Unearthly pit in Martian northern icecap
Cool image time! It is spring in the Martian north, and thus the Sun has risen and remains in the sky for most if not all of each day, circling the horizon. As such, it illuminates polar icecap features that are strange and weird and hard to decipher based on our expectations here on Earth.
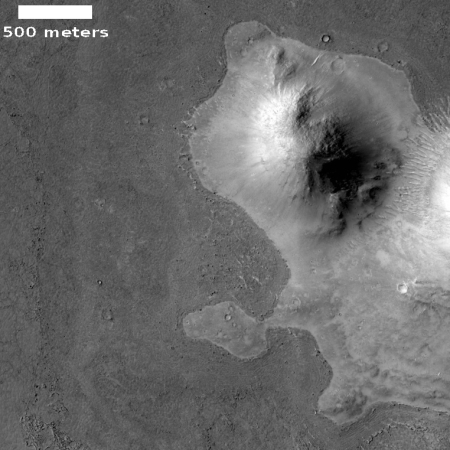
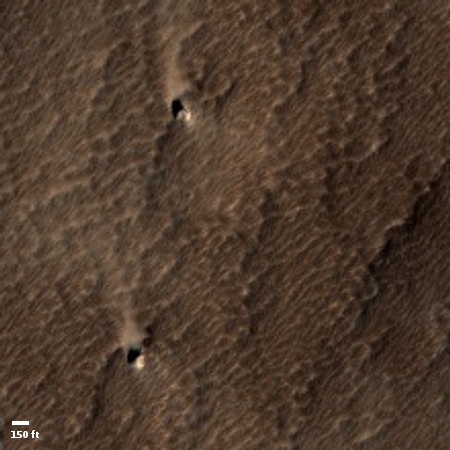
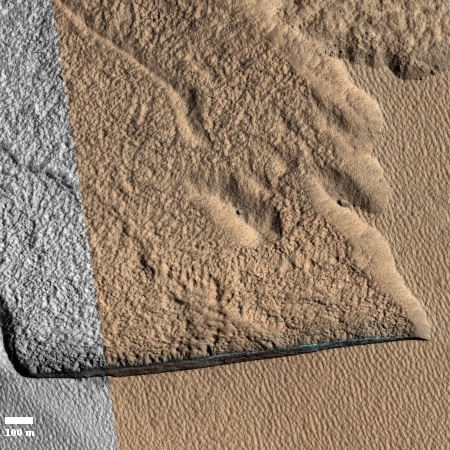
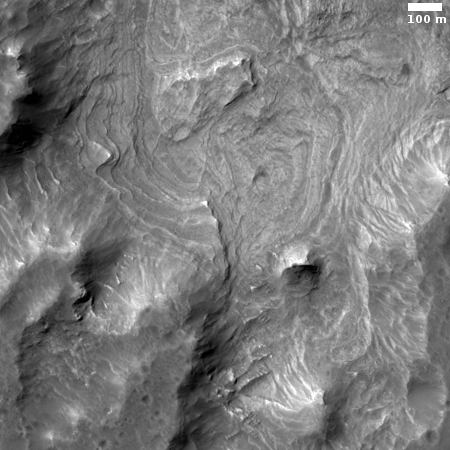
