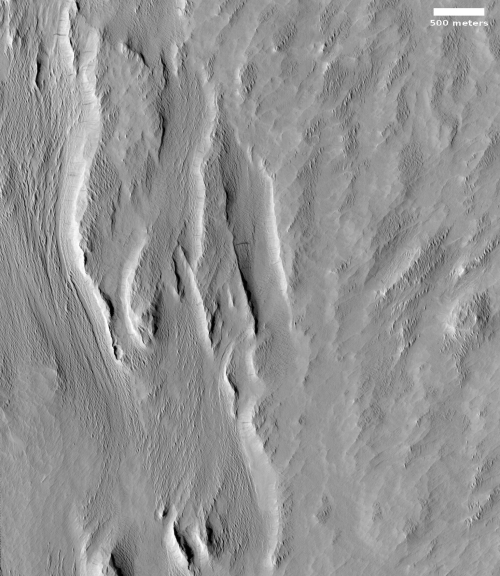
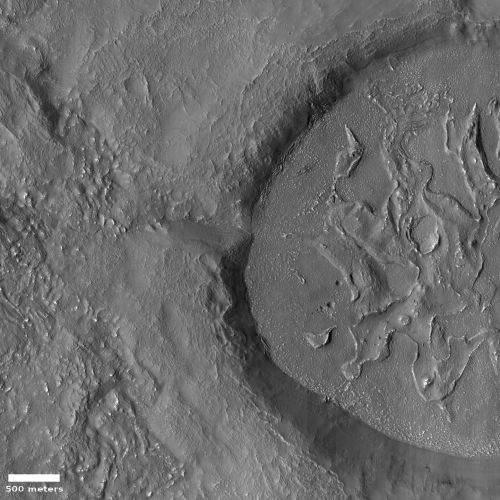
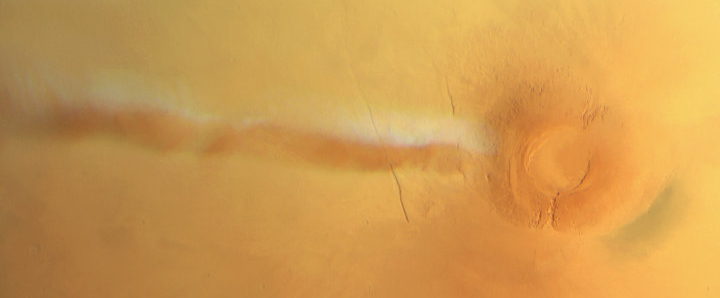
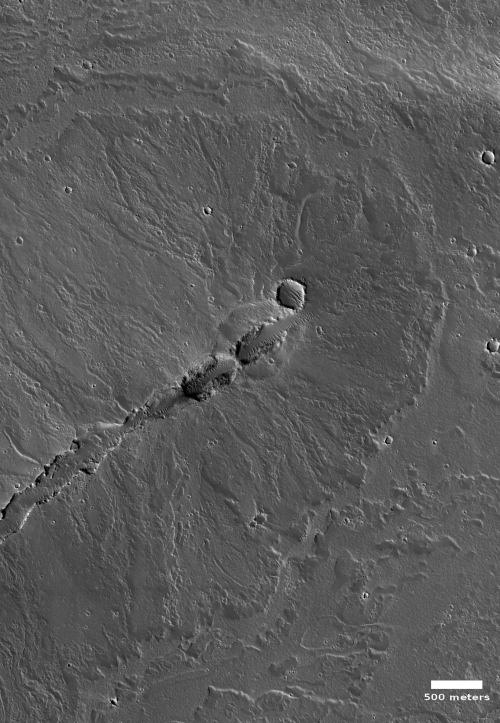
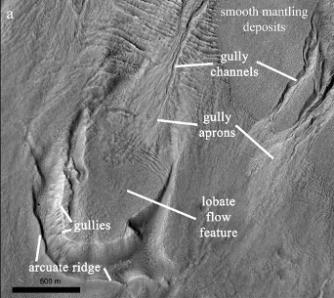
Today’s cool image to the right, rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, shows something that at first might resemble the features one would expect from an ice glacier, but in reality is actually a flow of volcanic ash being blown almost like a river, with the prevailing winds blowing from the south to the north.
The photo was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on November 1, 2020. The location, very close to the equator and in the transition zone dubbed the Cerberus Plains, is also smack dab between Mars’s biggest volcanoes, a region I like to dub Mars’s volcano country. The overview map below gives the context.
» Read more
Of the numerous cool images I’ve posted on Mars, many have documented the growing evidence that in the mid-latitudes of the Red Planet are many buried glaciers of ice.
Today’s cool image to the right, rotated, cropped and reduced to post here, shows something that at first might resemble the features one would expect from an ice glacier, but in reality is actually a flow of volcanic ash being blown almost like a river, with the prevailing winds blowing from the south to the north.
The photo was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on November 1, 2020. The location, very close to the equator and in the transition zone dubbed the Cerberus Plains, is also smack dab between Mars’s biggest volcanoes, a region I like to dub Mars’s volcano country. The overview map below gives the context.
» Read more