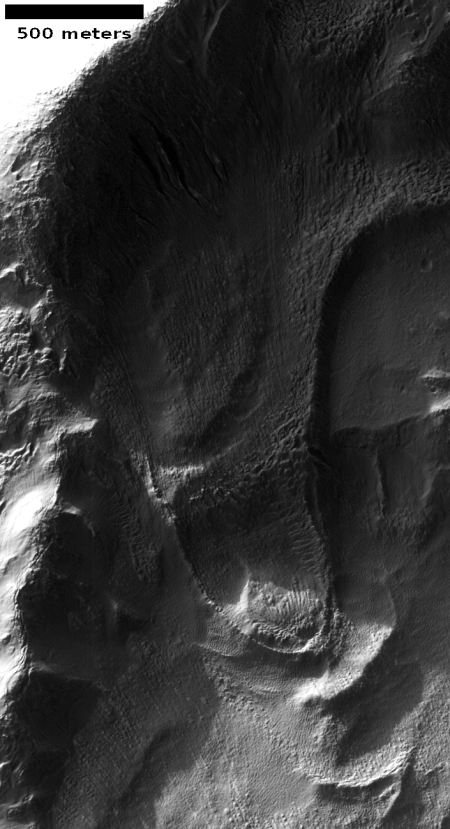
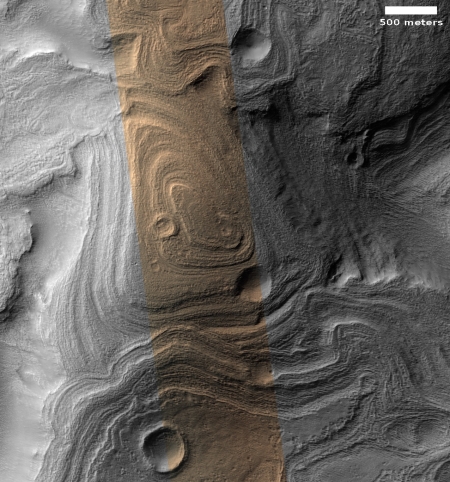
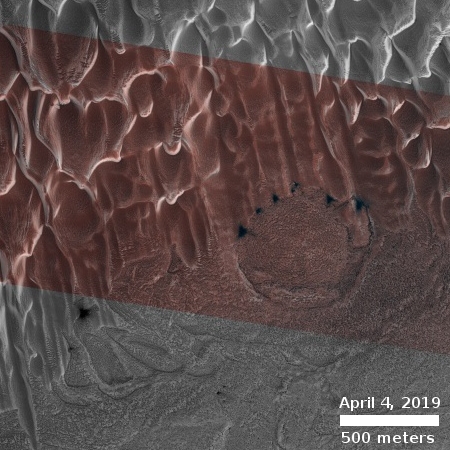
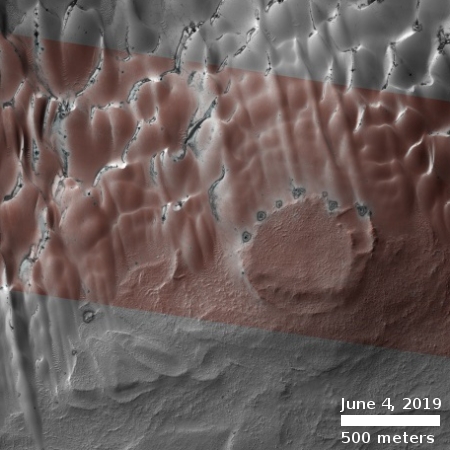
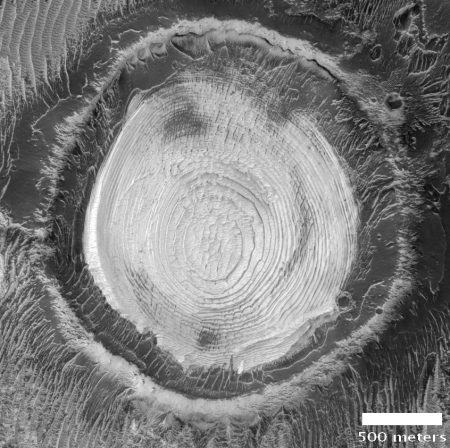
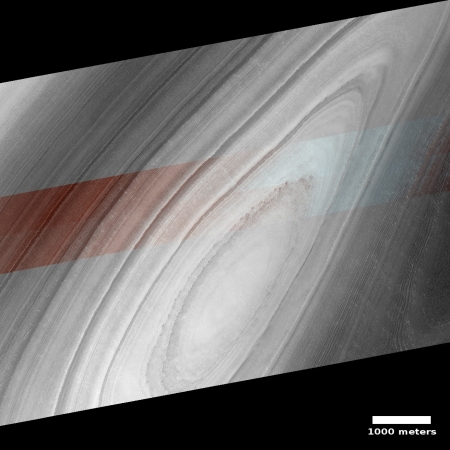
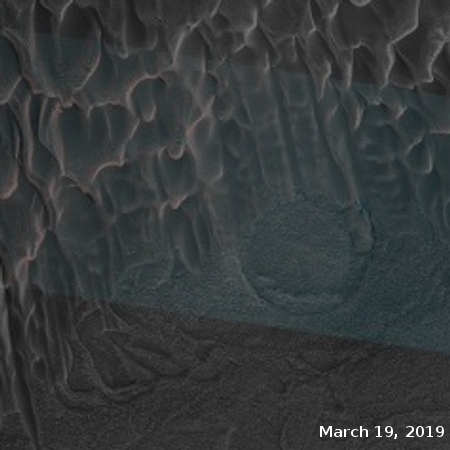
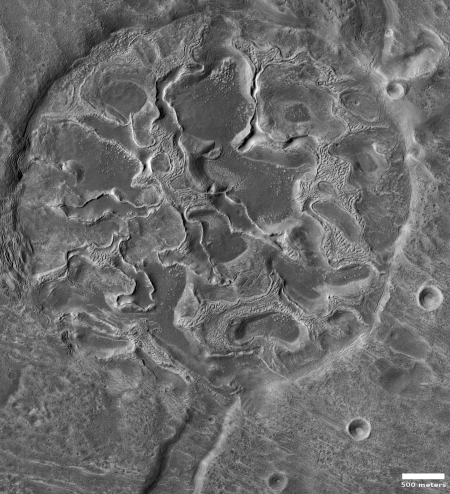
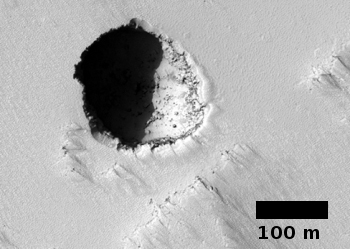
The photograph to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is a good example. It was taken on September 20, 2019 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows a pit in the outer regions of the polar icecap, an area where that water icecap remains relatively stable, but that is also at a low enough latitude that summer sunlight can cause some erosion and sublimation of the ice.
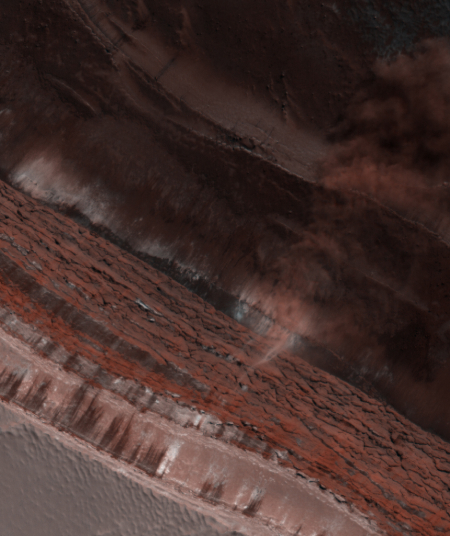
The bottom of the pit is the center of the bullseye, with the layered features in the surrounding walls showing the many layers inside the icecap, built up over centuries, then slowly revealed as the ice in this pit slowly sublimated away.
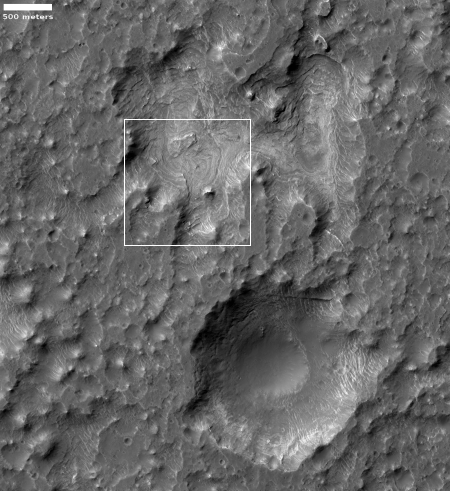
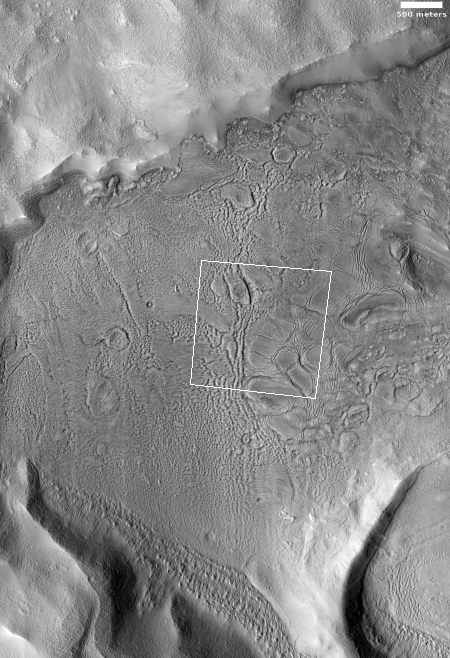
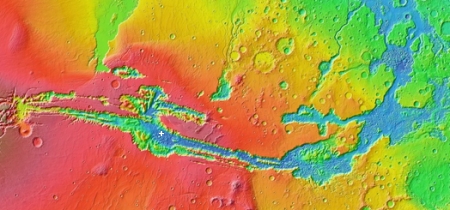
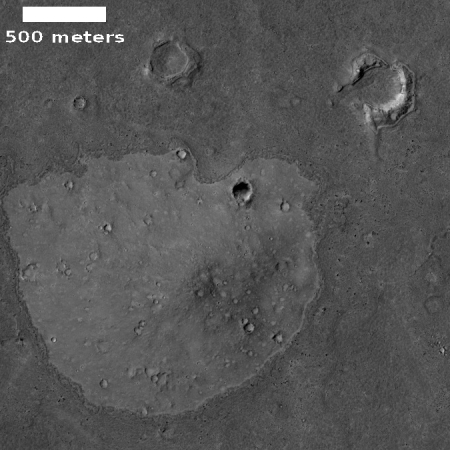
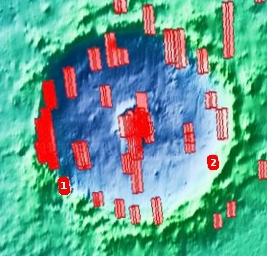
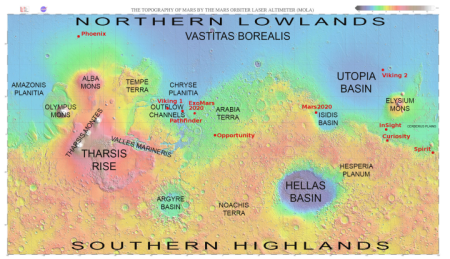
You can get a better sense of what you are looking at by the overview map below.
» Read more
Cool image time! It is spring in the Martian north, and thus the Sun has risen and remains in the sky for most if not all of each day, circling the horizon. As such, it illuminates polar icecap features that are strange and weird and hard to decipher based on our expectations here on Earth.
The photograph to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is a good example. It was taken on September 20, 2019 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows a pit in the outer regions of the polar icecap, an area where that water icecap remains relatively stable, but that is also at a low enough latitude that summer sunlight can cause some erosion and sublimation of the ice.
The bottom of the pit is the center of the bullseye, with the layered features in the surrounding walls showing the many layers inside the icecap, built up over centuries, then slowly revealed as the ice in this pit slowly sublimated away.
You can get a better sense of what you are looking at by the overview map below.
» Read more